The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port in your 1998 Buick Park Avenue is a crucial access point for diagnosing vehicle issues. If you’re experiencing problems connecting to this port, understanding its pinout is the first step in troubleshooting. This guide will provide you with the 1998 Buick Park Avenue OBD2 port pinout, common issues, and how to diagnose them, ensuring you can effectively communicate with your car’s computer system.
The OBD2 port, also known as the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), is standardized across most vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards. It allows mechanics and car owners to access the vehicle’s computer to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various diagnostic tests. For a 1998 Buick Park Avenue, this port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Having a functional OBD2 port is essential for routine inspections, diagnosing check engine lights, and ensuring your vehicle is running optimally. If you’re facing issues connecting your scanner or code reader to your 1998 Park Avenue’s OBD2 port, it can stem from several factors, ranging from simple connector problems to more complex electrical issues.
Understanding the pinout is key to diagnosing problems. Here’s a breakdown of the standard OBD2 port pinout, which applies to your 1998 Buick Park Avenue:
- Pin 1: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 2: J1850 Bus Positive
- Pin 3: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: K-Line ISO 9141-2 & ISO/DIS 14230-4
- Pin 8: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 9: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 10: J1850 Bus Negative
- Pin 11: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 12: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 13: Manufacturer Discretionary
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: L-Line ISO 9141-2 & ISO/DIS 14230-4
- Pin 16: Battery Power
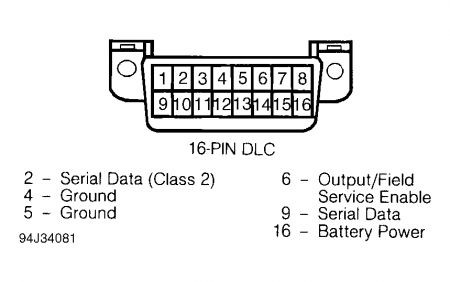 OBD2 Port Pinout Diagram for Diagnostic Checks
OBD2 Port Pinout Diagram for Diagnostic Checks
When troubleshooting a non-working OBD2 port on your 1998 Buick Park Avenue, start with these checks:
-
Visual Inspection: As suggested by the original poster in the forum, begin by visually inspecting the OBD2 port. Look for bent or corroded pins. Physical damage to the connector can prevent proper communication. Gently try cleaning the pins with a specialized electronic contact cleaner if they appear dirty or corroded.
-
Power and Ground Checks: A functioning OBD2 port requires both power and ground. Using a multimeter, check for voltage between:
- Pin 4 (Chassis Ground) and Pin 16 (Battery Power): You should read approximately 12V, as indicated in the forum discussion where the user found 12V between pins 4 and 16.
- Pin 5 (Signal Ground) and Pin 16 (Battery Power): Similarly, check for voltage here. The user also reported 12V between pins 5 and 16, which is expected as both pins 4 and 5 are grounds and pin 16 is power.
If you are not getting the expected voltage readings, you need to investigate the power and ground circuits. Check the fuses related to the diagnostic port and the vehicle’s computer system. Refer to your 1998 Buick Park Avenue owner’s manual for fuse box diagrams and fuse assignments.
-
Continuity Checks: If the power and ground checks are okay, but the port still isn’t working, there might be a break in the wiring. Use a multimeter to perform continuity tests on the power and ground wires leading to the OBD2 port. Trace the wires back to their source, checking for any breaks or loose connections.
-
Scanner Compatibility: While less likely with a standard OBD2 port, ensure your scanner is compatible with OBD2 protocols and specifically supports 1998 Buick Park Avenue vehicles. Some older or generic scanners might have compatibility issues.
-
Consult Wiring Diagrams: For more in-depth troubleshooting, refer to the 1998 Buick Park Avenue wiring diagrams. These diagrams will provide a detailed layout of the OBD2 port wiring and its connections to the vehicle’s computer (PCM/ECM).
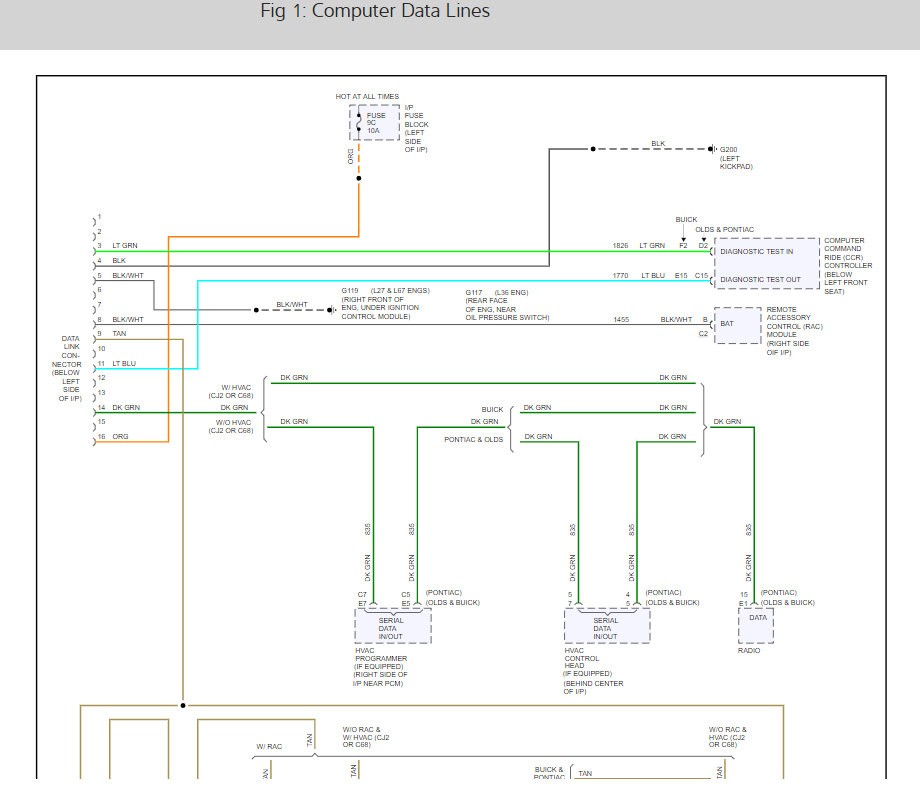 Wiring Diagram Example for OBD2 Port Inspection
Wiring Diagram Example for OBD2 Port Inspection
In some cases, as mentioned in the forum, confusion can arise with older vehicles around the OBD1/OBD2 transition period. While the 1998 Buick Park Avenue is definitively OBD2, some earlier models might have had hybrid systems or unique implementations. However, for a 1998 Park Avenue, you should expect a standard OBD2 port and protocol.
If you’ve performed these checks and are still unable to get your OBD2 port working, it’s advisable to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic with experience in automotive diagnostics can further investigate the issue, potentially using advanced tools like a Tech 1 scanner (mentioned in the forum) or other professional-grade diagnostic equipment to pinpoint the problem, whether it’s a wiring fault, a faulty port connector, or a deeper issue within the vehicle’s computer system.
Remember, a functional OBD2 port is crucial for maintaining your 1998 Buick Park Avenue. By understanding its pinout and following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose and address common issues, ensuring your vehicle is ready for inspection and running smoothly.