Experiencing issues with your OBD2 port on your 2004 Toyota Tundra can be frustrating, especially when you need to run diagnostics or pass an emissions test. If your OBD2 scanner isn’t connecting, a common culprit is a blown fuse. Let’s explore how to troubleshoot and fix the OBD2 fuse issue in your 2004 Toyota Tundra.
Understanding the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2004 Toyota Tundra
The OBD2 port in your 2004 Toyota Tundra is powered by a fuse, typically located in the engine bay fuse box. This fuse protects the diagnostic system from electrical overloads. If this fuse blows, your OBD2 port will lose power, preventing scanners from connecting and communicating with your truck’s computer. While some online resources might point to the EFI fuse, specifically for the OBD2 port fuse, you’ll want to check Fuse #7 in the engine bay fuse box. Always refer to your 2004 Toyota Tundra owner’s manual for the precise fuse location and amperage, as fuse box layouts can vary slightly depending on the model and trim. It’s usually a 7.5 amp or 10 amp fuse.
Troubleshooting Steps When Your OBD2 Port Isn’t Working
Before assuming a blown fuse, follow these troubleshooting steps to pinpoint the issue:
Check Your Scan Tool
The problem might not be your truck at all! First, ensure your OBD2 scan tool or cable is functioning correctly. Try using your scanner on another vehicle to see if it connects. If it doesn’t work on another car either, the issue likely lies with your scan tool itself. Consider testing with a different scanner at an auto parts store or repair shop to rule out a faulty device.
Inspect the OBD2 Fuse
Locate the engine bay fuse box in your 2004 Toyota Tundra. Consult your owner’s manual for the fuse box diagram. Identify the fuse associated with the OBD2 port, often Fuse #7. Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will usually have a broken wire inside or blackened appearance. Even if it looks okay, it’s a good practice to test the fuse with a fuse tester or multimeter for continuity to be certain.
Examine Wiring
While less common, wiring issues can also cause OBD2 port problems. Inspect the wiring leading to and from the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frays, or corrosion. Trace the wires back towards the fuse box and ECU if possible. This step might require more in-depth electrical knowledge and potentially a professional mechanic.
Battery Reset
Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve communication glitches. Disconnecting your Toyota Tundra’s battery for about 30 seconds and then reconnecting it can sometimes clear temporary electrical issues and restore OBD2 port functionality.
Try a Powered OBD2 Scanner
If a standard, unpowered OBD2 scanner isn’t working, consider using a powered scan tool. These scanners have their own internal battery and supply power to the OBD2 port independently. If a powered scanner works, but an unpowered one doesn’t, it suggests a potential power supply issue within your truck’s OBD2 system, possibly related to the fuse or wiring we’ve discussed.
Consider ECU Issues
In rare cases, a malfunctioning Engine Control Unit (ECU) could be the cause of OBD2 port problems. However, this is usually a last resort diagnosis after ruling out simpler causes like fuses and wiring. ECU issues are more complex and often require professional diagnostic equipment and expertise.
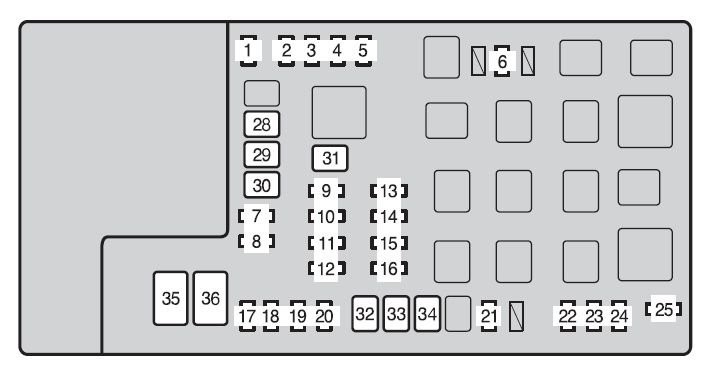 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
An example of an engine bay fuse box, similar in layout to what you might find in a 2004 Toyota Tundra. Locate the fuse diagram for your specific model to pinpoint the OBD2 fuse location.
Real-World Scenario and Solution
Imagine you’re getting ready for your 2004 Toyota Tundra’s routine maintenance, including an emissions test. You plug in your trusted OBD2 scanner, but it fails to connect. Panic sets in. After some initial troubleshooting, checking your scanner on another vehicle and confirming it’s functional, you turn your attention to your truck. Following the steps above, you locate the engine bay fuse box and identify the OBD2 fuse. Upon inspection, you find the 7.5 amp fuse is indeed blown. Replacing the fuse with a new one of the correct amperage restores power to the OBD2 port, and your scanner now connects without issue. This simple fuse replacement saves you time, money, and the headache of potentially unnecessary repairs.
Conclusion
A non-functioning OBD2 port on your 2004 Toyota Tundra can often be traced back to a blown fuse. By systematically checking the fuse, along with other potential causes like scan tool issues or wiring problems, you can effectively diagnose and resolve the problem. Remember to always consult your owner’s manual for the most accurate information regarding fuse locations and specifications for your specific 2004 Toyota Tundra model. And if you’re uncomfortable with electrical troubleshooting, seeking assistance from a qualified mechanic is always a wise decision.
