Experiencing issues with your 2003 Toyota 4Runner’s OBD2 port can be frustrating, especially when you need to run diagnostics or get your vehicle inspected. If your scan tool isn’t connecting, you might be facing a problem preventing communication with your vehicle’s computer. This article provides a troubleshooting guide, drawing from real-world experiences, to help you diagnose and potentially resolve a non-functional OBD2 port in your 2003 Toyota 4Runner.
Common Causes and Troubleshooting Steps
Based on collective experience and common diagnostic procedures, here’s a step-by-step approach to troubleshoot why your OBD2 port might not be working on your 2003 Toyota 4Runner:
1. Verify Your Scan Tool and Cable
The first step is to rule out any issues with your diagnostic equipment itself. Before assuming there’s a problem with your 4Runner, ensure your scan tool is functioning correctly.
- Test with another vehicle: If possible, try connecting your scan tool to another OBD2 compliant vehicle. If it works on another car, the issue is likely with your 4Runner.
- Inspect your cable: Check the OBD2 cable for any damage, bent pins, or loose connections. A faulty cable can prevent proper communication.
- Try a different scanner: Borrow or try a different OBD2 scanner. Auto parts stores often offer free OBD2 scans, which can help you determine if your scanner is the problem. Smog check stations and dealerships also use professional-grade tools that can help isolate the issue.
2. Check the OBD Fuse
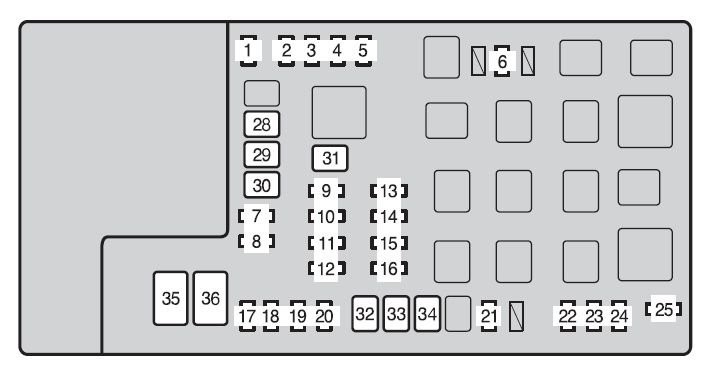
A blown fuse is a common culprit for a non-working OBD2 port. The OBD2 port is typically powered by a fuse, and if this fuse is blown, the port won’t receive power, preventing your scan tool from connecting.
- Locate the fuse box: For a 2003 Toyota 4Runner, the fuse box you need to check is typically located in the engine bay on the driver’s side and potentially another fuse box inside the cabin, often under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your 2003 Toyota 4Runner owner’s manual for the precise location of fuse boxes and fuse diagrams.
- Identify the OBD fuse: Refer to the fuse box diagram (usually printed on the fuse box cover or in your owner’s manual) to locate the fuse for the OBD or diagnostic port. It might be labeled as “OBD,” “DIAG,” “ACC,” or “ECU-B”. For many Toyota models of this era, it’s often a 7.5 amp or 15 amp fuse.
- Inspect the fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. A blown fuse will have a broken wire inside. You can also use a fuse tester to check for continuity.
- Replace the fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage. Important: If the fuse blows again immediately after replacement, there’s likely a short circuit in the wiring that needs further investigation.
 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
3. Inspect the Wiring
Wiring issues between the OBD2 port, fuse box, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) can also cause the port to malfunction.
- Visual inspection: Check the wiring around the OBD2 port for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frays, or corrosion.
- Check OBD2 port pins: Inspect the pins inside the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion. Bent or corroded pins can prevent proper contact with the scan tool connector.
- Trace the wiring: If you are comfortable and have some electrical knowledge, you can try to trace the wiring from the OBD2 port back to the fuse box and ECU, looking for any breaks or shorts. Wiring diagrams for the 2003 Toyota 4Runner can be helpful and are often available online or in repair manuals.
4. Battery Reset
Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve communication glitches. Disconnecting and reconnecting your car battery can sometimes reset the ECU and restore OBD2 port functionality.
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of your 2003 Toyota 4Runner’s battery.
- Wait: Let the vehicle sit for about 30 seconds to a few minutes to ensure any residual power dissipates.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal securely.
- Test again: Try connecting your OBD2 scanner again to see if it now works.
5. Try a Powered OBD2 Scanner
As highlighted in the original experience, some vehicles might have an issue where the OBD2 port isn’t providing enough power for certain scan tools, especially unpowered Bluetooth dongles.
- Powered scan tool: Try using a powered OBD2 scan tool. These scanners have their own power source (usually batteries) and don’t rely solely on the vehicle’s OBD2 port for power.
- Smog check stations/Dealerships: These facilities often use professional, powered scan tools. If they can connect to your 4Runner’s OBD2 port, it might indicate a power supply issue with your vehicle’s port when using unpowered tools.
6. ECU Issues (Less Likely, More Serious)
While less common, a faulty ECU could potentially be the reason for OBD2 port malfunction. However, ECU problems often manifest in other noticeable vehicle performance issues.
- Consider other symptoms: If you are experiencing other problems like engine performance issues, warning lights, or transmission problems along with a non-working OBD2 port, an ECU issue becomes more plausible.
- Professional diagnosis: If you’ve exhausted the simpler troubleshooting steps and still have no OBD2 port function, it’s advisable to take your 2003 Toyota 4Runner to a qualified mechanic or Toyota dealership for professional diagnosis. ECU diagnosis and repair can be complex and often require specialized tools and expertise.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a non-working OBD2 port on your 2003 Toyota 4Runner involves systematically checking potential causes, starting with the simplest and most common issues. By following these steps, from verifying your scan tool and checking fuses to considering wiring and power issues, you can effectively diagnose and potentially resolve the problem, ensuring your 4Runner is ready for diagnostics and inspections. Remember to consult your owner’s manual for specific fuse locations and diagrams relevant to your 2003 Toyota 4Runner model.
