The 4R44E transmission, also found in models like the 4R55E, 5R44E, and 5R55E, is a common automatic transmission. Experiencing a flashing Overdrive (OD) light in your vehicle can be concerning, often indicating a problem within this transmission system. Fortunately, modern vehicles equipped with OBD2 systems provide valuable diagnostic tools to pinpoint potential issues. This article will guide you through understanding OBD2 tests in relation to your 4R44E transmission, helping you to identify and address problems effectively.
Understanding OBD2 Codes for 4R44E Transmission Issues
When your vehicle’s Overdrive light starts flashing, it’s a signal that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has detected an anomaly within the transmission. This is often accompanied by Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the system, which can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner. Two common codes associated with a flashing OD light in 4R44E transmissions are:
- P0743 – Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical: This code suggests an electrical fault within the torque converter clutch (TCC) circuit.
- P0760 – Shift Solenoid C Malfunction: This code indicates a problem with the Shift Solenoid C, which, in the 4R44E, typically corresponds to the Overdrive solenoid.
These codes provide a starting point for diagnosis, pointing towards electrical or ratio issues within the transmission. Remember that while OBD2 codes are helpful, they are not always definitive and further investigation is usually required.
Initial Checks: Wiring and Electrical Connections
Before diving deeper into solenoid testing, a crucial first step is to inspect the external wiring and connectors associated with the 4R44E transmission. Like any electrical system in your vehicle, wiring and connections can degrade over time due to environmental factors, vibration, or physical damage.
Locate the 16-pin connector on the driver’s side of your transmission. This connector houses the wiring for all the transmission solenoids.
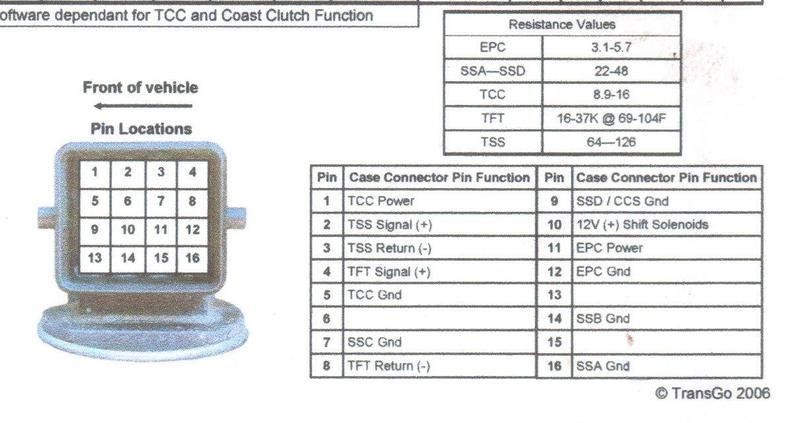 1998 5r55e 16 pin plug
1998 5r55e 16 pin plug
Carefully examine the connector and wiring for:
- Physical Damage: Look for any signs of cracked or broken connectors, frayed or cut wires.
- Corrosion: Check for green or white deposits on the connector pins, indicating corrosion.
- Loose Connections: Gently pull on each wire to ensure it is securely seated within the connector. A loose wire can cause intermittent or complete circuit failures.
Addressing any obvious wiring or connector issues can sometimes resolve the problem without further internal transmission diagnosis.
Testing 4R44E Transmission Solenoids with an Ohmmeter
If the wiring and connectors appear to be in good condition, the next step involves testing the solenoids within the transmission. This requires using a multimeter set to measure resistance (Ohms). Disconnect the 16-pin connector from the transmission before proceeding with these tests.
To perform these tests, you’ll need to identify the correct pins on the disconnected 16-pin connector. Referring to the image above and the pin assignments, you can test the resistance of the following solenoids:
- Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid: Measure resistance between Pin 1 and Pin 5. The expected range is 9 to 16 Ohms.
- Electronic Pressure Control (EPC) Solenoid: Measure resistance between Pin 11 and Pin 12. The expected range is 3 to 6 Ohms.
- Shift Solenoids (SSA, SSB, SSC, SSD): Measure resistance between Pin 10 and each of the pins corresponding to the shift solenoids. The expected range for each shift solenoid is 22 to 48 Ohms. (Consult a 4R44E wiring diagram for specific pin assignments for each shift solenoid – SSA, SSB, SSC, SSD).
Interpreting Resistance Readings:
- Readings within the specified range: Generally indicate that the solenoid coil is intact and likely functional electrically.
- Readings outside the specified range (too high or too low): May indicate a faulty solenoid. An open circuit (infinite resistance) or a short circuit (very low resistance) suggests the solenoid needs replacement.
Understanding Solenoid C (Overdrive) and Band Adjustments
Code P0760 specifically points to “Shift Solenoid C Malfunction,” which is often the Overdrive solenoid in the 4R44E transmission. If your testing indicates an issue with this solenoid, replacement may be necessary.
It’s also worth noting that the 4R44E transmission utilizes adjustable bands for controlling gear ratios. While not directly related to electrical OBD2 codes, incorrect band adjustments can contribute to performance issues that might indirectly trigger transmission fault codes. The original forum post mentions band adjustments, and while electrical testing is the primary focus for codes like P0743 and P0760, understanding the mechanical aspects of the transmission, like band adjustments, can be helpful in comprehensive diagnosis.
For further in-depth understanding of the solenoid operations and shift patterns in these transmissions, resources like the ATRA technical document can be valuable.
PCM Monitoring and Performance vs. Electrical Codes
The vehicle’s PCM is sophisticated enough to monitor not just the electrical circuits of the transmission but also its mechanical performance. It does this by comparing engine RPM with the transmission input shaft speed sensor (TSS) readings.
For example, when the PCM commands the Torque Converter Clutch to lock up, it expects the engine RPM and input shaft RPM to become closely synchronized. If the engine RPM increases but the input shaft RPM doesn’t follow suit, the PCM can infer that the torque converter is not locking up properly.
However, in your case with code P0743, the code is specifically an “electrical” code, not a “performance” code like P0741 (“Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off”). This distinction is important. P0743 points directly to an electrical fault in the TCC circuit, whereas P0741 suggests the electrical circuit might be working, but the mechanical lock-up of the torque converter is not performing as expected.
Similarly, P0760, while a “malfunction” code, is often triggered by electrical issues within the Shift Solenoid C circuit. Performance-related codes for overdrive might be different (though not specifically mentioned in the original post excerpt).
Conclusion: Systematic OBD2 Diagnosis for 4R44E Transmission Issues
Diagnosing 4R44E transmission problems using OBD2 testing requires a systematic approach:
- Retrieve OBD2 Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to read and record all DTCs.
- Initial Visual Inspection: Check wiring and connectors for obvious damage or corrosion.
- Solenoid Electrical Testing: Use an ohmmeter to test solenoid resistances and compare readings to specifications.
- Consult Resources: Utilize wiring diagrams and technical documents to understand solenoid functions and pin assignments.
- Consider Mechanical Factors: While OBD2 codes may point to electrical issues, be aware of mechanical aspects like band adjustments that can influence transmission performance.
By following these steps, you can effectively use OBD2 testing and electrical diagnostics to troubleshoot issues with your 4R44E transmission and address problems indicated by a flashing Overdrive light. Remember, if you are not comfortable performing these tests yourself, it is always recommended to consult a qualified automotive technician.