Understanding your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is crucial for modern car maintenance and repair. For 2006 Hyundai owners, knowing the specific OBD2 protocol used by your vehicle is the first step in effective diagnostics. This guide will delve into the OBD2 protocols relevant to 2006 Hyundai models, helping you understand how to communicate with your car’s computer and troubleshoot potential issues.
OBD2 Compliance and Protocol Variety
Since 1996, the OBD2 standard has been mandatory for all cars and light trucks sold in the United States. This standardization ensures that you can use universal scan tools to access diagnostic information, regardless of the vehicle manufacturer. However, while all OBD2 compliant vehicles share the same diagnostic connector (DLC) and a standardized set of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), they communicate using different protocols.
These communication protocols are essentially languages that scan tools use to “talk” to your car’s computer. The primary OBD2 protocols include:
- J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width)
- ISO9141-2
- ISO14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000)
- ISO15765-4/SAE J2480 (CAN – Controller Area Network)
It’s important to note that while US manufacturers weren’t permitted to use CAN protocol until 2003 models, by 2006, CAN was becoming increasingly common. By 2008, it became the mandatory protocol for all vehicles. For a 2006 Hyundai, it’s highly likely to utilize either an ISO protocol or the emerging CAN protocol.
Understanding the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC)
The gateway to accessing your Hyundai’s OBD2 system is the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC). Standardized under SAE J1962, DLCs come in two types: Type A and Type B. The key difference lies in the alignment tab shape, but functionally they serve the same purpose – providing a physical interface for diagnostic tools.
According to SAE J1962 standards, the Type A DLC, the more common type, “shall be located in the passenger or driver’s compartment in the area bounded by the driver’s end of the instrument panel to 300 mm (~1 ft) beyond the vehicle centerline, attached to the instrument panel and easy to access from the driver’s seat. The preferred location is between the steering column and the vehicle centerline.”
 J1962F, Type A
J1962F, Type A
Fig. 1 – J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A – Illustrating the Type A Diagnostic Link Connector as defined by SAE J1962.
Type B DLCs, while less frequent, “shall be located in the passenger or driver’s compartment in the area bounded by the driver’s end of the instrument panel, including the outer side, and an imagined line 750 mm (~2.5 ft) beyond the vehicle centerline. It shall be attached to the instrument panel and easy to access from the driver’s seat or from the Co-drivers seat or from the outside. The vehicle connector shall be mounted to facilitate mating and unmating.”
 J1962F, Type B
J1962F, Type B
Fig. 2 – J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type B – Depicting the Type B Diagnostic Link Connector with its unique alignment tab, as per SAE J1962 specifications.
Typically, you’ll find the DLC under the dashboard on the driver’s side of your 2006 Hyundai. Consult your owner’s manual for the precise location if needed.
Identifying Your 2006 Hyundai’s OBD2 Protocol via DLC Pinout
While scan tools are designed to automatically detect the protocol, understanding how to manually identify it via the DLC pinout can be beneficial for troubleshooting and ensuring compatibility, especially with older or basic scan tools. The pinout of the J1962 connector is the key to protocol identification.
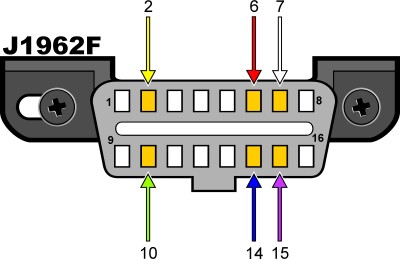 J1962F OBDII connector pinout
J1962F OBDII connector pinout
Fig. 3 – J1962 OBDII Connector Pinout – Diagram showing the standard pin assignments for the J1962 OBDII connector, essential for protocol identification.
The presence or absence of specific pins within the DLC helps determine the protocol in use. Refer to the table below to decipher your 2006 Hyundai’s protocol based on pin presence:
| Pin 2 | Pin 6 | Pin 7 | Pin 10 | Pin 14 | Pin 15 | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| must have | – | – | must have | – | – | J1850 PWM |
| must have | – | – | – | – | – | J1850 VPW |
| – | – | must have | – | – | may have* | ISO9141/14230 |
| – | must have | – | – | must have | – | ISO15765 (CAN) |
*Pin 15 (L-line) might be present in older ISO9141-2 or ISO14230-4 vehicles but is often optional in newer implementations of these protocols.
Therefore, based on the pin configuration, you can deduce the protocol:
PWM Connector must have pins 2, 4, 5, 10, and 16. VPW Connector must have pins 2, 4, 5, and 16, but not 10. ISO Connector must have pins 4, 5, 7, and 16. Pin 15 may or may not be present. CAN Connector must have pins 4, 5, 6, 14, and 16.
Regardless of the specific 2006 Hyundai model (e.g., Sonata, Elantra, Tucson), it will be OBD2 compliant and utilize one of these standard protocols. While CAN protocol was becoming increasingly dominant in 2006, some models might still use ISO protocols. Checking the DLC pinout is a reliable method for confirmation.
For further research, resources like the OBDII Generic Communication Protocols by Manufacturer can provide additional context, although direct pinout inspection is the most definitive method for your specific 2006 Hyundai vehicle. Understanding your vehicle’s OBD2 protocol empowers you to perform effective diagnostics and maintain your car efficiently.