As a website dedicated to car diagnostics, cardiagnosticnearme.com understands the importance of deciphering your vehicle’s health. If you’re a fleet manager or simply a vehicle owner, encountering OBD2 codes can seem daunting. However, these codes are essentially your car’s way of communicating potential issues, acting like digital messengers from under the hood.
Think of OBD2 codes as a diagnostic language spoken by your vehicle. Understanding this language empowers you to proactively maintain your cars, ensuring smooth operations and preventing minor issues from becoming major headaches.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the complexities of OBD2 codes, explaining what they are, how to interpret them, and why understanding “Obd2 Codes And Meanings” is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Whether you’re managing a fleet or caring for a personal vehicle, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to take control of your vehicle’s health.
Decoding OBD2 Codes: Understanding the Basics
On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) codes are alphanumeric codes generated by your vehicle’s onboard computer system. This system constantly monitors various components, from the engine and transmission to emission controls, acting as a central nervous system for your car. When the computer detects a problem or reading outside of normal parameters in these systems, it generates a specific OBD2 code.
These codes are essentially trouble alerts, signaling that something isn’t functioning as expected. The infamous “Check Engine Light” illuminates on your dashboard specifically because an OBD2 code has been triggered and stored in the vehicle’s computer.
To access these codes and understand the “obd2 codes and meanings”, you’ll need an OBD2 scanner. This tool plugs into your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically found beneath the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner retrieves the stored codes, translating the vehicle’s internal communication into a readable format. These codes then provide a starting point for diagnosing the issue, guiding you or a professional mechanic towards the root cause of the problem. Understanding “obd2 codes and meanings” is the first step in effective automotive troubleshooting.
 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Exploring the Types of OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
When an OBD2 code appears, knowing its category is essential for narrowing down the potential problem. OBD2 codes are categorized into four main types, each relating to a different area of your vehicle. Understanding these categories is key to grasping “obd2 codes and meanings”.
Powertrain Codes (P-Codes)
Powertrain codes, often starting with the letter ‘P’, are the most common type of OBD2 code. They indicate issues within the powertrain system, which encompasses the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. Essentially, powertrain codes relate to anything that contributes to the vehicle’s power generation and delivery.
For example, a common powertrain code is P0300, indicating a “Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected.” This “obd2 codes and meanings” points to a problem with engine combustion, potentially due to faulty spark plugs, fuel injectors, or vacuum leaks. Addressing powertrain codes promptly is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Body Codes (B-Codes)
Body codes, starting with ‘B’, signal problems within the vehicle’s body systems. These systems include components like airbags, power windows, climate control, and interior/exterior lighting. While not directly related to the engine’s mechanical operation, body codes are vital for safety and comfort systems.
For instance, B0001, a body code, might indicate “Driver Frontal Airbag Deployment Loop Resistance Low.” Understanding this “obd2 codes and meanings” is critical as it points to a potential malfunction in the airbag system, a crucial safety feature. Body codes often relate to electrical or sensor issues within these comfort and safety systems.
Chassis Codes (C-Codes)
Chassis codes, beginning with ‘C’, identify issues within the chassis systems. This category includes systems related to vehicle control and stability, such as the anti-lock braking system (ABS), traction control, electronic stability control, and steering. Chassis codes are directly related to vehicle handling and safety.
An example is C0044, indicating “Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.” Knowing this “obd2 codes and meanings” is important because a malfunctioning wheel speed sensor can affect ABS and traction control systems, compromising braking and stability, especially in adverse driving conditions.
Network Communication Codes (U-Codes)
Network communication codes, starting with ‘U’, relate to communication issues within the vehicle’s computer network. Modern vehicles have complex networks that allow various modules (like the engine control module, transmission control module, etc.) to communicate and share data. U-codes indicate disruptions in this communication.
For example, U0101 might indicate “Lost Communication With TCM (Transmission Control Module).” Understanding this “obd2 codes and meanings” suggests a problem in the vehicle’s internal communication network, potentially disrupting the interaction between the engine and transmission computers. Network communication issues can sometimes be complex to diagnose, often requiring specialized tools and expertise.
Decoding the Structure: Reading OBD2 Code Meanings
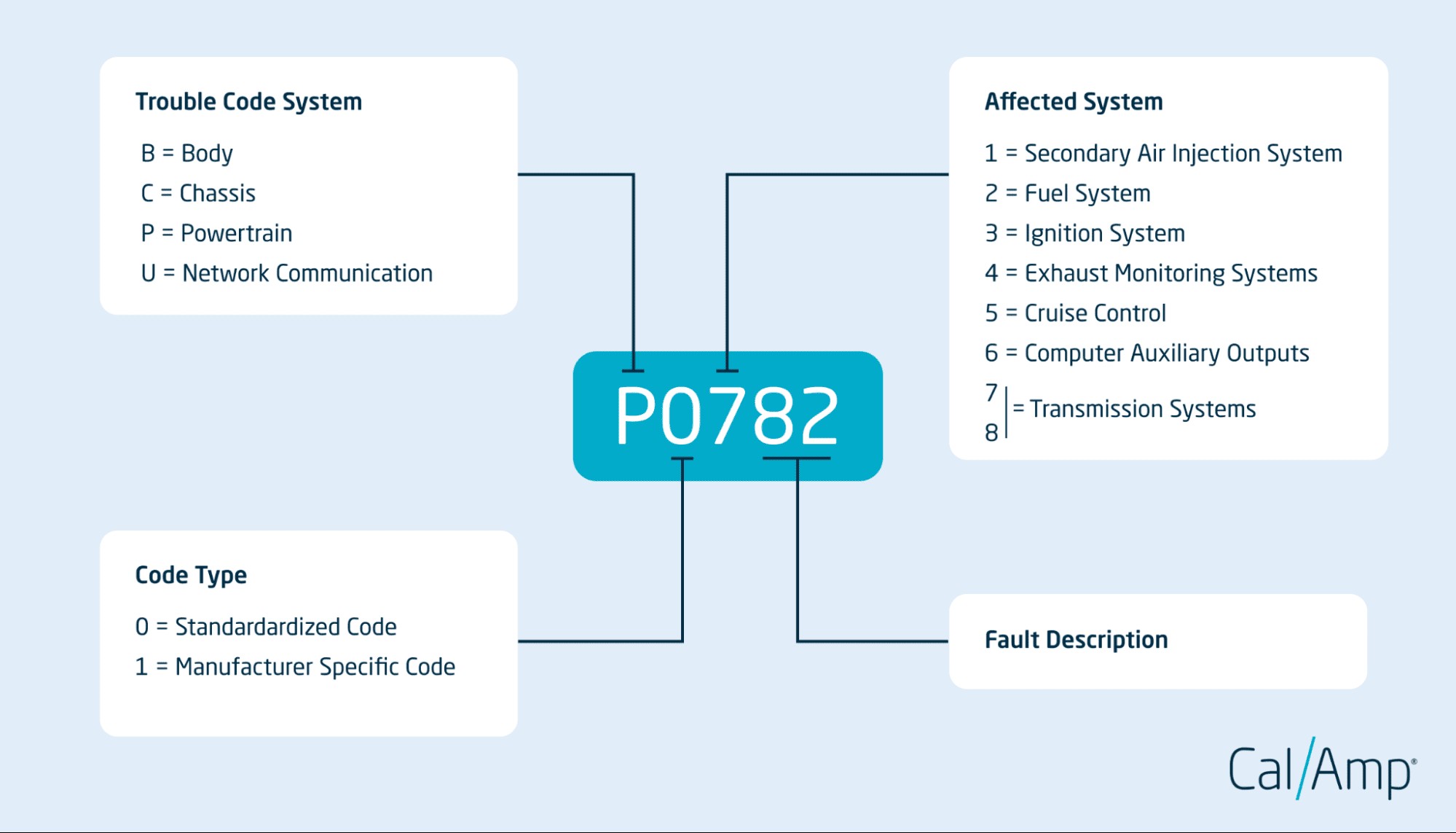
OBD2 codes are not random; they follow a structured format of five characters, each providing specific information. Understanding this structure is key to deciphering “obd2 codes and meanings” effectively.
Each character in the five-character OBD2 code provides a piece of the diagnostic puzzle:
-
First Character: Trouble Code System: This letter indicates the main system affected:
- P – Powertrain (Engine, Transmission)
- B – Body (Airbags, Comfort/Convenience Systems)
- C – Chassis (Brakes, Steering, Suspension)
- U – Network Communication
-
Second Character: Code Type: A digit indicating if the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0 – Generic (Standardized across all manufacturers)
- 1 – Enhanced (Manufacturer-specific – indicates more detailed information specific to the vehicle make)
-
Third Character: Affected System (Subsystem): A digit indicating the specific subsystem within the main system (indicated by the first character) that is experiencing the problem. Common subsystems include:
- 1 – Fuel and Air Metering
- 2 – Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3 – Ignition System or Misfire
- 4 – Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5 – Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 6 – Computer Output Circuit
- 7, 8 – Transmission
-
& 5. Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Code: These two digits provide a more precise identification of the fault within the identified system and subsystem. These are sequential numbers that pinpoint the exact nature of the problem. For example, in P0420, “20” specifies “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).”
By understanding this structure, you can begin to interpret “obd2 codes and meanings” even before consulting a detailed code definition. For instance, a code starting with ‘P03’ immediately tells you it’s a generic powertrain code related to the ignition system or misfires.
Clearing OBD2 Codes: When and How
While clearing OBD2 codes might seem like a quick fix, it’s crucial to understand when and how to do it appropriately. Generally, simply clearing a code without addressing the underlying issue is not recommended. The “Check Engine Light” will likely reappear if the problem persists. However, there are situations where clearing codes can be useful, particularly after repairs are made or for diagnostic purposes.
Here are common methods for clearing OBD2 codes:
Using an OBD2 Scanner for Code Clearing
OBD2 scanners are not only for reading codes but also for clearing them. After diagnosing and repairing the issue indicated by an OBD2 code, you can use a scanner to clear the code and turn off the “Check Engine Light.” This verifies that the repair was successful and resets the system.
Many OBD2 scanners have a dedicated “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” function. By selecting this option within the scanner’s menu and following the prompts, you can clear the stored codes from the vehicle’s computer.
Drive Cycle for Automatic Code Clearing
Some OBD2 codes, especially those related to minor or intermittent issues, may clear themselves after a “drive cycle.” A drive cycle is a specific set of driving conditions that allows the vehicle’s computer to re-evaluate the system that triggered the code. If the issue is no longer detected during the drive cycle, the code may automatically clear, and the “Check Engine Light” will turn off.
However, drive cycles are not a reliable method for clearing all codes, and they don’t address the root problem. They are more of a consequence of a problem resolving itself or being temporarily absent.
Professional Mechanic for Diagnosis and Code Clearing
If you’re unsure about the “obd2 codes and meanings”, the cause of the code, or how to properly address it, consulting a qualified mechanic is always the best approach. Mechanics have advanced diagnostic tools, expertise, and experience to accurately diagnose the underlying problem, perform necessary repairs, and then clear the OBD2 codes appropriately.
Mechanics ensure that the codes are cleared after a genuine fix, not just as a temporary measure. They can also identify and address any related issues that might not be immediately obvious from the initial OBD2 code.
Preventing OBD2 Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Prevention is always better than cure, and this holds true for OBD2 codes. Regular and proactive vehicle maintenance is the most effective way to prevent OBD2 codes from appearing and avoid costly repairs down the line. Understanding “obd2 codes and meanings” starts with preventing them in the first place.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance Schedules
Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is crucial. This schedule, typically outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual, includes routine tasks like:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes with the correct type of oil are vital for engine lubrication and preventing engine-related OBD2 codes.
- Fluid Checks and Flushes: Regularly checking and replacing fluids like coolant, transmission fluid, brake fluid, and power steering fluid ensures optimal system performance and prevents component failures that can trigger codes.
- Air and Fuel Filter Replacements: Clean air and fuel filters are essential for efficient engine operation. Clogged filters can lead to fuel mixture issues and trigger OBD2 codes related to engine performance and emissions.
- Spark Plug and Ignition System Maintenance: Properly functioning spark plugs and ignition components are critical for efficient combustion. Faulty components can cause engine misfires and trigger powertrain codes.
- Brake System Inspections: Regular brake inspections and maintenance ensure safe braking and prevent issues with brake sensors that can trigger chassis codes.
- Tire Rotations and Inspections: Maintaining proper tire pressure and rotating tires regularly ensures even wear and optimal vehicle handling, indirectly contributing to overall system health and potentially preventing chassis-related issues.
Using Quality Fuel and Fluids
Using high-quality fuel and fluids is another key preventative measure. Lower quality fuel can lead to incomplete combustion, deposit buildup, and issues with fuel injectors and catalytic converters, all of which can trigger OBD2 codes, particularly powertrain and emissions-related codes. Similarly, using the correct, high-quality fluids ensures proper lubrication and cooling, preventing premature wear and tear on engine and transmission components.
- Choose Reputable Fuel Stations: Opt for well-known and reputable gas stations that are less likely to sell contaminated or low-quality fuel.
- Use Recommended Octane Fuel: Use the fuel octane rating recommended for your vehicle by the manufacturer. Using lower octane fuel than recommended can lead to engine knocking and potential damage.
- Use Manufacturer-Recommended Fluids: Always use fluids (oil, coolant, transmission fluid, etc.) that meet or exceed the specifications recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
Managing OBD2 Codes for Fleets: Efficiency and Proactive Maintenance
For fleet managers, handling OBD2 codes efficiently is paramount to minimizing vehicle downtime and controlling maintenance costs. Centralized tracking and proactive monitoring are key strategies for fleet OBD2 management.
Centralized OBD2 Code Tracking Systems
Implementing a system to centralize OBD2 code data from all fleet vehicles provides a consolidated view of vehicle health. Modern fleet management software, like CalAmp iOn mentioned in the original article, can automatically collect and track OBD2 codes, providing real-time alerts and historical data.
This centralized approach allows fleet managers to:
- Quickly Identify Issues: See all active OBD2 codes across the fleet in one dashboard.
- Track Recurring Problems: Identify patterns and trends in specific vehicles or vehicle types, indicating potential systemic issues.
- Prioritize Maintenance: Focus resources on vehicles with critical OBD2 codes to minimize downtime.
- Generate Maintenance Reports: Analyze historical OBD2 code data to optimize maintenance schedules and predict potential failures.
Ongoing Fleet Monitoring with Telematics
Integrating telematics systems into fleet vehicles provides continuous monitoring of vehicle health, including OBD2 codes. Telematics systems transmit real-time data on vehicle location, performance, and diagnostic information, including OBD2 codes, to a central platform.
This proactive monitoring enables fleet managers to:
- Receive Instant OBD2 Code Alerts: Be notified immediately when an OBD2 code is triggered in any vehicle.
- Remotely Diagnose Issues: Get preliminary diagnostic information without physically inspecting each vehicle.
- Proactively Schedule Maintenance: Schedule maintenance as soon as an issue is detected, preventing minor problems from escalating.
- Reduce Downtime: Minimize vehicle downtime by addressing issues quickly and efficiently.
Prioritizing Repairs Based on OBD2 Code Severity
Not all OBD2 codes are equally critical. Fleet managers should implement a system for prioritizing repairs based on the severity and potential impact of each code.
- Categorize Codes by Severity: Classify codes as high, medium, or low severity based on their potential impact on vehicle safety, performance, and downtime.
- Prioritize High-Severity Codes: Address high-severity codes immediately to prevent breakdowns and safety risks. These might include codes related to critical engine, braking, or safety systems.
- Schedule Medium-Severity Codes: Schedule repairs for medium-severity codes promptly but with some flexibility. These codes might relate to issues affecting performance or emissions.
- Plan Low-Severity Code Maintenance: Low-severity codes, indicating minor issues, can be addressed during routine maintenance intervals.
In Conclusion: Mastering OBD2 Codes and Meanings for Vehicle Health
Understanding “obd2 codes and meanings” is no longer just for mechanics. For vehicle owners and fleet managers alike, deciphering these codes is a vital skill for maintaining vehicle health, preventing costly repairs, and ensuring safe and efficient operation.
OBD2 codes are your vehicle’s way of communicating its needs. By learning to listen to this diagnostic language, you can take proactive steps to keep your vehicles running smoothly and reliably for years to come. Whether you utilize an OBD2 scanner for personal diagnostics or implement a comprehensive telematics system for fleet management, mastering “obd2 codes and meanings” puts you in control of your vehicle’s health and longevity.
For further insights and tools to help you manage your vehicle diagnostics, explore more resources at cardiagnosticnearme.com.