Diagnosing issues with your 1990 Chrysler TC can seem daunting, especially when trying to locate the diagnostic port for troubleshooting. While modern vehicles utilize the standardized OBD2 port, vehicles from the early 1990s, like the 1990 Chrysler TC, often employ earlier diagnostic systems. This guide will help you understand the diagnostic port situation for your 1990 Chrysler TC and provide troubleshooting steps for common no-start conditions.
It’s important to clarify upfront: the 1990 Chrysler TC does not have a standardized OBD2 port. OBD2 became mandatory in the United States in 1996. Vehicles from 1990, including the Chrysler TC, typically used an OBD-I system or a manufacturer-specific diagnostic system. Therefore, searching for a “1990 Chrysler Tc Obd2 Port Location” based on the modern OBD2 standard will be misleading.
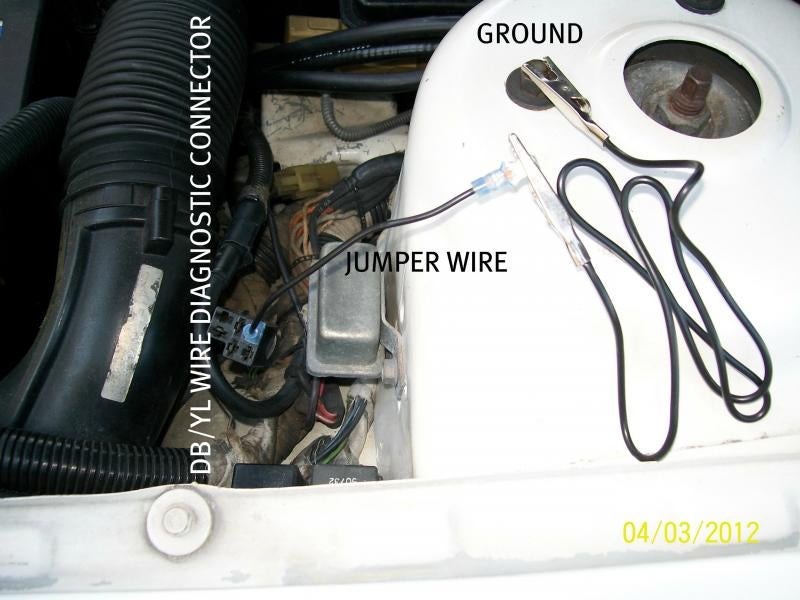
Instead of an OBD2 port, your 1990 Chrysler TC will likely have a Chrysler diagnostic connector that is part of their earlier engine control systems. The location of this port can vary, but common places to check include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side: Look for a connector, possibly near the steering column or fuse box area. It may be a rectangular connector and not the trapezoidal shape of OBD2.
- In the engine compartment: Some early diagnostic connectors were located under the hood, often near the firewall or on the inner fender.
To accurately locate the diagnostic port on your 1990 Chrysler TC, consult your vehicle’s repair manual or a Chrysler service manual specific to the 1990 TC model. These resources will provide precise diagrams and locations for all components, including the diagnostic connector.
While pinpointing the diagnostic port is crucial for advanced diagnostics, let’s address common reasons why your 1990 Chrysler TC might not be starting. These are based on the original troubleshooting advice and expanded for better understanding:
Common Reasons Your 1990 Chrysler TC Won’t Start
If your 1990 Chrysler TC is failing to start, consider these potential issues, starting with simpler checks and moving to more complex ones:
1. Factory Vehicle Theft Alarm (VTA) Issues
Early vehicle theft alarm systems can sometimes malfunction and prevent the engine from starting. While it’s mentioned that it’s unsure if a VTA was available in ’89 (likely applicable to early 1990 models too), it’s worth investigating.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for Alarm System Activation: Look for visual or auditory cues indicating the alarm might be active (flashing lights, siren sounds).
- Door Lock/Unlock Procedure: Try locking and then unlocking both the driver’s and passenger’s side doors using the key. This action could disarm a factory VTA system if present. Refer to your owner’s manual for specific alarm disarming procedures if you suspect a factory alarm.
- Scanner for “Theft Alarm” Status: If you have access to an older diagnostic scanner compatible with early Chrysler systems (not OBD2 scanners), it might be able to read a “Theft Alarm” status. This would definitively confirm if the VTA is armed and preventing starting. However, accessing this information without specialized equipment can be challenging.
2. Aftermarket Alarm System Problems
Many older vehicles have aftermarket alarm systems installed. If your 1990 Chrysler TC has one, issues with its installation or removal can cause starting problems.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect for Aftermarket Alarm Components: Look for signs of an aftermarket alarm system, such as extra wiring, control boxes, or sirens that are not factory standard.
- Wiring Inspection: If an aftermarket alarm was partially removed, improperly reconnected wiring could be the issue. Carefully examine any non-factory wiring in the ignition and fuel system circuits. Wiring diagrams for the 1990 Chrysler TC will be invaluable here. If you are not comfortable with automotive electrical work, consult a professional.
3. Fuel Pressure or Ignition Issues
A lack of fuel or spark is a fundamental reason for a no-start condition.
Fuel Pressure Checks:
- Rent a Fuel Pressure Gauge: Auto parts stores like AutoZone often loan fuel pressure gauges. This is a cost-effective way to check fuel pressure.
 www.turbododge.com
www.turbododge.com
- Locate Fuel Pressure Test Port: Your 1990 Chrysler TC should have a fuel pressure test port on the fuel rail. Consult your repair manual for its exact location.
- Connect and Read Gauge: Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the test port and check the pressure when you turn the key to the “ON” position (without starting the engine) and while cranking.
- Compare to Specifications: Refer to your service manual for the correct fuel pressure specifications for your 1990 Chrysler TC’s engine. Low fuel pressure indicates a potential issue with the fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel pressure regulator, or fuel lines.
Ignition System Checks:
- Spark Test: Check for spark at the spark plugs. You’ll need a spark tester for this. Remove a spark plug wire, insert the spark tester between the plug wire and spark plug, and crank the engine. A healthy spark should be visible at the tester.
- Distributor (If Applicable): If your 1990 TC has a distributor, inspect the distributor cap and rotor for cracks, carbon tracking, or moisture.
- Ignition Coil: Test the ignition coil resistance according to your service manual’s specifications. A faulty coil can prevent spark.
4. Controller Ground Issues
Proper grounding is essential for the engine control unit (ECU) and other sensors to function correctly. Grounding problems can lead to a variety of issues, including no-start conditions.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Locate Main Controller Grounds: Identify the main ground points for the engine controller. These are often connected to the engine block, chassis, or firewall.
- Inspect Ground Connections: Visually inspect these ground connections for corrosion, looseness, or damage. Clean any corroded connections with a wire brush and ensure they are securely fastened.
- Test Ground Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the ground circuits. Ensure there is a good, low-resistance path to ground for all critical components.
- Refer to Wiring Diagrams: Consult wiring diagrams specific to your 1990 Chrysler TC to pinpoint all relevant ground locations and circuits.
5. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Voltage Issues
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) tells the ECU the throttle valve’s position. An incorrect TPS reading can prevent the engine from starting.
TPS Voltage Checks:
- Backprobe TPS Connector: Access the TPS connector. You’ll need to “backprobe” the signal and signal return wires. Backprobing means carefully inserting probes into the back of the connector without disconnecting it, allowing you to measure voltage while the sensor is connected.
- Identify TPS Wires: The original post mentions an Orange/Dark Blue (OR/DB) wire for the signal line and a Black/Light Blue (BK/LB) wire for the signal return. However, always confirm wire colors with your specific vehicle’s wiring diagram as they can vary.
- Use a Digital Voltmeter: Connect a digital voltmeter to backprobe these wires.
- Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Voltage Reading: With the key in the “ON” position but the engine off, measure the voltage.
- Cranking Voltage Reading: Measure the voltage while cranking the engine.
- Check for “Clear Flood” Mode: A TPS voltage above 2.50 volts with the key on or during cranking can signal to the ECU that the engine is flooded. In this “clear flood” mode, the ECU will stop pulsing the fuel injectors to prevent further flooding.
- Closed Throttle Voltage Specification: The closed throttle voltage should typically be between 0.30 and 0.90 volts. Voltages significantly outside this range can indicate a faulty TPS or an adjustment issue.
- Fault Codes (Potentially): While a high TPS voltage (>2.50V) causing a “clear flood” won’t necessarily set a fault code, extremely low (<0.20V) or high (>4.80V) voltages with a closed throttle should set a TPS fault code in the ECU’s memory. Again, accessing these codes on a 1990 Chrysler TC requires compatible diagnostic equipment beyond standard OBD2 scanners.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a no-start condition on a 1990 Chrysler TC requires a systematic approach. Remember that locating the “1990 chrysler tc obd2 port location” based on OBD2 standards will be unsuccessful. Focus on identifying the correct diagnostic connector for your vehicle using service manuals. Start with basic checks like fuel pressure, ignition spark, and ground connections. Understanding the function of components like the TPS and the potential impact of alarm systems are also crucial.
If you are uncomfortable performing these diagnostic steps yourself, or if the issue is complex, it is always best to consult a qualified mechanic experienced with older vehicles and early Chrysler fuel injection systems. They will have the necessary tools, knowledge, and diagnostic equipment to accurately pinpoint the problem and get your 1990 Chrysler TC back on the road.