The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port in your vehicle is a crucial interface for accessing your car’s computer system. It’s how mechanics diagnose issues, and how you can use scan tools to understand your vehicle’s health. However, if your OBD2 port isn’t working, you’ll be unable to connect a scanner, leaving you in the dark about potential problems. One common culprit for a dead OBD2 port is a blown fuse, and while the specific term “05 Ion Obd2 Fuse” might be slightly unusual, it likely refers to a fuse related to the OBD2 port’s power supply. Let’s explore how to troubleshoot this and other potential issues.
To understand where problems can arise, let’s first look at the OBD2 port pinout and what each pin is responsible for:
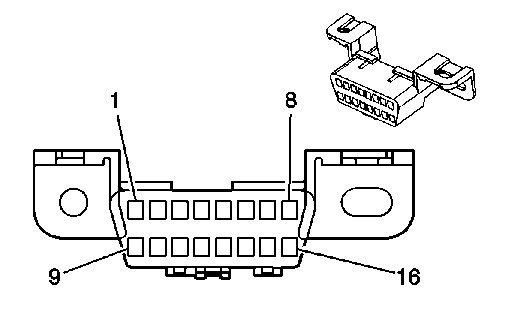 OBD2 port pin numbering
OBD2 port pin numbering
And here’s a breakdown of the typical OBD2 pin functions:
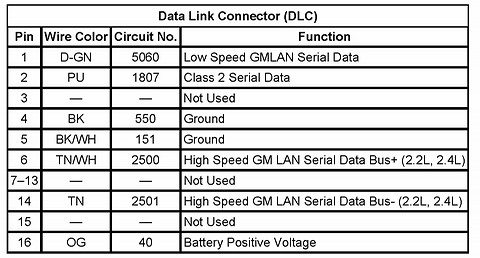 OBD2 pin function
OBD2 pin function
Checking the “05 Ion OBD2 Fuse” (Power Fuse)
While “05 ion” might not be a standard fuse specification, it’s highly probable that it points to a fuse related to the power supply for your OBD2 port. OBD2 ports need power to operate, typically drawing it from the car’s electrical system, and like any electrical circuit, it’s protected by a fuse. This fuse is designed to blow and break the circuit if there’s an overload, protecting the system from damage.
Here’s how to check the fuse:
- Locate your fuse box(es): Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual to find the location of the fuse box(es). They are commonly found under the dashboard, in the glove compartment, or under the hood.
- Identify the OBD2 fuse: Refer to the fuse box diagram in your owner’s manual. Look for a fuse labeled “OBD,” “Diagnostic,” “Accessory,” or “Cigar Lighter” (as sometimes the OBD2 port shares a fuse with the cigarette lighter/accessory socket). The amperage rating might be around 5, 10, or 15 amps, but the specific number is less crucial than finding the correct circuit. It’s possible “05” in “05 ion” refers to a 5 amp fuse, but verify against your car’s documentation.
- Inspect the fuse: Use a fuse puller (often found in the fuse box) or needle-nose pliers to gently remove the fuse. Visually inspect the fuse. If the thin wire inside the fuse is broken or melted, the fuse is blown and needs replacement.
- Replace the fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Do not use a fuse with a higher rating, as this can cause damage to the circuit.
- Test your OBD2 port: After replacing the fuse, try connecting your OBD2 scanner again to see if it now powers up and establishes a connection.
If replacing the fuse solves the problem, you’ve likely found the issue. However, if the fuse blows again quickly, or if the OBD2 port still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse, there might be other underlying problems.
Other Potential Causes of OBD2 Port Failure
If the fuse isn’t the issue, or keeps blowing, consider these other potential problems:
Pin Connection Problems
As highlighted in the original article, issues with the pins inside the OBD2 port are common:
- Pushed-back pins: Sometimes, the metal sockets inside the OBD2 port can get pushed back, especially if a scanner is forcefully plugged in or removed. Shine a flashlight into the port and look parallel to the pin sockets. Compare the depth of each socket. If any appear recessed compared to others, they might not be making proper contact with the scanner pins.
- Bent scanner pins: Inspect the pins on your OBD2 scanner plug itself. Bent pins can prevent proper insertion and contact. Carefully straighten any bent pins with extreme caution.
- Socket receiver damage: Repeated use or accidental damage can widen the socket receivers in the OBD2 port, leading to a loose connection.
Wiring and Connector Issues
- Loose wiring: The wires connected to the back of the OBD2 port can become loose or disconnected over time due to vibration or damage. If you suspect a loose wire, you might carefully try to access the back of the connector (if possible, and with the car off) to check for loose connections. However, this is often best left to a professional.
- Corrosion: Moisture or corrosion on the pins or wiring can impede electrical conductivity.
Scanner Malfunction
While less likely if you’ve used the scanner successfully before, the scanner itself could be faulty. Try using your scanner on another vehicle (if possible) to rule out scanner issues.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve checked the fuse, inspected the pins, and are still experiencing OBD2 port problems, it’s time to consult a qualified mechanic. Diagnosing electrical issues can be complex, and a professional technician has the tools and expertise to:
- Properly test the OBD2 port: They can use specialized tools to check for power and ground at the correct pins and verify communication signals.
- Diagnose wiring problems: They can trace wiring circuits to identify breaks, shorts, or corrosion that you might not be able to find easily.
- Identify deeper electrical issues: In rare cases, problems with the car’s computer system itself could be affecting the OBD2 port.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a non-working OBD2 port often starts with checking the “05 ion OBD2 fuse” – or more accurately, the fuse associated with the OBD2 port’s power circuit. Pin connection issues are also frequent culprits. By systematically checking these potential causes, you can often resolve the problem. However, for complex electrical faults, professional diagnosis is recommended to ensure proper and safe repairs.