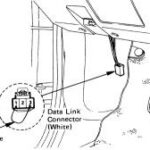
Experiencing problems with your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually Obd2 port reader and transmission performance can be frustrating. Many owners of these robust trucks encounter situations where diagnostic scanners fail to communicate with the vehicle’s computer, alongside unusual transmission behaviors after maintenance or repairs. This article addresses common diagnostic steps for tackling OBD2 port communication failures and related transmission downshifting issues specifically in your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually.
When your OBD2 port isn’t working on your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually, the first step is to verify the basics. Begin by checking the OBD2 port itself for any physical damage or corrosion. Next, confirm that your diagnostic scanner is compatible with OBD2 protocols and is functioning correctly on other vehicles if possible. Assuming the scanner is not the issue, focus on the power supply to the OBD2 port. Pin 16 should have battery voltage, while pins 4 and 5 are ground. Use a multimeter to test for both power and ground at these pins. A blown fuse is a frequent culprit, so inspect the fuses related to the cigarette lighter or auxiliary power, as they often share circuits with the OBD2 port.
If power and ground are confirmed at the OBD2 port of your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually, the problem might lie in the communication wiring or the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The diagnostic communication wires, typically violet and black/white, run between the OBD2 port, the instrument cluster, and the PCM. Check the continuity of these wires for any breaks or shorts using a multimeter, as demonstrated by the original poster who checked resistance and wire continuity. If the wiring is intact, the PCM itself becomes a prime suspect. A faulty PCM can cause both OBD2 communication failure and various transmission problems.
Regarding the transmission downshifting issue mentioned, it’s plausible that electrical problems affecting the PCM or related sensors could contribute to erratic transmission behavior in your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually. As the original poster described, swapping pressure sensors and solenoids can sometimes lead to partial fixes but might not resolve underlying issues fully. If you’ve already addressed the transmission components and the problem persists alongside OBD2 issues, a deeper diagnostic scan by a professional mechanic with advanced tools is highly recommended. They can assess PCM functionality, sensor readings, and perform more in-depth electrical system checks to pinpoint whether the PCM is indeed the root cause or if there are other contributing factors affecting both the OBD2 port and transmission operation in your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually.
In conclusion, troubleshooting OBD2 and transmission problems in a 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually requires a systematic approach. Start with basic checks of fuses and OBD2 port power, progress to wiring continuity tests, and consider the PCM as a potential point of failure if other checks are inconclusive. For complex issues involving both systems, professional diagnostic expertise is invaluable to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective repairs for your 1999 Dodge 3500 Dually.