For owners and enthusiasts of the classic 1998 Range Rover, understanding your vehicle’s diagnostic systems is crucial for maintenance and repair. Like many vehicles manufactured in the late 1990s, the 1998 Range Rover is equipped with an OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port. This standardized port allows mechanics and DIYers to access the vehicle’s computer system, read error codes, and diagnose potential issues. Locating this port is the first step in understanding what might be causing that pesky check engine light to illuminate.
Finding the OBD2 Connector in Your 1998 Range Rover
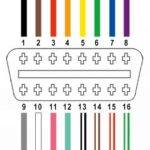
The OBD2 connector in a 1998 Range Rover is typically located within the cabin, making it easily accessible for diagnostic checks. You’ll want to look under the dashboard on the driver’s side. In most cases, it’s positioned near the steering column or integrated into the lower dash panel. It’s designed to be easily found and accessed, without needing any tools for access. The OBD2 port is a 16-pin trapezoidal connector, a standardized shape across all OBD2 compliant vehicles, making it universally compatible with OBD2 scanners and code readers.
Once you’ve located the OBD2 port, you can connect a compatible OBD2 scanner. These scanners range from basic code readers that display error codes and allow you to clear them, to more advanced professional-grade tools that offer live data streaming, sensor testing, and in-depth diagnostic capabilities.
Decoding the Check Engine Light on a 1998 Range Rover
If your 1998 Range Rover’s check engine light is on, the OBD2 port is your gateway to understanding why. Common culprits for a check engine light in vehicles of this era can range from minor issues like a loose gas cap or a faulty sensor to more significant problems within the engine management or emission control systems.
Potential issues that could trigger the CEL in a 1998 Range Rover include:
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor exhaust gases and are crucial for fuel efficiency and emissions control. Failure is common in older vehicles.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: The MAF sensor measures the air entering the engine. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to incorrect fuel mixture and performance issues.
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency: Problems with the catalytic converter, responsible for reducing harmful emissions, can trigger the CEL.
- Ignition System Issues: Problems with spark plugs, ignition coils, or timing can also cause the check engine light to come on.
- EVAP System Leaks: Evaporative Emission Control System leaks, even small ones, can be detected by the system and trigger a code.
Using an OBD2 scanner, you can retrieve the specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in your Range Rover’s computer. These codes provide valuable information about the area of the vehicle experiencing a problem. For example, a code starting with “P0” typically indicates a powertrain issue (engine or transmission related).
Conclusion
Knowing the location of the OBD2 connector in your 1998 Range Rover is a fundamental step in modern vehicle maintenance. It empowers owners to take a proactive approach to vehicle diagnostics, whether you’re simply curious about a check engine light or performing more involved troubleshooting. By utilizing the OBD2 port and a compatible scanner, you can gain valuable insights into your Range Rover’s health, potentially saving time and money on repairs and ensuring your classic SUV remains in top condition for years to come.