If you’re involved in vehicle maintenance, whether you manage a car fleet or simply care for your own car, you’ve likely encountered OBD2 codes. These codes might seem complex, but they are essentially your vehicle’s way of communicating about its health. Think of them as diagnostic messages from your car, providing insights into what’s happening under the hood. For anyone concerned with vehicle upkeep, understanding these codes is crucial for proactive maintenance and ensuring smooth operation.
This guide will demystify Global Obd2 Codes, explaining what they are, how they function, and why they are indispensable for effective vehicle management, regardless of the scale of your operation. We’ll explore how to effectively utilize OBD2 systems to maintain vehicle health and performance.
Decoding OBD2 Codes: A Universal Language for Vehicle Health
On-board diagnostics (OBD2) codes are standardized alphanumeric codes generated by your vehicle’s computer system. They act as a communication method, alerting you to issues detected within your vehicle’s various systems. The OBD2 system is designed to monitor a wide array of components, from the engine and transmission to emission controls, ensuring comprehensive vehicle oversight.
When the vehicle’s computer detects an anomaly in operation, it generates a corresponding diagnostic trouble code (DTC). These codes can signal a spectrum of problems, ranging from minor glitches to potentially serious malfunctions. The illumination of the “Check Engine” light is a common indicator that an OBD2 code has been triggered, signifying that a system within the vehicle is not performing as expected.
To decipher these codes, you’ll need an OBD2 code reader. This tool connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located beneath the dashboard, and retrieves the numerical trouble code. This code serves as a crucial clue, pointing you or a technician towards the specific area of the problem. It’s a valuable resource for efficient troubleshooting and informed decision-making in vehicle maintenance and repair.
 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Types of Global OBD2 Codes: Navigating the Diagnostic Categories
When an OBD2 code appears, identifying its specific category is the first step to understanding the nature of the issue. These global OBD2 codes are categorized into four primary types, each relating to a different area of the vehicle. Recognizing these categories will streamline the diagnostic process and help you address problems effectively.
Powertrain Codes (P-Codes) – Engine and Transmission Deep Dive
Powertrain codes, starting with the letter ‘P’, are perhaps the most frequently encountered OBD2 codes. They indicate issues within the powertrain system, which encompasses the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. These codes provide critical insights into problems affecting your vehicle’s power generation and delivery.
For example, the powertrain code P0301 signals a cylinder 1 misfire. This means that cylinder number one in the engine is not firing correctly, which could be due to various issues like faulty spark plugs, fuel injectors, or ignition coils. Addressing powertrain codes promptly is essential as they can impact engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions.
Body Codes (B-Codes) – Beyond the Mechanics: Body System Issues
Body codes, identified by the letter ‘B’, relate to problems within the vehicle’s body systems. This broad category includes components such as airbags, power windows, anti-theft systems, and climate control. While not directly related to engine performance, body codes are crucial for safety and comfort features.
An example is the body code B0010, which could indicate a problem with the passenger-side airbag sensor. A malfunctioning airbag system is a serious safety concern, and body codes like this highlight issues that require immediate attention to ensure occupant safety.
Chassis Codes (C-Codes) – Handling, Braking, and Stability Concerns
Chassis codes, beginning with ‘C’, point to issues within the vehicle’s chassis systems. This includes components related to braking, steering, suspension, and stability control. Chassis codes are particularly important as they often relate to vehicle safety and handling.
For instance, the chassis code C0051 might indicate a problem with the steering angle sensor. A faulty steering angle sensor can affect systems like Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), compromising the vehicle’s handling and braking performance, especially in critical driving situations.
Network Communication Codes (U-Codes) – Connectivity Problems in Modern Cars
Network communication codes, designated by ‘U’, are increasingly relevant in modern vehicles due to their complex electronic networks. These codes indicate problems in the communication between various computer modules and control units within the vehicle. Modern cars rely heavily on these networks for seamless operation of various systems.
A common network communication code is U0100, indicating a ‘Lost Communication With ECM/PCM’. This means there’s a communication breakdown with the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), which are essentially the brains of the vehicle. Such communication failures can lead to a wide range of issues, affecting engine performance, transmission control, and even safety systems.
Reading Global OBD2 Codes: Tools and Techniques
Reading OBD2 codes is a straightforward process, primarily requiring an OBD2 scanner. These scanners range from basic handheld devices to sophisticated professional tools. Understanding how to use these tools and interpret the codes is key to effective vehicle diagnostics.
How to Read Codes: Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Refer to your vehicle’s manual if you have trouble finding it.
- Plug in the Scanner: With the vehicle’s ignition turned off, plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn Ignition to ‘On’ Position: Turn the ignition key to the ‘on’ position, but do not start the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s systems and the scanner.
- Power On the Scanner and Read Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on and initiate a code reading. The scanner will communicate with the vehicle’s computer and display any stored OBD2 codes.
- Record the Codes: Note down all displayed codes. It’s helpful to record them accurately for later reference and diagnosis.
- Interpret the Codes: Use resources (like this guide or online databases) to understand what each code means.
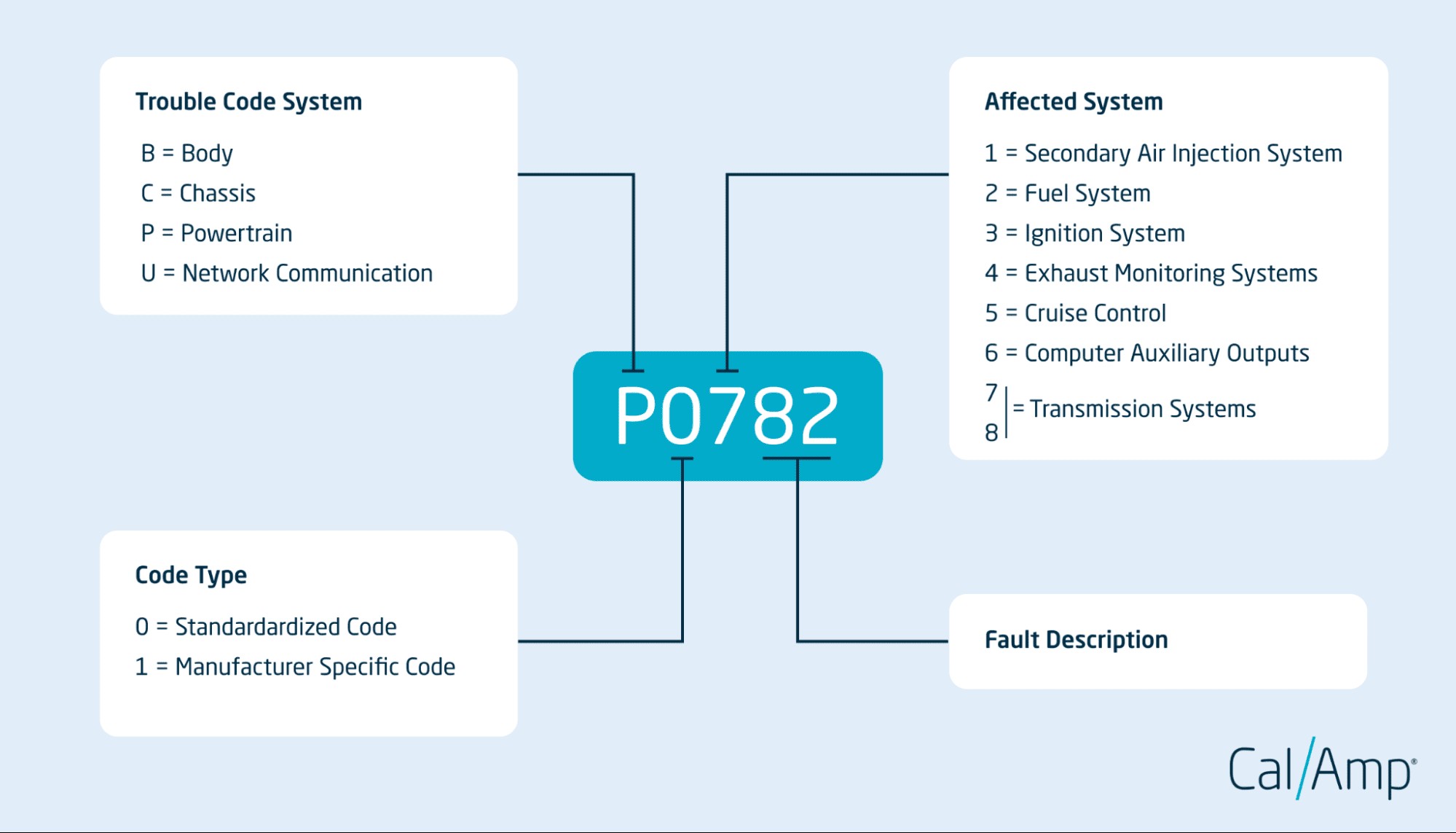
Understanding the Code Structure
OBD2 codes are structured as a five-character alphanumeric code. Each position provides specific information about the issue:
- First Character (Letter): Indicates the system affected (P=Powertrain, B=Body, C=Chassis, U=Network).
- Second Character (Digit): Indicates if the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). ‘0’ signifies a standardized global OBD2 code, common across all makes and models. ‘1’ indicates a code specific to a particular vehicle manufacturer.
- Third Character (Digit): Specifies the subsystem affected. For Powertrain codes, common categories include:
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 2: Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 4: Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5: Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 6: Computer Output Circuit
- 7 & 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters (Digits): These two digits are specific and indicate the exact fault within the identified system and subsystem. For example, in P0420, ‘420’ pinpoints a specific issue with the catalytic converter efficiency in the exhaust system.
Understanding this structure allows for a more informed interpretation of the OBD2 codes and helps in narrowing down the potential problem areas.
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: Global Compatibility Considerations
When selecting an OBD2 scanner, consider its compatibility with your vehicles, especially if you are dealing with a diverse fleet or vehicles from different regions. Most modern scanners support global OBD2 protocols (like ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4, SAE J1850, and ISO 15765-4/CAN), ensuring broad compatibility. However, for manufacturer-specific codes or advanced functions, you might need scanners with enhanced capabilities or software updates for specific makes and models.
Clearing Global OBD2 Codes: When and How
Clearing OBD2 codes should generally be done after diagnosing and addressing the underlying issue. Simply clearing a code without fixing the problem is like turning off a warning light without resolving the danger – the problem is likely to return. However, there are legitimate scenarios where clearing codes is necessary, such as after completing repairs or for diagnostic purposes.
Methods to Clear Codes
- Using an OBD2 Scanner: Most OBD2 scanners have a ‘clear codes’ or ‘erase codes’ function. After connecting the scanner and reading codes, navigate to this option and follow the prompts to clear the codes. This method is quick and allows you to clear codes immediately after repairs.
- Drive Cycle: Some generic codes might clear automatically after the vehicle completes a successful ‘drive cycle’. A drive cycle is a set of specific driving conditions that allows the vehicle’s computer to re-run diagnostics and confirm that the issue is resolved. The specifics of a drive cycle vary by manufacturer and vehicle model.
- Disconnecting the Battery (Caution Advised): Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery can reset the computer and clear OBD2 codes. However, this method is not recommended as a primary way to clear codes because it can also erase other important computer settings and may not effectively clear all types of codes. Moreover, improper battery disconnection can cause electrical issues in some vehicles.
Cautions: When Not to Clear Codes and Seek Professional Help
- Before Diagnosis: Never clear OBD2 codes before properly diagnosing the problem. Clearing codes will erase valuable diagnostic information that technicians need to identify the root cause.
- Serious Issues: If the OBD2 code indicates a serious mechanical or safety issue (e.g., airbag malfunction, braking problems, severe engine misfires), do not clear the code and continue driving. Seek immediate professional inspection and repair.
- Recurring Codes: If a code reappears shortly after being cleared, it indicates that the underlying problem has not been resolved. In such cases, professional diagnosis is essential.
Preventing Global OBD2 Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Preventing OBD2 codes is always better than dealing with them. Proactive vehicle maintenance is the most effective way to minimize the occurrence of these diagnostic alerts and ensure the long-term health of your vehicles.
Regular Maintenance: The Key to Prevention
Regularly scheduled maintenance is crucial for preventing OBD2 codes. This includes:
- Routine Inspections: Regular checks of engine components, hoses, belts, fluids, and electrical connections can identify potential issues before they trigger OBD2 codes.
- Fluid Changes: Timely oil changes, transmission fluid flushes, coolant replacements, and brake fluid services are essential for maintaining system health and preventing wear and tear that can lead to diagnostic codes.
- Filter Replacements: Regularly replacing air filters and fuel filters ensures optimal engine performance and prevents issues related to air and fuel delivery, which are common causes of OBD2 codes.
- Spark Plug and Ignition System Maintenance: Faulty spark plugs and ignition components are frequent triggers for misfire codes. Regular inspection and replacement of spark plugs and related parts are important.
- Brake System Checks: Regular brake inspections and maintenance prevent issues related to braking performance and ABS/ESC systems, which can trigger chassis-related OBD2 codes.
Fuel and Fluid Quality: Global Standards and Recommendations
Using high-quality fuels and fluids that meet or exceed manufacturer specifications is vital for preventing OBD2 codes.
- Fuel Quality: Use fuel from reputable sources and adhere to the recommended octane rating for your vehicle. Low-quality fuel can lead to incomplete combustion, deposit buildup, and issues with fuel delivery and emissions systems, triggering OBD2 codes.
- Fluid Quality: Use manufacturer-recommended engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, power steering fluid, and brake fluid. These fluids are formulated to meet specific vehicle requirements and provide optimal lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic performance. Using substandard fluids can lead to premature wear, overheating, and system malfunctions, resulting in OBD2 codes.
- Regular Fluid Level Checks: Periodically check fluid levels (oil, coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid) and top them off as needed. Low fluid levels can lead to system stress and potential damage, triggering diagnostic codes.
Global OBD2 Code Management for Fleets: Efficiency and Optimization
For fleet managers, efficiently managing OBD2 codes across a large number of vehicles is crucial for minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Centralized systems and proactive monitoring are key strategies.
Centralized Tracking Systems for Global Fleets
Implementing a centralized system for tracking OBD2 codes across your fleet can significantly streamline maintenance operations. Modern fleet management software can integrate with vehicle telematics systems to automatically collect and centralize OBD2 code data from all vehicles. This provides a single dashboard view of vehicle health across the entire fleet, enabling fleet managers to:
- Real-time Code Alerts: Receive immediate notifications when OBD2 codes are triggered in any vehicle.
- Historical Code Data Analysis: Analyze trends and patterns in OBD2 codes to identify recurring issues with specific vehicle types or systems, facilitating proactive maintenance planning.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Integrate OBD2 code data with maintenance schedules to prioritize repairs based on code severity and vehicle usage.
Real-time Monitoring and Telematics Solutions
Telematics systems offer real-time vehicle monitoring, including the detection of OBD2 codes as they occur. These systems transmit vehicle data, including diagnostic codes, location, and performance metrics, to a central platform. Real-time monitoring enables fleet managers to:
- Immediate Issue Detection: Identify OBD2 codes and potential problems as soon as they arise, allowing for rapid response and minimizing vehicle downtime.
- Remote Diagnostics: In some advanced systems, remote diagnostic capabilities allow technicians to access OBD2 data remotely, enabling preliminary assessments and faster troubleshooting.
- Predictive Maintenance: By monitoring trends in OBD2 codes and vehicle performance data, telematics systems can help predict potential maintenance needs, enabling proactive scheduling and preventing breakdowns.
Prioritizing Repairs: A Strategic Approach for Global Operations
Effective OBD2 code management for fleets requires a strategic approach to prioritizing repairs. Codes should be categorized based on severity and potential impact on vehicle operation and safety.
- High-Severity Codes: Codes indicating critical safety issues (e.g., braking system, airbag faults) or potential for major engine damage should be prioritized for immediate repair to prevent accidents and minimize downtime.
- Medium-Severity Codes: Codes indicating issues that can affect vehicle performance, fuel economy, or emissions but are not immediately critical should be scheduled for repair as soon as practically possible.
- Low-Severity Codes: Codes indicating minor issues that do not pose immediate risks can be scheduled for repair during routine maintenance intervals.
By strategically prioritizing repairs based on OBD2 code severity, fleet managers can optimize resource allocation, minimize vehicle downtime, and maintain efficient fleet operations.
In Summary
Global OBD2 codes are an essential diagnostic tool for modern vehicles. Understanding these codes, their types, and how to manage them is crucial for vehicle owners and fleet managers alike. By proactively monitoring OBD2 codes, performing regular maintenance, and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure vehicle longevity, optimal performance, and safety. Whether you are managing a large fleet or maintaining your personal vehicle, mastering the basics of global OBD2 codes empowers you to take better care of your vehicles and keep them running smoothly on roads worldwide.