Understanding the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) protocols in your 2000 Ford F-150 is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and repair. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of OBD2, specifically tailored to your 2000 F-150, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to diagnose and address vehicle issues efficiently.
Decoding OBD2 for Your 2000 Ford F-150
OBD2 is a standardized system that allows you to access your vehicle’s self-diagnostic information. For owners of a 2000 Ford F-150, understanding OBD2 protocols means you can tap into a wealth of data about your truck’s performance and health.
You’ve probably seen the “Check Engine Light” (malfunction indicator light) illuminate on your F-150’s dashboard. This is your truck’s way of signaling that something needs attention. To decipher this signal, mechanics use OBD2 scanners, which connect to a 16-pin OBD2 connector, typically located near the steering wheel. This connection allows communication between the scanner and your F-150’s computer system. The scanner sends requests, and your truck responds with data like speed, engine temperature, and importantly, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that pinpoint potential problems.
OBD2 Compliance and Your 2000 F-150
The good news for 2000 Ford F-150 owners is that yes, your vehicle is OBD2 compliant. OBD2 became mandatory in the USA for cars and light trucks in 1996. Therefore, your 2000 F-150 is equipped with an OBD2 system.
However, it’s important to note that while all OBD2-compliant vehicles use the same 16-pin connector, the underlying communication protocols can vary. For a 2000 Ford F-150, the primary OBD2 protocol is SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). This is one of the five original OBD2 protocols and was commonly used by Ford vehicles of that era.
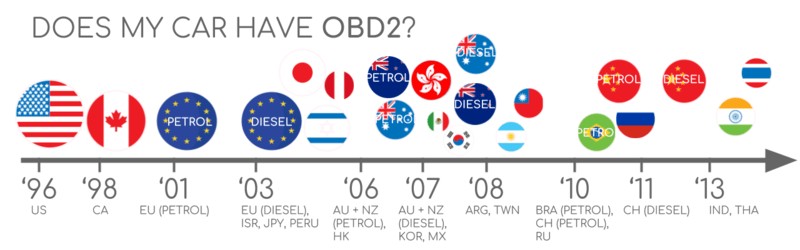 OBD2 Compliance Timeline for Vehicles in EU and US markets
OBD2 Compliance Timeline for Vehicles in EU and US markets
A Brief History of OBD2 and its Relevance to Your F-150
OBD2’s origins trace back to California, driven by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) to monitor vehicle emissions starting in 1991. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) played a key role in standardizing OBD2, including DTCs and the universal OBD connector (SAE J1962).
The timeline of OBD2 implementation is important for understanding your 2000 F-150:
- 1996: OBD2 becomes mandatory in the USA for cars and light trucks – directly impacting your 2000 F-150.
- Pre-2008: Vehicles used a mix of five OBD2 protocols, including SAE J1850 PWM likely used in your F-150.
- 2008: CAN (ISO 15765-4) becomes mandatory in the US, but this change is for vehicles manufactured after 2008 and does not affect your 2000 F-150’s original protocol.
Understanding this history clarifies why your 2000 F-150 utilizes SAE J1850 PWM and not the more modern CAN protocol, which became dominant later.
OBD2 Connector and SAE J1962 for 2000 F-150
Your 2000 Ford F-150 features the standard 16-pin OBD2 connector, as defined by SAE J1962. This connector is the physical interface point for accessing diagnostic data.
Key things to know about your F-150’s OBD2 connector:
- Location: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column. It might be slightly hidden, so check your owner’s manual if needed.
- Pin 2: Specifically for SAE J1850 PWM (+) protocol, which is crucial for your 2000 F-150.
- Pin 16: Provides battery power to the diagnostic tool.
- Pinout: The specific pinout is defined by SAE J1962, ensuring standardized communication regardless of the vehicle manufacturer or protocol.
For 2000 Ford F-150, you’ll primarily be concerned with the Type A OBD2 connector, common in cars and light trucks. Type B connectors are more often found in medium and heavy-duty vehicles and operate on different voltage and sometimes baud rates, which are not relevant to your F-150.
SAE J1850 PWM Protocol: The Language of Your 2000 F-150’s OBD2
SAE J1850 PWM is the specific communication protocol used by your 2000 Ford F-150’s OBD2 system. Unlike CAN (ISO 15765), which is a serial communication protocol, J1850 PWM uses voltage pulses to transmit data.
Key characteristics of SAE J1850 PWM for your 2000 F-150:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Data is encoded in the width of voltage pulses.
- Data Rate: Typically operates at 41.6 kbps.
- Single Wire: Uses a single wire for communication (Pin 2 of the OBD2 connector).
- Ford Dominance: Predominantly used by Ford in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
When selecting an OBD2 scanner for your 2000 F-150, ensure it explicitly supports SAE J1850 PWM protocol to guarantee compatibility and accurate diagnostics. Many modern scanners are multi-protocol and will automatically detect and communicate using J1850 PWM.
Understanding OBD2 Modes and PIDs for 2000 F-150 Diagnostics
Regardless of the underlying protocol (like SAE J1850 PWM), OBD2 utilizes standardized modes (services) and Parameter IDs (PIDs) to request and receive diagnostic information. These are consistent across all OBD2 vehicles, including your 2000 F-150.
OBD2 Modes (Services): These are commands sent to your F-150’s computer to request specific types of diagnostic data. Common modes include:
- Mode 01 (Show current data): Requests real-time data like engine speed (RPM), vehicle speed, coolant temperature, etc.
- Mode 03 (Show stored DTCs): Retrieves Diagnostic Trouble Codes that have triggered the Check Engine Light.
- Mode 04 (Clear DTCs and stored values): Resets the Check Engine Light and clears stored diagnostic information (use with caution).
- Mode 09 (Request vehicle information): Used to retrieve the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
Parameter IDs (PIDs): Within each mode, PIDs are used to request specific data parameters. For example, in Mode 01, PID 0C requests Engine RPM, and PID 0D requests Vehicle Speed.
While the general OBD2 modes and PIDs are standardized, the specific PIDs supported by your 2000 F-150 may vary. Typically, older vehicles like the 2000 F-150 support a subset of the total standardized PIDs, primarily focusing on emissions-related data.
To effectively diagnose your 2000 F-150, you’ll want to:
- Use an OBD2 scanner that supports SAE J1850 PWM.
- Start with Mode 01 PID 00. This PID is a “Supported PIDs” request. Your F-150 will respond indicating which PIDs within the 01-20 range it supports.
- Use PID 20, 40, 60, etc. to check support for further PID ranges in Mode 01.
- Consult OBD2 PID resources to understand the meaning and scaling of the supported PIDs for your 2000 F-150.
Practical OBD2 Diagnostics for Your 2000 F-150
Understanding the protocols and PIDs is only the first step. Here’s how you can practically use OBD2 for your 2000 F-150:
-
Reading and Clearing DTCs: Use Mode 03 to read stored DTCs when the Check Engine Light is on. Record these codes for diagnosis. After addressing the issue, use Mode 04 to clear the codes and turn off the light.
-
Monitoring Real-time Data: Use Mode 01 to monitor live engine parameters. This is helpful for diagnosing intermittent issues or observing engine performance under different driving conditions. For a 2000 F-150, relevant PIDs to monitor might include:
- PID 04: Calculated Engine Load
- PID 05: Coolant Temperature
- PID 0C: Engine RPM
- PID 0D: Vehicle Speed
- PID 10: Mass Air Flow Rate
-
Vehicle Information: Use Mode 09 PID 02 to retrieve your F-150’s VIN, which can be useful for confirming vehicle details or in anti-theft scenarios.
OBD2 Limitations and Beyond for Older Vehicles
While OBD2 is invaluable, it’s essential to recognize its limitations, especially with older vehicles like a 2000 F-150:
- Emissions Focus: OBD2 was primarily designed for emissions monitoring. Diagnostics for other systems (ABS, Airbag, Transmission) may be limited or require proprietary scan tools.
- Limited PIDs: Older vehicles often support a smaller subset of OBD2 PIDs compared to newer models.
- Protocol Complexity: SAE J1850 PWM is an older protocol. While robust, it’s less data-rich and slower compared to CAN.
For more advanced diagnostics on your 2000 F-150, especially for non-emissions systems, you might need to consider:
- Enhanced OBD2 Scanners: Some scanners offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities beyond standard OBD2, potentially including Ford-specific diagnostics.
- Professional Scan Tools: Dealership-level scan tools provide the most comprehensive diagnostic coverage.
Conclusion: OBD2 – Your Diagnostic Ally for the 2000 F-150
For your 2000 Ford F-150, understanding OBD2 protocols, particularly SAE J1850 PWM, is key to unlocking your truck’s diagnostic potential. By using an OBD2 scanner and understanding the modes and PIDs, you can effectively diagnose engine-related issues, monitor performance, and maintain your vehicle. While OBD2 has limitations, especially for older vehicles, it remains a powerful and accessible tool for vehicle owners and DIY mechanics alike.
For further exploration of OBD2 and vehicle diagnostics, consider exploring resources on SAE J1850 PWM, OBD2 PID lists, and diagnostic tools compatible with your 2000 Ford F-150. Equipped with this knowledge, you can confidently approach vehicle maintenance and ensure your 2000 F-150 continues to run reliably.
Looking to diagnose your 2000 F-150? Start with an OBD2 scanner today!
Find OBD2 Scanners (Replace with actual relevant link)
