Experiencing trouble connecting your OBD2 scanner to your 2003 Ford Expedition can be frustrating when you’re trying to diagnose a Check Engine Light or other vehicle issues. A non-responsive OBD2 port immediately halts your diagnostic process. Before assuming a major electronic malfunction, a simple fuse check can often reveal the culprit. This guide will walk you through checking the fuse box and exploring other potential causes for a failed OBD2 connection in your 2003 Expedition, ensuring you can get back to diagnosing and resolving your vehicle’s problems efficiently.
Understanding the OBD2 Port and Its Importance
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a crucial interface in your Ford Expedition, acting as the gateway for communication between diagnostic tools and your vehicle’s computer systems. Mechanics and vehicle owners alike use this port to read trouble codes, monitor sensor data, and verify system health. Without a functioning OBD2 connection, diagnosing even minor issues can become significantly more challenging. Therefore, ensuring this port is active is a fundamental first step in any diagnostic procedure.
Checking the Fuse Box for OBD2 Connection Issues
Often, a blown fuse is the simplest explanation for why your OBD2 scanner isn’t connecting. The fuse box protects the circuits powering the OBD2 port, and an overload or short circuit can easily cause a fuse to fail. Locating and inspecting the relevant fuses is a quick and easy step anyone can perform.
Location of the Fuse Box in a 2003 Ford Expedition
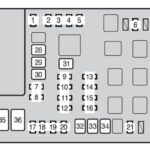
In the 2003 Ford Expedition, the primary fuse box that you’ll need to access for OBD2 port related fuses is located inside the passenger compartment. Specifically, it’s positioned under the right-hand side of the instrument panel. You may need to crouch down in the passenger footwell to access it comfortably.
Key Fuses to Check for OBD2 Problems
Once you’ve located the fuse box, you’ll need to identify the fuses that are related to the OBD2 port and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which is essential for diagnostic communication. Referencing the fuse box diagram is crucial. According to the diagram for the 2003-2006 Ford Expedition, here are some key fuses to inspect:
- Fuse #41 (20A): Cigarette lighter, OBD II diagnostic connector: This is the most directly related fuse to your OBD2 port. If this fuse is blown, it’s a prime suspect.
- Fuse #5 (7.5A): Powertrain Control Module (PCM) (KA power): The PCM is the central computer of your engine and transmission. If it’s not powered, OBD2 communication will be impossible.
- Fuse #34 (15A): PCM, Fuel injectors, Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor: This is another fuse related to PCM operation, and should be checked to ensure the PCM is functioning correctly for diagnostics.
It’s always recommended to consult the specific fuse box diagram for your vehicle’s year to confirm these fuse locations and amperages, as there can be slight variations.
How to Check Fuses
Checking a fuse is straightforward. First, ensure your vehicle’s ignition is turned off. Then, using a fuse puller (often found in the fuse box itself or your vehicle’s toolkit), gently remove each fuse you suspect might be related to the OBD2 port. Inspect the fuse element – if it’s broken or melted, the fuse is blown and needs replacement. Replace blown fuses with new fuses of the exact same type and amperage rating.
Beyond Fuses: Other Reasons for OBD2 Connection Failure
If you’ve checked and replaced any blown fuses and your OBD2 port is still not connecting, the issue might be more complex. Here are some other potential causes:
Faulty OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port itself can sometimes be damaged or have corroded pins, preventing a good connection with your scanner. Visually inspect the port for any damage. You can also try using a different OBD2 scanner to rule out an issue with your tool.
PCM Issues
While fuse issues are more common, problems within the PCM itself can also cause OBD2 communication failures. This could range from software glitches to internal hardware failures within the PCM. Diagnosing PCM issues often requires professional equipment and expertise.
Wiring Problems
Damage to the wiring harness leading to the OBD2 port or PCM can also interrupt the communication pathway. This could involve shorts, breaks, or corrosion in the wiring. Tracing wiring issues can be time-consuming and may require diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact location of the problem.
Scanner Compatibility
Although less common, scanner incompatibility can sometimes be the reason for a failed connection. Ensure your OBD2 scanner is compatible with 2003 Ford Expedition models and supports the necessary communication protocols. Consult your scanner’s manual for compatibility information.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting an OBD2 connection issue in your 2003 Ford Expedition should begin with a thorough fuse box inspection, particularly checking Fuses #41, #5, and #34. Often, a simple fuse replacement can restore the connection and allow you to proceed with your vehicle diagnostics. However, if fuses are not the issue, further investigation into the OBD2 port, PCM, wiring, or scanner compatibility may be necessary. If you’re unable to identify and resolve the problem yourself, seeking assistance from a qualified mechanic will ensure accurate diagnosis and repair, getting your Expedition back to optimal running condition.