Maintaining the electrical system of your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L is crucial for its overall performance and reliability. Fuses are essential components that protect your vehicle’s electrical circuits from overloads, preventing potential damage and costly repairs. If you’re experiencing electrical issues in your Ranger, such as malfunctioning lights, accessories, or even a non-responsive OBD2 port, checking the fuses should be your first step. This guide will help you locate the fuse boxes in your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L and identify the specific fuses related to different electrical components, including those relevant to your OBD2 system. Understanding your vehicle’s fuse layout is a fundamental skill for any Ford Ranger owner, empowering you to perform basic troubleshooting and maintenance.
Understanding Fuse Boxes in Your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L
Your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L is equipped with two primary fuse boxes: the passenger compartment fuse panel and the power distribution box located in the engine compartment. Each fuse box serves different circuits and components within your vehicle. Knowing the location and function of each fuse box is the first step in diagnosing and resolving electrical problems.
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
The passenger compartment fuse panel in your 2002 Ford Ranger is conveniently located inside the vehicle, making it easily accessible for inspection and fuse replacement.
Location: You can find the passenger compartment fuse panel on the left end of the instrument panel, typically on the driver’s side. To access it, you’ll need to remove the fuse panel cover. This is usually done by inserting your finger into a divot or notch on the cover and gently pulling it outwards.
Purpose: This fuse panel houses fuses that protect various interior electrical circuits and accessories, such as power windows, interior lighting, radio, and certain engine management components. It’s also where you’ll find fuses related to systems like the airbags and anti-theft system.
Once you’ve located and accessed the passenger compartment fuse panel, you can refer to the fuse diagram, often found on the inside of the fuse panel cover, to identify the specific fuse you need to check.
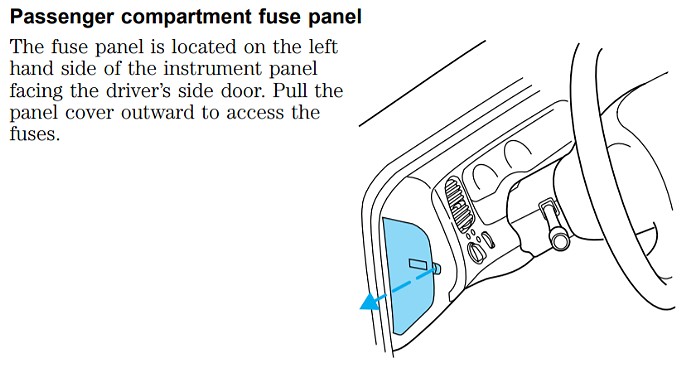 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location in a Ford Ranger
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel Location in a Ford Ranger
Below is a diagram and table detailing the fuses within the passenger compartment fuse panel for 2001-2003 Ford Rangers, including the 2002 3.0L model. This will help you identify the fuse number, amperage, and protected circuits.
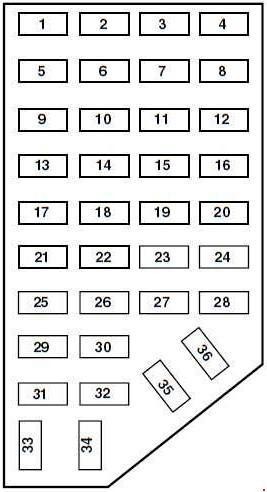 1998-2000 Ford Ranger Passenger Compartment Fuse Box Diagram
1998-2000 Ford Ranger Passenger Compartment Fuse Box Diagram
| No. | AMPS | Protected circuits |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | Power Mirror Switch |
| 2 | 10 | Daytime Running Lights (DRL), Back-up Lamps, Transmission, Passenger Air Bag Deactivation Switch, Blower Motor Relay |
| 3 | 7.5 | 2001-2002: Right Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector 2003: Left Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector |
| 4 | — | Not Used |
| 5 | 15 | 4×4 Control Module |
| 6 | 2 | 2002-2003: Brake Pressure Switch |
| 7 | 7.5 | 2001-2002: Left Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector 2003: Right Stop/Turn Trailer Tow Connector |
| 8 | — | Not Used |
| 9 | 7.5 | Brake Pedal Position Switch |
| 10 | 7.5 | Speed Control Servo/Amplifier Assembly, Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Shift Lock Actuator, Turn Signals, 4×4 |
| 11 | 7.5 | Instrument Cluster, 4×4, Main Light Switch, Truck Central Security Module (TCSM), GEM |
| 12 | — | Not Used |
| 13 | 20 | Brake Pedal Position Switch |
| 14 | 10 | ABS Control Module |
| 15 | — | Not Used |
| 16 | 30 | Windshield Wiper Motor, Wiper Hi-Lo Relay, Wiper Run/Park Relay |
| 17 | 20 | Cigar Lighter, Data Link Connector (DLC) |
| 18 | — | Not Used |
| 19 | 25 | Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Power Diode, Ignition, PATS |
| 20 | 7.5 | Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Radio |
| 21 | 15 | Flasher (Hazard) |
| 22 | 20 | Auxiliary Power Socket |
| 23 | — | Not Used |
| 24 | 7.5 | Clutch Pedal Position (CPP) switch, Starter Interrupt Relay |
| 25 | — | Not Used |
| 26 | 10 | Battery Saver Relay, Auxiliary Relay Box, Restraint Central Module (RCM), Generic Electroic Module (GEM), Instrument Cluster |
| 27 | — | Not Used |
| 28 | 7.5 | Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Radio |
| 29 | 20 | Radio |
| 30 | — | Not Used |
| 31 | — | Not Used |
| 32 | — | Not Used |
| 33 | 15 | Headlamps, Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) Module, Instrument Cluster |
| 34 | — | Not Used |
| 35 | 15 | Horn Relay if Not Equipped with Truck Central Security Module |
| 36 | — | Not Used |
Power Distribution Box
The power distribution box, also known as the engine compartment fuse box, handles high-current fuses and relays that protect critical engine and vehicle systems.
Location: As the name suggests, the power distribution box is located in the engine compartment. Specifically, you’ll find it on the driver’s side, mounted on a bracket attached to the fender apron, near the fender.
Purpose: This box contains fuses and relays for essential vehicle functions such as the engine control module (PCM), fuel pump, headlights, ABS system, blower motor, and power windows. Fuses in this box are generally of higher amperage due to the greater power demands of these systems.
When troubleshooting engine-related or major electrical malfunctions, the power distribution box should be a primary focus of your inspection.
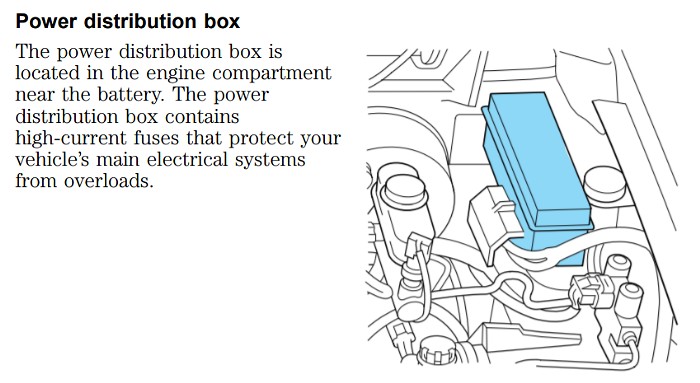 Power Distribution Box Location in Engine Compartment
Power Distribution Box Location in Engine Compartment
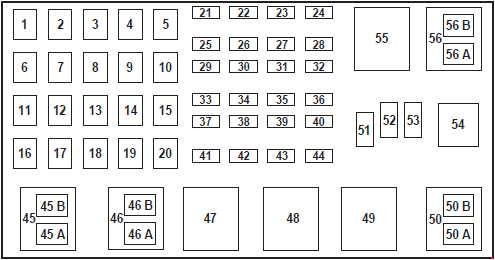
The following images and table provide a detailed layout of the power distribution box for the 2002-2003 Ford Ranger 3.0L engine. Note the variations depending on the engine type and model year, ensuring you’re looking at the correct diagram for your 2002 Ranger 3.0L.
 2001 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 2.3L Engine
2001 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 2.3L Engine
2.3L Engine (above)
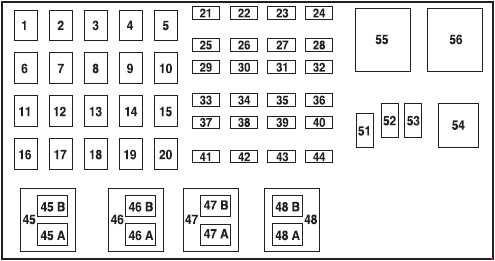
 2001 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 3.0L & 4.0L Engines
2001 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 3.0L & 4.0L Engines
3.0L & 4.0L Engines (2001)(above)
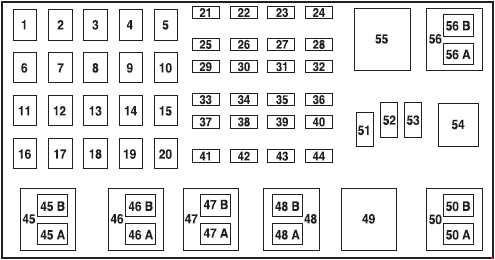
 2003 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 3.0L & 4.0L Engines
2003 Ford Ranger Power Distribution Box – 3.0L & 4.0L Engines
3.0L & 4.0L Engines (2002-2003)(above)
| No. | AMP | Protected circuits |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | I/P Fuse Panel |
| 2 | 50 | Amplifier (Tremor audio system only) |
| 3 | — | Not Used |
| 4 | — | Not Used |
| 5 | — | Not Used |
| 6 | 50 | ABS Pump Motor |
| 7 | 30 | Powertrain Control Module (PCM) |
| 8 | 20 | Power Door Locks and Remote Entry |
| 9 | — | Not Used |
| 10 | — | Not Used |
| 11 | 50 | Starter Relay, Ignition Switch |
| 12 | 20 | Power Windows |
| 13 | 20 | 3.0L and 4.0L engines: 4×4 Motor |
| 14 | — | Not Used |
| 15 | — | Not Used |
| 16 | 40 | Blower Motor |
| 17 | 20 | 2.3L engine: Auxiliary Cooling Fan |
| 18 | — | Not Used |
| 19 | — | Not Used |
| 20 | — | Not Used |
| 21 | 10 | PCM Memory |
| 22 | — | Not Used |
| 23 | 20 | Fuel Pump Motor |
| 24 | 30 | Headlamps |
| 25 | 10 | A/C Clutch Solenoid |
| 26 | — | Not Used |
| 27 | — | Not Used |
| 28 | 30 | 4WABS Module |
| 29 | — | Not Used |
| 30 | 15 | Trailer Tow |
| 31 | 20 | Foglamps, Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) |
| 32 | — | Not Used |
| 33 | 15 | Park Lamp |
| 34 | — | Not Used |
| 35 | — | Not Used |
| 36 | — | Not Used |
| 37 | — | Not Used |
| 38 | 10 | Left Headlamp Low Beam |
| 39 | — | Not Used |
| 40 | — | Not Used |
| 41 | 20 | Heated Oxygen Sensors |
| 42 | 10 | Right Headlamp Low Beam |
| 43 | — | 2.3L engine: (Resistor) |
| 44 | — | Not Used |
| 51 | — | Not Used |
| 52 | — | Not Used |
| 53 | — | Diode: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) |
| Relay | ||
| 45A | Wiper HI/LO | |
| 45B | Wiper Park/Rim | |
| 46A | 2.3L engine: Fuel Pump 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2002-2003): Fuel Pump | |
| 46B | 2.3L engine: Trailer Tow 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): Front Washer Pump 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2002-2003): Trailer tow | |
| 47 | 2.3L engine: Starter 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): A/B – Not Used | |
| 47A | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2002-2003): A/C clutch solenoid | |
| 47B | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2002-2003): Front washer pump | |
| 48 | 2.3L engine: Auxiliary Cooling Fan | |
| 48A | 3.0L and 4.0L engines: Fog Lamps | |
| 48B | 3.0L and 4.0L engines: Fog Lamp Relay | |
| 49 | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): Starter | |
| 50 | Not Used | |
| 50A | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): Not Used | |
| 50B | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): Fuel Pump | |
| 54 | Powertrain Control Module (PCM) | |
| 55 | Blower | |
| 56 | 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2002-2003): Starter | |
| 56A | A/C Clutch Solenoid | |
| 56B | 2.3L engine: Front Washer Pump 3.0L and 4.0L engines (2001): Trailer Tow |
How to Check and Replace Fuses in Your 2002 Ford Ranger
Once you have located the relevant fuse box and identified the fuse you suspect is blown, follow these steps to check and replace it:
-
Access the Fuse Panel: For the passenger compartment fuse panel, remove the cover as described earlier. For the power distribution box, simply open the box cover in the engine compartment.
-
Locate the Fuse: Refer to the fuse diagram on the inside of the cover to pinpoint the fuse number you need to inspect. The diagram will show you the fuse layout and corresponding numbers.
-
Inspect the Fuse: Visually check the fuse to see if it’s blown. Look at the thin wire inside the clear plastic casing. If the wire is broken or melted, the fuse is blown and needs replacement.
Alternatively, you can use a fuse tester for a more definitive check without removing the fuse. A fuse tester, like a Bussmann fuse tester, allows you to test the fuse in place. Simply align the tester prongs with the metal contacts on top of the fuse. If the indicator light illuminates, the fuse is good; if not, it’s blown.
-
Remove the Blown Fuse: If the fuse is blown, use the fuse pulling tool, usually located in the passenger compartment fuse panel, to gently remove it. If a tool isn’t available, you can carefully use pliers, but be cautious not to damage the surrounding fuses or the fuse panel.
-
Replace with the Correct Fuse: It is crucial to replace a blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. The amperage rating is indicated by a number on the fuse and often by its color. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can overload the circuit and cause significant damage, potentially leading to a fire. The spare fuses are often located on the underside of the passenger compartment fuse panel cover.
-
Replace the Fuse Panel Cover: Once you’ve replaced the fuse, securely reattach the fuse panel cover in the passenger compartment or close the power distribution box cover in the engine compartment.
*WARNING: Always use the correct amperage fuse replacement. Incorrect fuse ratings can lead to severe electrical damage and fire hazards.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, check if the affected electrical component is now working correctly. If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after replacement, it indicates an underlying electrical problem in the circuit that requires further professional diagnosis and repair.
Fuse Color and Ratings
Fuses are color-coded to easily identify their amperage ratings. This color-coding system is standardized, making it simple to select the correct replacement fuse.
 Fuse Color Ratings Chart
Fuse Color Ratings Chart
Remember these common fuse colors and their corresponding amperage:
- Yellow: 20 Amp
- Blue: 15 Amp
- Red: 10 Amp
- Orange: 5 Amp
Consult your 2002 Ford Ranger owner’s manual for a complete list of fuse colors and ratings specific to your vehicle.
OBD2 Port and Fuse Connection
While not explicitly labeled as an “OBD2 fuse,” the Data Link Connector (DLC), which is the OBD2 port, is often protected by a fuse within the vehicle’s electrical system. In the passenger compartment fuse panel diagram provided, you’ll notice fuse number 17 (20 Amp) is listed as protecting the “Cigar Lighter, Data Link Connector (DLC)”.
If you are experiencing issues with your OBD2 scanner not powering on or failing to connect to your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L’s computer, checking fuse #17 in the passenger compartment fuse panel is a crucial step. A blown fuse here can directly disable the OBD2 port, preventing communication and diagnostics.
By understanding the fuse locations and taking the time to check and replace blown fuses, you can effectively troubleshoot many common electrical issues in your 2002 Ford Ranger 3.0L, including problems related to your OBD2 system. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic for complex electrical problems or persistent fuse failures.


