For car owners and enthusiasts looking to understand their vehicle’s diagnostic system, knowing the OBD2 protocol is essential. Since 1996, vehicles sold in the United States have been mandated to be OBD-II compliant, and this includes the 2006 Hyundai Elantra. But what does OBD-II compliance mean for your Elantra, and which specific protocol does it utilize? This article will break down the essentials of OBD-II, focusing on the 2006 Hyundai Elantra and its diagnostic communication.
OBD-II Compliance and Protocols Explained
OBD-II, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system that allows you to access your vehicle’s health information. It’s a crucial tool for mechanics and DIYers alike to diagnose issues and maintain vehicle performance. While all OBD-II compliant vehicles share the same connector type (SAE J1962), they can communicate using different protocols. These protocols are essentially languages that diagnostic tools use to talk to your car’s computer.
There are five main OBD-II communication protocols:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Primarily used by Ford.
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used by General Motors.
- ISO9141-2: Used by Chrysler and European and Asian manufacturers.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Also common among European and Asian manufacturers, and sometimes used interchangeably with ISO9141-2.
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network): The modern standard, becoming mandatory for all vehicles in the US from model year 2008 onwards, but increasingly used before then.
For the 2006 Hyundai Elantra, it’s highly likely to utilize the ISO15765-4 CAN protocol. By 2006, CAN was becoming the dominant protocol due to its speed and reliability. However, to confirm this and for diagnostic purposes, understanding the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) is important.
Decoding the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC)
The DLC is the physical interface where you connect a scan tool to your vehicle. Standardized under SAE J1962, it comes in two types: Type A and Type B. The primary difference lies in the alignment tab shape, but functionally they serve the same purpose – providing access to the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
Type A DLCs are typically located within the driver’s compartment, between the steering column and the vehicle’s centerline, attached to the instrument panel for easy access from the driver’s seat.
 J1962F, Type A
J1962F, Type A
Fig. 1 – Type A J1962 Vehicle Connector: Common in many passenger vehicles, offering easy access for diagnostic tools in the driver’s area.
Type B DLCs can be in the passenger or driver’s compartment, potentially further from the vehicle’s centerline, and accessible from the driver’s seat, co-driver’s seat, or even outside the vehicle. These are also attached to the instrument panel and designed for easy connection and disconnection.
 J1962F, Type B
J1962F, Type B
Fig. 2 – Type B J1962 Vehicle Connector: Another standard connector type, designed for flexible access from various locations inside or near the vehicle.
For a 2006 Hyundai Elantra, you will most likely find a Type A DLC located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Pinout and Protocol Identification for your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
While visually inspecting the DLC is helpful, the pinout configuration provides clues to the protocol used. The SAE J1962 standard defines the function of each pin. Certain pin combinations are associated with specific protocols.
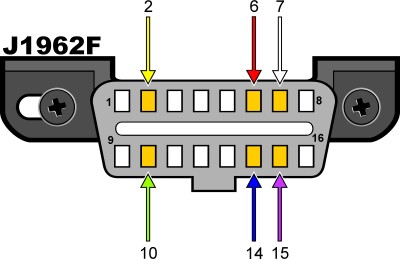 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
Fig. 3 – OBDII Connector Pinout: Diagram showing pin assignments, crucial for identifying the communication protocol used by the vehicle.
To determine the protocol, focus on these pins:
| Pin 2 | Pin 6 | Pin 7 | Pin 10 | Pin 14 | Pin 15 | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| must | must | J1850 PWM | ||||
| must | J1850 VPW | |||||
| must | may* | ISO9141/14230 | ||||
| must | must | ISO15765 (CAN) |
*Pin 15 (L-line) is optional in newer vehicles using ISO9141-2 or ISO14230-4.
Additionally, pins 4 (Chassis Ground), 5 (Signal Ground), and 16 (Battery Positive) are essential for power and grounding in all OBD-II connectors.
Based on this, we can deduce protocol types from pin presence:
Pin Configuration PWM Pins 2, 4, 5, 10, and 16 must be present VPW Pins 2, 4, 5, and 16 must be present, but not 10 ISO Pins 4, 5, 7, and 16 must be present. Pin 15 may be present. CAN Pins 4, 5, 6, 14, and 16 must be present
For a 2006 Hyundai Elantra, to confirm the likely ISO15765 CAN protocol, you should check for the presence of pins 4, 5, 6, 14, and 16 in the DLC. This pin configuration strongly indicates CAN communication.
Steps to Verify the OBD2 Protocol on Your 2006 Hyundai Elantra
- Locate the DLC: Check under the dashboard on the driver’s side of your 2006 Hyundai Elantra.
- Visually Inspect the Connector: Note the shape and confirm it’s a 16-pin J1962 connector.
- Check the Pinout: Carefully examine the pins inside the DLC, referring to the pinout diagram (Fig. 3) and the table above. Specifically look for pins 6 and 14, which are indicative of CAN protocol.
- Consult your Vehicle Manual: The owner’s manual might provide information about the OBD-II protocol supported.
- Use an OBD2 Scan Tool: A scan tool will automatically detect the protocol when connected to your vehicle. This is the most definitive method.
Understanding the OBD2 protocol of your 2006 Hyundai Elantra is the first step in effective vehicle diagnostics. Knowing it likely uses the CAN protocol allows you to select the correct scan tools and procedures for maintaining your vehicle’s health. Always ensure compatibility before using any diagnostic equipment to avoid communication errors or potential damage.
