Experiencing issues with your 2001 Dodge Cummins OBD2 port? You’re not alone. A non-functional OBD2 port can prevent you from diagnosing engine problems, checking trouble codes, and performing essential maintenance. This article, as your expert auto repair content creator from cardiagnosticnearme.com, will guide you through troubleshooting steps to get your 2001 Dodge Cummins OBD2 port working again. We’ll cover common causes, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions, ensuring you have the knowledge to tackle this issue effectively.
Understanding the Importance of Your OBD2 Port
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port is a crucial component in modern vehicles. It serves as the communication gateway between your truck’s computer system (PCM/ECM) and diagnostic scan tools. Without a working OBD2 port, mechanics and DIYers alike are essentially working in the dark. For a 2001 Dodge Cummins, this port should be readily accessible and functional, allowing for quick diagnosis of various engine and transmission related problems.
Diagnosing a Dead OBD2 Port: Step-by-Step
Let’s get down to the troubleshooting process. If your scan tool isn’t powering up or connecting when plugged into your 2001 Dodge Cummins OBD2 port, follow these steps:
1. Initial Checks: Power and Ground
The most common culprits for a non-working OBD2 port are often the simplest to check: power and ground. The OBD2 port requires both power and a solid ground connection to function.
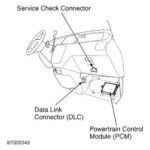
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Check for Power: Use a multimeter to check for 12V power at pin 16 of the OBD2 port. Ground your multimeter to a known good ground point on the vehicle.
- Verify Ground: Check for a good ground connection at pins 4 and 5 (chassis ground and signal ground respectively) using your multimeter in continuity mode, or by checking for 12V between pin 16 and pins 4 or 5.
If you are missing power or ground, you’ve identified a likely area to investigate further.
2. Fuse Inspection: The First Line of Defense
Fuses protect your vehicle’s electrical circuits from overloads. A blown fuse is a common reason for a loss of power to the OBD2 port.
- Locate Fuse Boxes: Consult your 2001 Dodge Cummins owner’s manual to find the location of the fuse boxes. There’s usually one under the dash and another under the hood.
- Identify Relevant Fuses: Look for fuses related to “diagnostic port,” “PCM,” “ECM,” or “instrument cluster.” The owner’s manual will be your best guide here.
- Inspect Fuses: Visually inspect each fuse. A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament inside. You can also use a multimeter to test for continuity across the fuse terminals.
- Replace Blown Fuses: If you find a blown fuse, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Important: If the fuse blows again immediately, you have a short circuit that needs further investigation.
3. Wiring and Connector Integrity: Tracing the Path
If fuses are not the issue, the problem might lie in the wiring between the OBD2 port and the PCM or other related modules.
- Inspect OBD2 Port Connector: Check the OBD2 port itself for any signs of damage, corrosion, or bent pins. Ensure the connector is clean and in good condition.
- Trace Wiring: Refer to a wiring diagram for your 2001 Dodge Cummins (available in repair manuals or online resources). Identify the wires for power, ground, and data communication lines going to the OBD2 port.
- Check for Wire Damage: Carefully inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or melted insulation. Pay close attention to areas where the harness might rub against metal parts.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to perform continuity tests on the wires between the OBD2 port and the PCM/instrument cluster. The original poster in the provided text mentioned checking the violet and blk/white wires from the cluster to the PCM, which is a good step. Verify these and other relevant wires based on wiring diagrams.
4. PCM/ECM Issues: A Potential Root Cause
While less common than fuse or wiring problems, a faulty Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Engine Control Module (ECM) can also cause a non-working OBD2 port. The PCM is responsible for managing communication through the OBD2 port.
- Consider PCM/ECM Faults: If you’ve ruled out power, ground, fuses, and wiring, a faulty PCM becomes a more likely possibility.
- Look for Other Symptoms: Are you experiencing other engine performance issues, warning lights, or transmission problems? A faulty PCM can manifest in various ways. In the original poster’s case, they are also experiencing transmission shifting issues, which could be related, but it’s not definitively linked to the OBD2 port problem.
- Professional Diagnosis: Diagnosing a faulty PCM often requires specialized tools and expertise. Consider taking your 2001 Dodge Cummins to a qualified mechanic or dealership for PCM testing.
Addressing the Transmission Issue and OBD2 Port Connectivity
The original poster mentioned transmission issues alongside the OBD2 port problem. While these might be unrelated, it’s worth considering potential connections:
- Electrical Glitches: Electrical problems can sometimes affect multiple systems. It’s possible a wiring issue or voltage problem is impacting both the OBD2 port and the transmission control system.
- PCM Involvement: The PCM controls both engine and transmission functions. A PCM malfunction could theoretically affect both OBD2 communication and transmission operation.
However, it’s crucial to diagnose each issue systematically. First, focus on getting the OBD2 port working so you can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes. These codes will provide valuable clues about any engine or transmission problems.
Conclusion: Getting Your 2001 Dodge Cummins Back on Track
Troubleshooting a non-working OBD2 port on your 2001 Dodge Cummins requires a methodical approach. By systematically checking power, ground, fuses, wiring, and considering the PCM, you can effectively pinpoint the problem. Once your OBD2 port is functional, you can use a scan tool to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes, providing a clearer path to resolving any underlying engine or transmission issues.
If you’re uncomfortable performing these diagnostic steps yourself, or if you suspect a more complex issue like a PCM failure, it’s always best to seek assistance from a qualified automotive technician. They have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair your 2001 Dodge Cummins, ensuring it’s back on the road running smoothly.