Are you looking to understand the diagnostic capabilities of your 2003 Chevy Silverado? The On-Board Diagnostics 2 (OBD2) system is a crucial part of modern vehicle maintenance and repair. For 2003 Silverado owners, understanding ISO OBD2 compatibility is the first step to effectively diagnosing and maintaining your truck. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of OBD2, specifically tailored to your 2003 Silverado, ensuring you can leverage this powerful system for optimal vehicle health.
Understanding OBD2 and Your 2003 Silverado
OBD2 is essentially your truck’s built-in health monitoring system. It’s a standardized protocol that allows you, or a mechanic, to access a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and identify potential issues. You’ve likely seen the “check engine light” – that’s OBD2 in action, alerting you to a problem detected by your Silverado’s internal sensors.
When that light comes on in your 2003 Silverado, or if you’re simply performing routine maintenance, an OBD2 scanner becomes an invaluable tool. Mechanics connect these scanners to the OBD2 16-pin connector, typically located near the steering wheel. This connection allows the scanner to send ‘OBD2 requests’ and receive ‘OBD2 responses’ from your Silverado. This data can include everything from engine speed and coolant temperature to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that pinpoint specific problems.
Understanding the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) and OBD2 diagnostics for your vehicle.
Does a 2003 Silverado Have OBD2? Absolutely.
The short answer is yes, your 2003 Chevrolet Silverado is equipped with OBD2. In fact, OBD2 compliance became mandatory in the USA for cars and light trucks starting in 1996. By 2003, OBD2 was a standard feature on virtually all vehicles sold in North America, including your Silverado.
This standardization is critical because it ensures that regardless of the manufacturer, any OBD2 compliant scanner can communicate with your 2003 Silverado’s computer system. This wasn’t always the case; older diagnostic systems were often proprietary and manufacturer-specific. OBD2 brought about a universal approach to vehicle diagnostics, making it easier and more cost-effective to maintain your vehicle.
OBD2 History and the 2003 Mandate
The journey to OBD2 standardization began in California, driven by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) to control vehicle emissions. The need for a standardized system became clear, leading the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) to recommend the OBD2 standard. This included standardized DTCs and the universal OBD connector we use today (SAE J1962).
The rollout of OBD2 was a phased process:
- 1996: OBD2 became mandatory in the USA for cars and light trucks. This is the key year that confirms your 2003 Silverado, being a light truck, will definitely have OBD2.
- 2001: Required in the EU for gasoline cars.
- 2003: Required in the EU for diesel cars as well (EOBD). This year is particularly relevant as it highlights the global adoption of OBD2 around the time your Silverado was manufactured.
- 2005-2010: Further expansions to medium and heavy-duty vehicles in the US.
A timeline illustrating the history of OBD2 and its evolution for emission control.
A visual timeline overview of the key milestones in OBD2 history.
OBD2 Standards Relevant to Your 2003 Silverado: ISO and More
OBD2 operates as a higher layer protocol. Think of it as a language that your 2003 Silverado’s computer and a diagnostic scanner can both understand. For the 2003 Silverado, it’s important to understand the underlying communication methods. While newer cars predominantly use CAN (Controller Area Network) bus, vehicles of the 2003 era might utilize different physical layer protocols, though CAN was becoming increasingly common.
The OBD2 standards define several key aspects:
- OBD2 Connector: Standardized physical connector (SAE J1962 / ISO 15031-3).
- Lower-Layer Protocols: Communication methods used to transmit data.
- OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs): Codes used to request specific data parameters.
For a 2003 Silverado, it’s highly likely to use ISO 15765-4 (CAN) as its communication protocol, which became mandatory in the US in later years but was already widely adopted by 2003. However, it’s also possible that older protocols like ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000), ISO 9141-2, or even SAE J1850 variants could be present, though less probable for a Silverado of this year, which was geared towards modern standards.
The OSI model illustrating the relationship between OBD2 and CAN Bus standards, including ISO specifications.
Locating the OBD2 Connector in Your 2003 Silverado
The OBD2 connector in your 2003 Chevy Silverado is designed for easy access. You’ll typically find it within the driver’s side compartment of your truck. Common locations include:
- Underneath the dashboard on the driver’s side: Look for it near the steering column or around the area where your knees would be.
- Above the pedals: In some cases, it might be positioned slightly higher, above the brake and accelerator pedals.
The connector is a standard 16-pin SAE J1962 Type A female connector. It’s designed to be easily accessible for diagnostic tools. While generally not hidden, it might be tucked away slightly, so a quick look with a flashlight can be helpful if you’re having trouble locating it initially.
Pinout diagram of a Type A OBD2 connector, commonly found in cars and light trucks like the 2003 Silverado.
OBD2 and CAN Bus: ISO 15765-4 in Your Silverado
As mentioned, it is highly probable that your 2003 Silverado uses CAN bus as the lower-layer protocol for OBD2 communication, adhering to ISO 15765-4 standards. ISO 15765-4, also known as Diagnostics over CAN (DoCAN), is a set of specifications that define how OBD2 messages are transmitted over a CAN network.
Key aspects of ISO 15765-4 relevant to your 2003 Silverado include:
- CAN bus bit-rate: Typically either 250K or 500K. For passenger vehicles like the Silverado, 500K is more common.
- CAN IDs: Can use both 11-bit and 29-bit identifiers. 11-bit is more frequently used for OBD2 in cars.
- Standardized CAN IDs: Specific IDs are reserved for OBD2 requests and responses, ensuring consistent communication.
- Data Length: Diagnostic CAN frames are typically 8 bytes in length.
Understanding that your 2003 Silverado likely uses CAN bus and ISO 15765-4 is important when selecting an OBD2 scanner and interpreting the data. It ensures compatibility and correct data interpretation.
Comparison of OBD2 Connector Type A and Type B, highlighting differences in power supply and typical vehicle applications.
Diagram illustrating the relationship between OBD2 and CAN bus according to ISO 15765 standards.
OBD2 Communication: Requests, Responses, and CAN IDs for 2003 Silverado
OBD2 communication is based on a request-response system. A diagnostic tool sends a request, and your 2003 Silverado’s engine control unit (ECU) or other relevant modules respond with the requested data.
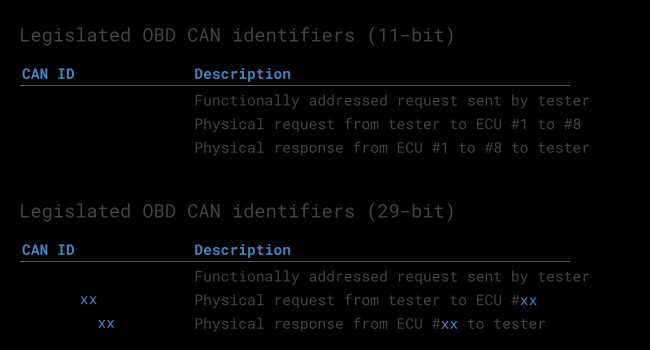
For most 2003 Silverados using 11-bit CAN IDs for OBD2:
- Functional Addressing Request ID:
0x7DF. This ID is used to send a general request to all OBD2-compliant ECUs in your Silverado. - Physical Addressing Request IDs:
0x7E0–0x7E7. These are less commonly used for general OBD2 scanning but can target specific ECUs if needed. - Response IDs:
0x7E8–0x7EF. The most common response ID you’ll see is0x7E8, which typically comes from the Engine Control Module (ECM).
In some heavier-duty versions or specific configurations of the Silverado, 29-bit CAN IDs might be used for OBD2. In this case:
- Functional Addressing CAN ID:
0x18DB33F1. - Response IDs:
0x18DAF100to0x18DAF1FF.
For typical diagnostics on a 2003 Silverado, you will most likely encounter 11-bit CAN IDs and the functional request ID 0x7DF.
Illustrating the request and response frame structure in OBD2 communication, showing Mode, PID, and data bytes.
 OBD2 OBD CAN bus Identifiers 7DF 7E8 7E0
OBD2 OBD CAN bus Identifiers 7DF 7E8 7E0
Using an OBD2 Scanner on Your 2003 Silverado: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using an OBD2 scanner on your 2003 Silverado is straightforward:
- Locate the OBD2 port: As discussed, it’s usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn the ignition to ‘Key On, Engine Off’ (KOEO): This means turn the key to the position just before starting the engine. This powers up the vehicle’s electronics without the engine running.
- Plug in the OBD2 scanner: Connect your scanner to the 16-pin OBD2 port. Ensure it’s firmly seated.
- Power on the scanner: Most scanners will power on automatically once connected or have a power button.
- Initiate scanning: Follow your scanner’s instructions to begin a scan. Typically, you’ll select options like “Read Codes,” “Diagnostic Scan,” or similar.
- View DTCs and Data: The scanner will display any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and may also show real-time data parameters (PIDs).
- Interpret DTCs: Use the scanner’s built-in DTC definitions or consult a reliable OBD2 DTC lookup resource to understand what each code means.
- Clear Codes (Optional): After addressing the issue, you can use the scanner to clear the DTCs and turn off the check engine light. However, ensure the problem is resolved; otherwise, the light will likely reappear.
- Disconnect the scanner: Once you’re finished, turn the ignition off and disconnect the OBD2 scanner.
For a 2003 Silverado, common OBD2 functions you might use are reading and clearing trouble codes, viewing live engine data, and performing emissions readiness checks.
Common OBD2 PIDs for 2003 Silverado Diagnostics
OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs) are codes used to request specific pieces of data from your 2003 Silverado. While there are hundreds of standardized PIDs, your Silverado, like most vehicles, will only support a subset.
Some useful OBD2 PIDs to monitor on a 2003 Silverado include:
- PID 0x04: Calculated Engine Load: Indicates the percentage of maximum engine power being used.
- PID 0x05: Engine Coolant Temperature: Crucial for monitoring engine health and preventing overheating.
- PID 0x0C: Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute of the engine crankshaft.
- PID 0x0D: Vehicle Speed: Speed of the vehicle.
- PID 0x0E: Intake Air Temperature: Temperature of the air entering the engine.
- PID 0x0F: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): Pressure in the intake manifold, important for fuel and air mixture calculations.
- PID 0x10: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Rate: Amount of air entering the engine by weight.
- PID 0x11: Throttle Position: Percentage of throttle valve opening.
- PID 0x2C: Commanded EGR Duty Cycle & PID 0x2D: EGR Error: For monitoring the Exhaust Gas Recirculation system, important for emissions.
To check which PIDs your 2003 Silverado supports, you can use Mode 0x01 PID 0x00. Requesting this PID will return a bitmask indicating supported PIDs from 0x01 to 0x20. Similarly, PID 0x20, 0x40, etc., will indicate support for subsequent PID ranges.
Breakdown of an OBD2 message structure, showing the position of Mode, PID, and data bytes within a frame.
OBD2 Services (Modes) and Your 2003 Silverado
OBD2 defines 10 diagnostic services, also known as modes. These services allow you to access different types of diagnostic information. For your 2003 Silverado, the most commonly used modes are:
- Mode 0x01: Show current data: Displays real-time data parameters (PIDs) like engine speed, temperature, etc.
- Mode 0x03: Show stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Retrieves currently stored DTCs that have triggered the check engine light.
- Mode 0x04: Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes and stored values: Clears DTCs and resets certain system values. Use with caution and only after addressing the underlying issue.
- Mode 0x07: Show pending Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Displays DTCs that have not yet triggered the check engine light but are detected as potential issues.
- Mode 0x09: Request vehicle information: Used to retrieve vehicle information like the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
Less frequently used modes, which might still be supported in your 2003 Silverado, include freeze frame data (Mode 0x02), oxygen sensor test results (Mode 0x05), and on-board monitoring test results (Mode 0x06).
Overview of the 10 standardized OBD2 diagnostic services (modes) and their functions.
Troubleshooting Common 2003 Silverado Issues with OBD2
OBD2 is incredibly helpful for diagnosing common problems in a 2003 Silverado. Here are a few examples:
-
Check Engine Light (MIL) On: An OBD2 scan will retrieve the DTC(s) causing the light. Common codes for a 2003 Silverado might relate to:
- P0171/P0174 (System Too Lean): Could indicate vacuum leaks, MAF sensor issues, or fuel delivery problems.
- P0300 (Random Misfire): Points to issues with ignition, fuel, or compression in one or more cylinders.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold): Often related to a failing catalytic converter or oxygen sensor issues.
- P0440/P0455 (Evaporative Emission Control System Leak): Indicates leaks in the EVAP system, potentially from a loose gas cap or faulty components.
-
Rough Running or Misfires: Monitor PIDs like Engine RPM (0x0C), Engine Load (0x04), MAF Rate (0x10), and Misfire counts (if supported by your scanner) to help pinpoint the cause. DTCs like P0300 series will also be crucial.
-
Poor Fuel Economy: Check PIDs like Calculated Engine Load (0x04), MAF Rate (0x10), Oxygen Sensor readings (if your scanner supports them), and look for codes related to fuel trim (P0171, P0174) or oxygen sensors (P0130 series, P0150 series).
By using an OBD2 scanner and understanding the DTCs and PIDs, you can significantly narrow down the potential causes of issues in your 2003 Silverado, saving time and diagnostic costs.
Conclusion: OBD2 – Your Diagnostic Partner for Your 2003 Silverado
For owners of a 2003 Chevy Silverado, understanding and utilizing the ISO OBD2 system is essential for vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting. Your truck is fully equipped to communicate with OBD2 scanners, providing valuable insights into its health and performance. By knowing where your OBD2 port is, understanding the basics of OBD2 protocols like CAN bus, and learning to use an OBD2 scanner, you can take a proactive approach to vehicle care.
Whether you’re addressing a check engine light, monitoring engine parameters, or performing routine diagnostics, OBD2 empowers you to understand your 2003 Silverado better and ensure it remains reliable for years to come. Remember to always consult repair manuals and professional mechanics for complex issues, but OBD2 provides a powerful first step in understanding your vehicle’s needs.
For more in-depth information on OBD2, advanced diagnostics, and vehicle repair, visit cardiagnosticnearme.com – your resource for automotive diagnostic expertise.
