For owners and automotive enthusiasts diving into the diagnostics of a 2008 Silverado 2500HD, understanding the On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is crucial. This guide provides an in-depth look at the OBD2 protocol, specifically tailored for your Silverado, focusing on the ECU (Engine Control Unit) and Parameter IDs (PIDs). Whether you’re troubleshooting a check engine light, monitoring performance, or simply curious about your truck’s data, this expert breakdown will equip you with the knowledge you need.
Understanding OBD2 for Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 is essentially your 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s built-in health monitor. It’s a standardized system that allows you to access real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from your vehicle’s computer system via the OBD2 connector.
Have you ever seen the malfunction indicator lamp – often called the “check engine light” – illuminate on your Silverado’s dashboard?
That light is your truck signaling a potential issue. To pinpoint the problem, mechanics use OBD2 scanners to communicate with your Silverado’s computer.
This communication happens through the OBD2 16-pin connector, usually located beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side of your 2008 Silverado 2500HD. An OBD2 scanner sends requests, and your Silverado responds with data like speed, engine temperature, and those all-important Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), allowing for faster and more accurate troubleshooting.
Alt Text: OBD2 scanner diagnosing a vehicle, highlighting the malfunction indicator light (MIL), essential for understanding your 2008 Silverado 2500HD OBD2 system.
Does Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD Use OBD2? Absolutely.
For a 2008 model year vehicle like your Silverado 2500HD, OBD2 support is standard. In fact, OBD2 has been mandatory in the US for cars and light trucks since 1996. Your Silverado not only supports OBD2, but it also likely utilizes the CAN bus protocol, which became mandatory in US vehicles in 2008.
To confirm OBD2 compliance, you can generally check the vehicle’s owner’s manual or look for an OBD2 sticker, often found under the hood. However, for a 2008 Silverado 2500HD, OBD2 is a given.
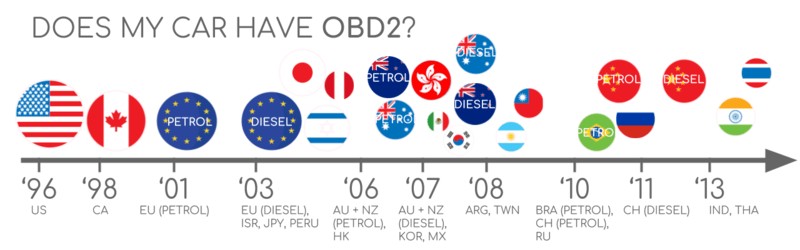 Does My Car Have OBD2?
Does My Car Have OBD2?
Alt Text: Chart illustrating OBD2 compliance by region and year, confirming OBD2 support for US vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
A Brief History of OBD2 and its Relevance to Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
OBD2’s origins are rooted in California, driven by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) in the early 1990s for emission control. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) played a key role in standardizing OBD2, ensuring consistency across different manufacturers through standards like SAE J1962.
Here’s how the OBD2 standard timeline aligns with your 2008 Silverado 2500HD:
- 1996: OBD2 becomes mandatory in the USA for cars and light trucks.
- 2005: OBD2 is required in the US for medium-duty vehicles.
- 2008: US vehicles, including your Silverado 2500HD, are mandated to use ISO 15765-4 (CAN) as the foundation for OBD2 communication.
- 2010: OBD2 becomes mandatory in US heavy-duty vehicles.
For your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, the critical milestone is 2008 – the year CAN bus became the mandatory protocol for OBD2 in US vehicles. This means your truck communicates diagnostic data using the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol over OBD2.
Alt Text: Infographic depicting the history of OBD2, highlighting emission control and the adoption of CAN bus, crucial context for understanding the 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s diagnostic system.
Alt Text: OBD2 history timeline overview, visually representing key dates and milestones in OBD2 development, relevant to the 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s OBD2 system.
Alt Text: Illustration of OBD3 concept, showing future trends in remote diagnostics and emissions testing, beyond the OBD2 system of a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 Standards: SAE J1979, ISO 15031, and ISO 15765 in Your Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 operates as a higher-layer protocol, much like a language, while CAN bus is the communication method, similar to a telephone line. For your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, understanding the relevant standards is key:
- SAE J1979 & ISO 15031-5: These standards define the diagnostic services (modes) and Parameter IDs (PIDs) used in OBD2 communication. They dictate how to request data and interpret responses from your Silverado’s ECU.
- SAE J1962 & ISO 15031-3: These standards specify the physical OBD2 connector – the 16-pin port in your Silverado – ensuring standardized access to vehicle data.
- ISO 15765-4 (Diagnostics on CAN): This is the most critical standard for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD. It mandates CAN bus as the lower-layer protocol for OBD2 and defines parameters for CAN communication in diagnostics.
These standards ensure that any OBD2 compliant scanner can effectively communicate with your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, retrieve diagnostic information, and monitor vehicle parameters.
Alt Text: OSI model diagram showing OBD2 and CAN bus layers, illustrating the protocol stack used in a 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s OBD2 communication.
Alt Text: OBD2 connector pinout diagram, type A, detailing pin assignments for data and power, essential for connecting to a 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s OBD2 port.
The OBD2 Connector in Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD: SAE J1962
The 16-pin OBD2 connector, standardized by SAE J1962, is your access point to your 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s diagnostic data.
Key points about the OBD2 connector in your Silverado:
- Location: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It might be slightly hidden, but it’s usually easily accessible.
- Pin 16: Provides battery power, even when the ignition is off, allowing scanners to operate.
- CAN Bus Pins: Pins 6 (CAN-High) and 14 (CAN-Low) are crucial as they are the CAN bus communication lines, the primary protocol for OBD2 in your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Understanding the OBD2 connector pinout is essential if you’re building custom diagnostic tools or need to troubleshoot communication issues.
OBD2 Connector Type: Type A for Your Silverado 2500HD
Passenger vehicles like your 2008 Silverado 2500HD typically use the Type A OBD2 connector. Type B connectors are more common in medium and heavy-duty vehicles, which operate at 24V systems, unlike the 12V system in your Silverado.
The key difference between Type A and Type B is the voltage supply output and sometimes the baud rate. However, for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, Type A (12V) is the standard and correct connector type.
Alt Text: Diagram comparing OBD2 connector Type A and Type B, highlighting voltage differences and applications, clarifying the Type A connector used in a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Alt Text: Illustration contrasting OBD2 and CAN bus within the ISO 15765 framework, emphasizing CAN bus as the communication layer for OBD2 in vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 and CAN Bus: ISO 15765-4 Protocol for Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
Since 2008, CAN bus (ISO 15765-4) has been the mandatory lower-layer protocol for OBD2 in all US vehicles, including your 2008 Silverado 2500HD. ISO 15765-4, also known as Diagnostics over CAN (DoCAN), specifies how OBD2 communication is conducted over a CAN network.
Key aspects of ISO 15765-4 relevant to your Silverado:
- CAN Bit-rate: Must be either 250K or 500K. 500K is the more common rate for passenger vehicles and likely the rate used in your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
- CAN IDs: Can be 11-bit or 29-bit. 11-bit CAN IDs are typically used for OBD2 communication in cars and light trucks.
- Specific CAN IDs for OBD2: Standardized CAN IDs are used for OBD2 requests and responses (more on this below).
- Data Length: Diagnostic CAN frames are limited to 8 bytes of data.
- Cable Length: The OBD2 adapter cable should be a maximum of 5 meters to ensure reliable communication.
OBD2 CAN Identifiers (11-bit) in Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 communication on your 2008 Silverado 2500HD involves request and response messages using CAN IDs. Typically, 11-bit CAN IDs are used.
- Functional Addressing (Request): The CAN ID 0x7DF is used for ‘Functional Addressing’. This is a broadcast request, asking all OBD2-compliant ECUs in your Silverado if they have data to report for the requested parameter.
- Physical Addressing (Request): CAN IDs from 0x7E0 to 0x7E7 can be used for ‘Physical Addressing’, targeting specific ECUs. This is less commonly used for generic OBD2 requests.
- Response IDs: ECUs respond with CAN IDs from 0x7E8 to 0x7EF.
- 0x7E8: Most common response ID, typically from the ECM (Engine Control Module) in your Silverado.
- 0x7E9: Often used by the TCM (Transmission Control Module).
When you use an OBD2 scanner with your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, it usually sends requests using CAN ID 0x7DF and expects responses on IDs like 0x7E8.
Alt Text: Diagram illustrating OBD2 request and response frames, detailing the structure of PID data parameters, crucial for understanding data flow in a 2008 Silverado 2500HD. 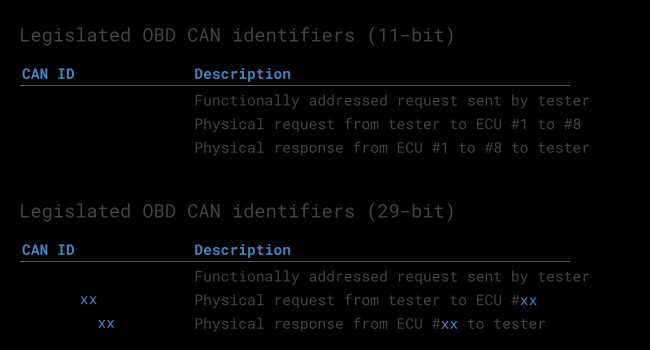 OBD2 OBD CAN bus Identifiers 7DF 7E8 7E0
OBD2 OBD CAN bus Identifiers 7DF 7E8 7E0
Alt Text: Comparison of OBD2 and proprietary CAN bus protocols, showing OBD2 as a standardized diagnostic layer separate from OEM-specific data in vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 vs. OEM-Specific CAN Protocols in Your Silverado 2500HD
It’s important to understand that OBD2 is a diagnostic protocol layered on top of your 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s internal communication network. Your truck’s ECUs primarily use OEM-specific CAN protocols for their core functions. These proprietary protocols are how the various modules in your Silverado communicate with each other for vehicle operation.
OBD2 provides a standardized window into some of this data, primarily for emissions-related and basic diagnostic information. When you connect an OBD2 scanner, you are typically accessing this standardized OBD2 data stream, not the full breadth of OEM-specific CAN data. In some cases, especially with advanced tools, you might be able to access some OEM-specific PIDs or services, but these are outside the standard OBD2 scope.
In essence, think of OBD2 as an “add-on” protocol that runs in parallel to the core OEM-specific CAN protocol within your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Bit-rate and ID Validation for OBD2 on Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
While 500K bit-rate and 11-bit CAN IDs are common for OBD2 in vehicles like your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, diagnostic tools often perform an initialization sequence to confirm the correct settings. ISO 15765-4 outlines a process to systematically validate the bit-rate and CAN ID format.
This validation process typically involves sending specific OBD2 requests and checking for valid responses. This ensures reliable communication regardless of minor variations in vehicle implementations.
Alt Text: Flowchart illustrating the OBD2 bit-rate and CAN ID validation process as per ISO 15765-4, ensuring correct communication settings for vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Alt Text: Diagram showing the five lower-layer OBD2 protocols, including CAN (ISO 15765), and older protocols, emphasizing CAN as the standard for modern vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Five Lower-Layer OBD2 Protocols (Though CAN is Key for Your Silverado)
While CAN (ISO 15765) is the dominant and mandatory protocol for OBD2 in your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, it’s worth knowing about the other historical lower-layer protocols used for OBD2 in older vehicles:
- ISO 15765 (CAN bus): Standard for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD and most modern vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Used in some early 2000s vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Found in some European and Asian vehicles from the late 90s to early 2000s.
- SAE J1850 (VPW & PWM): Used primarily in older GM and Ford vehicles, respectively.
However, for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, you will be focused on the ISO 15765 (CAN bus) protocol.
Transporting OBD2 Messages: ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2) in Your Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 data, when transmitted over CAN bus, uses the ISO Transport Protocol (ISO-TP or ISO 15765-2). This protocol is essential because it allows for sending data payloads larger than the 8-byte limit of a standard CAN frame. This is necessary for OBD2 services that require more data, such as retrieving the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
ISO-TP handles segmentation (splitting large messages into smaller CAN frames), flow control (managing data transfer), and reassembly (putting the message back together at the receiving end). For many simpler OBD2 requests and responses, the data fits within a single CAN frame. In these cases, ISO-TP uses “Single Frame” (SF) messages.
Alt Text: Diagram showing ISO 15765-2 ISO-TP OBD2 frame types, including single frame, first frame, consecutive frame, and flow control frame, illustrating message handling in a 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s OBD2 system.
The OBD2 Diagnostic Message: SAE J1979, ISO 15031-5 and Your Silverado 2500HD’s PIDs
Let’s break down the structure of a “Single Frame” OBD2 CAN message as used in your 2008 Silverado 2500HD. An OBD2 message consists of:
- CAN Identifier: e.g., 0x7DF (request) or 0x7E8 (response).
- Data Length & Protocol Control Information (PCI Field): The first byte of the CAN data payload, indicating the data length and frame type (for ISO-TP).
- OBD2 Data: This includes:
- Mode (Service): Defines the type of diagnostic service requested (e.g., read current data, read DTCs).
- Parameter ID (PID): Identifies the specific parameter being requested within a given mode (e.g., engine speed, coolant temperature).
- Data Bytes: The actual data payload containing the value of the requested parameter or other diagnostic information.
Alt Text: OBD2 message structure breakdown diagram, explaining the components of an OBD-II frame including mode, PID, ID, and data bytes, essential for interpreting data from a 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s OBD2 system.
Example: Requesting Vehicle Speed PID (0x0D) from Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
Let’s illustrate with a practical example relevant to your Silverado: requesting the Vehicle Speed PID (PID 0x0D).
-
Request Message: An OBD2 scanner sends a request to your Silverado with:
- CAN ID: 0x7DF (Functional Request)
- Data Payload:
02 01 0D(2 bytes of payload; Mode 0x01: Show current data; PID 0x0D: Vehicle Speed)
-
Response Message: Your Silverado 2500HD responds with:
- CAN ID: 0x7E8 (Response from ECM)
- Data Payload:
03 41 0D 3C(3 bytes of payload; Mode 0x41: Response to Mode 0x01; PID 0x0D; Vehicle Speed Data Byte(s))
In this example, the vehicle speed value is encoded in the last byte (0x3C). You need to consult the OBD2 PID documentation (SAE J1979 or ISO 15031-5) to understand how to convert this hexadecimal value into a physical speed value (e.g., km/h or mph). For PID 0x0D, it’s typically a direct value in km/h.
Alt Text: OBD2 request and response example with CAN IDs 7DF and 7E8, illustrating a vehicle speed PID request and response sequence for a vehicle like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Alt Text: OBD2 PID example for vehicle speed (PID 0D), detailing the request and response data bytes and conversion to physical value, relevant for monitoring a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Alt Text: OBD2 services modes diagram, listing the 10 standard OBD2 modes such as current data, freeze frame, and clear DTCs, available for diagnostic requests on a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
The 10 OBD2 Services (Modes) Supported by Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 defines 10 diagnostic services, also called modes. These modes are used to request different types of diagnostic information from your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Commonly supported OBD2 modes include:
- Mode 0x01: Show current data: Requests real-time data like engine RPM, speed, temperatures, etc.
- Mode 0x02: Show freeze frame data: Retrieves data captured when a DTC was set.
- Mode 0x03: Show stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Requests current DTCs that have triggered the check engine light.
- Mode 0x04: Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes and stored values: Clears DTCs and resets related system values.
- Mode 0x09: Request vehicle information: Used to request vehicle information like VIN, calibration IDs, etc.
Not all vehicles support all 10 modes, and even within supported modes, not all PIDs are always available. However, for a 2008 Silverado 2500HD, modes 0x01, 0x03, and 0x09 are typically supported. In OBD2 messages, the mode is indicated in the second byte of the data payload in the request. In the response, 0x40 is added to the requested mode value (e.g., 0x01 request becomes 0x41 response).
OBD2 Parameter IDs (PIDs) in Detail for Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
Within each OBD2 mode, Parameter IDs (PIDs) specify the exact data you are requesting. Mode 0x01, for instance, includes a wide range of standardized PIDs – around 200 – covering real-time engine and vehicle parameters.
Examples of PIDs relevant to your 2008 Silverado 2500HD within Mode 0x01:
- 0x0C: Engine RPM
- 0x0D: Vehicle Speed
- 0x04: Calculated Engine Load
- 0x05: Engine Coolant Temperature
- 0x0F: Intake Air Temperature
- 0x10: Mass Air Flow Rate
However, it’s important to note that not every PID is supported by every vehicle. The support for specific PIDs can vary based on manufacturer, model, and year.
A special PID is PID 0x00 in Mode 0x01 (Supported PIDs [01-20]). If an ECU supports any OBD2 services, it must support Mode 0x01 PID 0x00. When you request PID 0x00, the ECU responds with a bitmask indicating which PIDs from 0x01 to 0x20 are supported. Similarly, PIDs 0x20, 0x40, 0x60, etc., are used to determine support for subsequent PID ranges within Mode 0x01. This makes PID 0x00 a fundamental starting point for discovering what data your 2008 Silverado 2500HD makes available via OBD2.
Alt Text: OBD2 protocol request and response frames, highlighting PID data parameters, essential for understanding data requests and responses in a 2008 Silverado 2500HD’s diagnostic communication.
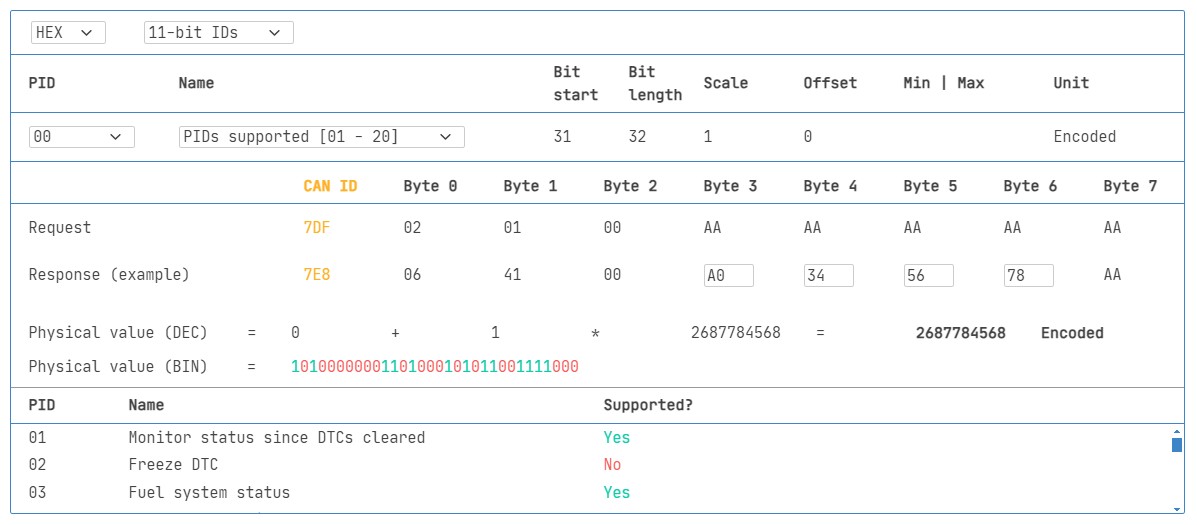 OBD2 PID overview tool
OBD2 PID overview tool
Alt Text: OBD2 PID overview tool interface, showing service 01 parameters, useful for exploring available PIDs and their descriptions for vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Tip: Using an OBD2 PID Overview Tool for Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
To effectively work with OBD2 PIDs on your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, a PID overview tool is invaluable. These tools provide scaling and decoding information for standard OBD2 PIDs, as defined in SAE J1979 and ISO 15031-5.
Using an OBD2 PID tool, you can:
- Look up specific PIDs and their descriptions.
- Understand the data format and scaling for each PID.
- Construct OBD2 request frames correctly.
- Decode OBD2 response data into physical values (e.g., convert raw data bytes into km/h, °C, RPM).
Our OBD2 PID overview tool is a great resource to help you explore and understand the PIDs available for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 PID overview tool
Alt Text: Link to an online OBD2 PID overview tool, providing access to PID details and decoding information, useful for diagnosing and monitoring a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Logging and Decoding OBD2 Data from Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
Now, let’s explore how you can practically log OBD2 data from your 2008 Silverado 2500HD using tools like the CANedge CAN bus data logger.
The CANedge allows you to configure custom CAN frames for transmission, making it suitable for sending OBD2 requests. Paired with an OBD2-DB9 adapter cable, you can easily connect it to your Silverado’s OBD2 port.
Alt Text: OBD2 PID data logger setup, illustrating the request (7DF) and response (7E8) CAN IDs used for logging data from a vehicle like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
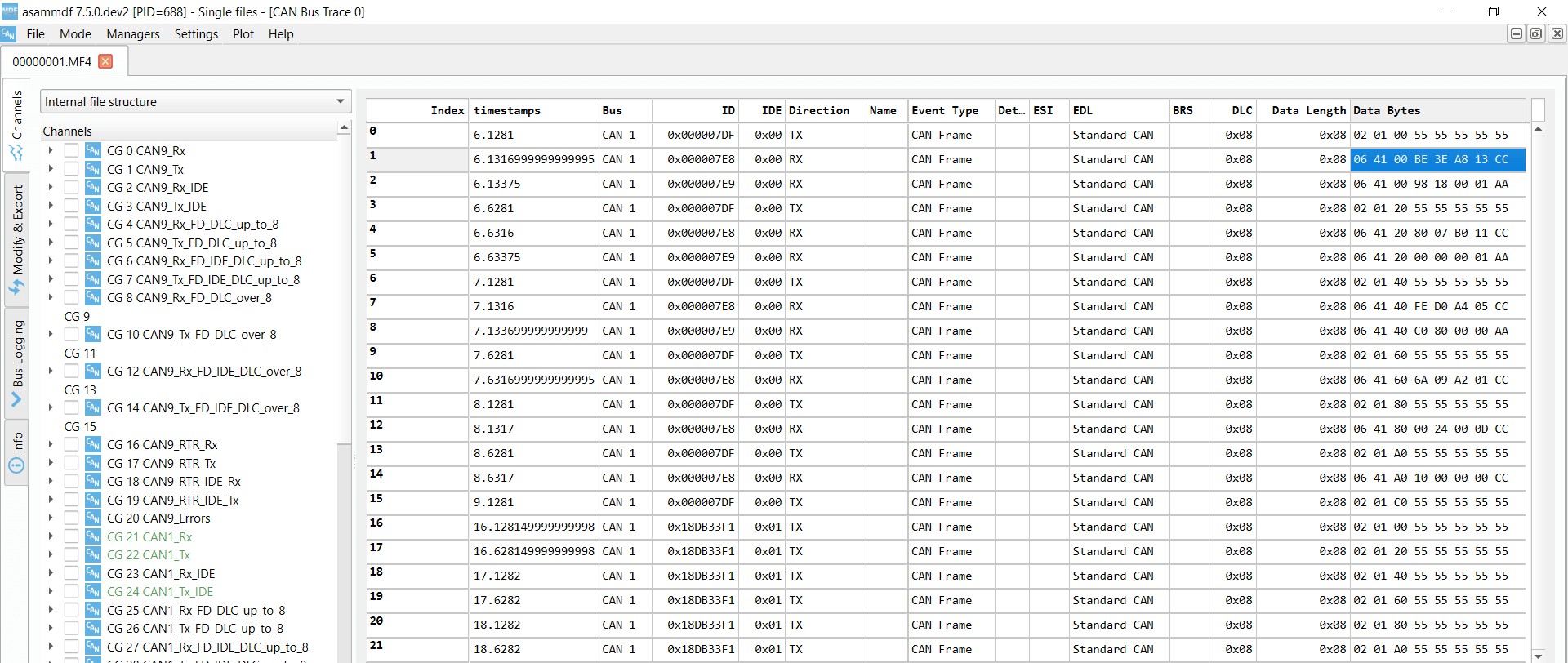 OBD2 Supported PIDs Test Alt Text: Screenshot of asammdf software showing OBD2 supported PIDs test responses, displaying data received from PID requests to a vehicle including a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 Supported PIDs Test Alt Text: Screenshot of asammdf software showing OBD2 supported PIDs test responses, displaying data received from PID requests to a vehicle including a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
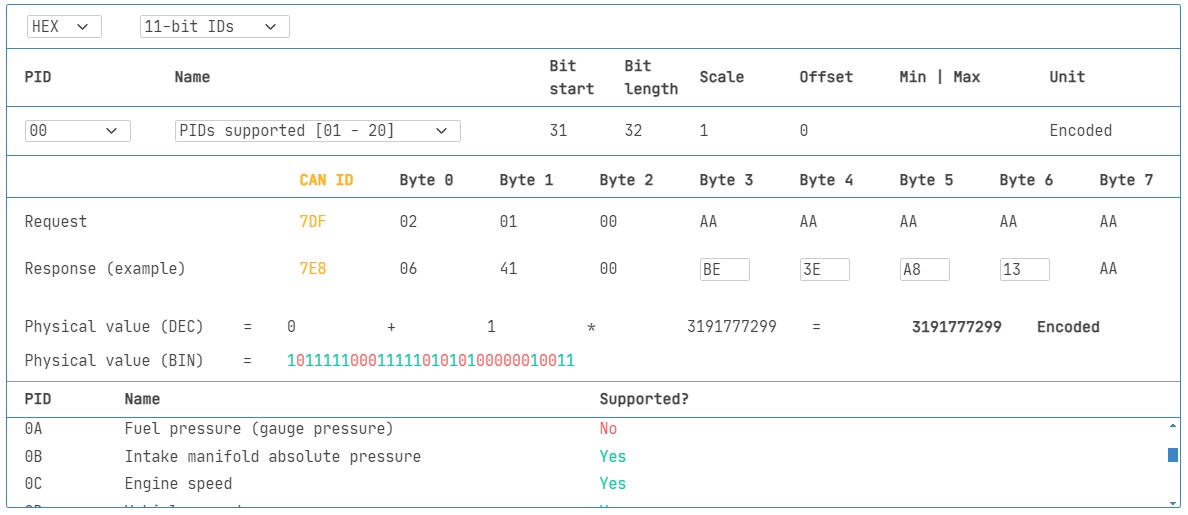 Review supported PIDs via OBD2 lookup tool
Review supported PIDs via OBD2 lookup tool
Step #1: Validate Bit-rate, CAN IDs, and Supported PIDs on Your Silverado 2500HD
Before logging specific PIDs, it’s good practice to validate the communication parameters with your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Here’s how you can do it using a CANedge or similar tool:
- Test Bit-rate: Start by sending a CAN frame at 500K bit/s. If successful (frame is transmitted without errors), use 500K. If not, try 250K. For a 2008 Silverado 2500HD, 500K is the likely bit-rate.
- Use Validated Bit-rate: Use the confirmed bit-rate for all subsequent OBD2 communication.
- Request Supported PIDs: Send ‘Supported PIDs’ requests (Mode 0x01, PID 0x00, 0x20, 0x40, etc.) to your Silverado.
- Analyze Responses: Review the responses to determine:
- CAN IDs used for responses (to confirm 11-bit vs. 29-bit, though 11-bit is standard for your Silverado).
- Supported PIDs: Identify which PIDs your Silverado actually supports based on the response data.
Plug-and-play configurations are often available for tools like CANedge to automate these initial tests. Most 2008+ non-electric vehicles support a good range of PIDs (40-80+) using 500K bit-rate, 11-bit CAN IDs, and the OBD2/OBDonEDS protocol.
As shown in the asammdf GUI screenshot, you might see multiple responses to a single OBD2 request, especially when using the functional request ID 0x7DF. This is because multiple ECUs might respond. For efficiency, once you identify the ECM (0x7E8) as the primary response ECU, you can switch to ‘Physical Addressing’ (request IDs 0x7E0-0x7E7) for subsequent requests to target specific ECUs and reduce bus load.
Step #2: Configure OBD2 PID Requests for Your Silverado 2500HD
Once you know the supported PIDs and communication settings for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD, configure your data logger to request the PIDs you are interested in.
Consider these points when setting up your OBD2 PID requests:
- CAN IDs: For efficiency, use ‘Physical Addressing’ request IDs (e.g., 0x7E0 for ECM) to target specific ECUs directly.
- Request Spacing: Insert a delay of 300-500 ms between each OBD2 request. Overly rapid requests can overwhelm ECUs, leading to no responses.
- Power Management: Use triggers to stop transmitting requests when the vehicle is inactive to prevent battery drain, especially if logging with the ignition off.
- Filtering: Set up filters to record only OBD2 responses if your Silverado also outputs OEM-specific CAN data, to keep your logs focused.
With these configurations, your data logger is ready to record raw OBD2 data from your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
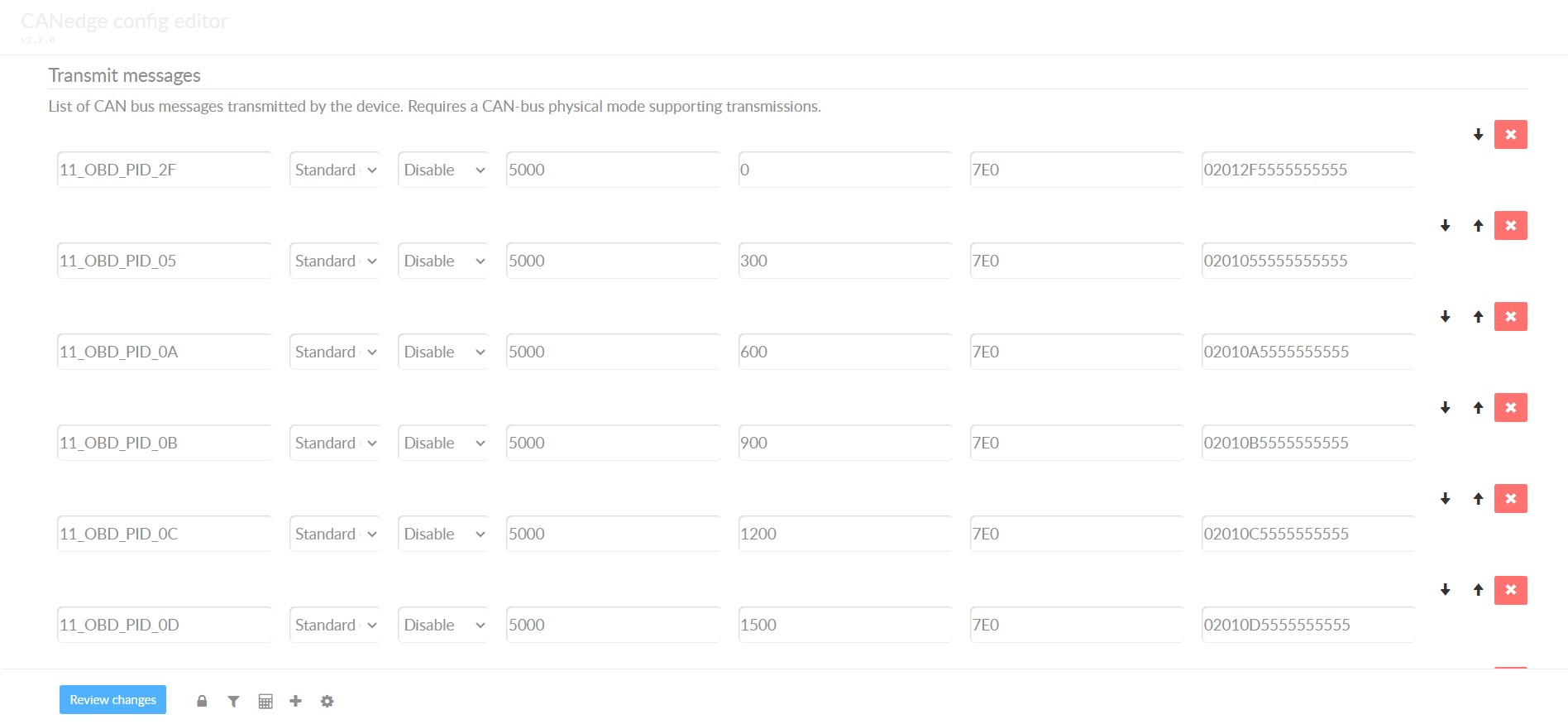 obd2-transmit-list-example-canedge Alt Text: Example of an OBD2 transmit list in CANedge configuration, showing PID requests for data logging from a vehicle including a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
obd2-transmit-list-example-canedge Alt Text: Example of an OBD2 transmit list in CANedge configuration, showing PID requests for data logging from a vehicle including a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
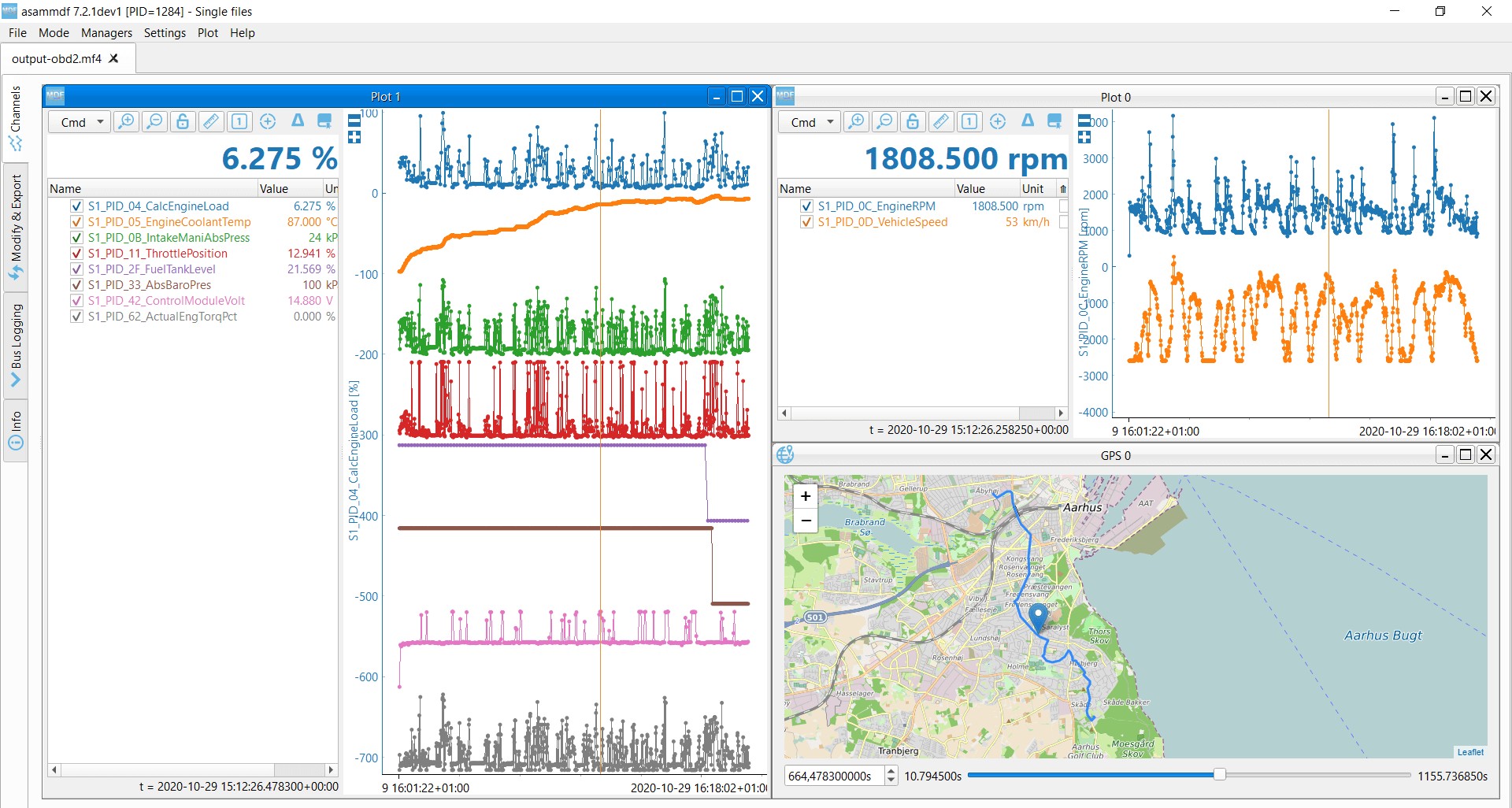 OBD2 data decoded visual plot asammdf CAN bus DBC file Alt Text: Decoded OBD2 data visualized in asammdf software using a DBC file, showing plotted parameters from a CAN bus log, representing data from a vehicle like a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
OBD2 data decoded visual plot asammdf CAN bus DBC file Alt Text: Decoded OBD2 data visualized in asammdf software using a DBC file, showing plotted parameters from a CAN bus log, representing data from a vehicle like a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Step #3: DBC Decode Raw OBD2 Data for Analysis
To make sense of the raw OBD2 data, you need to decode it into physical values. This is where DBC (CAN database) files come in.
Decoding OBD2 data involves more than just standard CAN signal decoding because the same CAN ID (e.g., 0x7E8) is used for multiple PIDs. You need to consider the CAN ID, OBD2 mode, and PID to correctly identify and decode the signal. This is a form of ‘extended multiplexing‘.
To decode OBD2 data from your 2008 Silverado 2500HD:
- Use an OBD2 DBC File: Download a suitable OBD2 DBC file. We provide a free OBD2 DBC file that simplifies this process for many standard OBD2 PIDs.
- DBC Decoding Software: Use CAN bus analysis software that supports DBC decoding (like asammdf, Vector CANalyzer, etc.). Import the OBD2 DBC file into your software.
- Decode and Visualize: The software will use the DBC file to interpret the raw OBD2 data and display it as physical values. You can then visualize and analyze the decoded data.
Our DBC file implements the ‘extended multiplexing’ logic needed to correctly decode OBD2 data, making analysis straightforward.
CANedge: Your OBD2 Data Logger for the 2008 Silverado 2500HD
The CANedge is an ideal OBD2 data logger for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD. It offers:
- Easy OBD2 Logging: Connect to your Silverado’s OBD2 port and start logging to an SD card (8-32GB).
- Free Software & APIs: Use our free software and APIs (CAN bus software/API tools) for configuration and data analysis.
- OBD2 DBC Support: Utilize our free OBD2 DBC file for easy decoding.
OBD2 logger intro CANedge
Call to action links to OBD2 logger intro and CANedge product page.
OBD2 Multi-Frame Examples (ISO-TP) for Advanced Diagnostics on Your Silverado 2500HD
While many OBD2 interactions use single-frame messages, some services, like retrieving the VIN or DTCs, require multi-frame communication using ISO-TP (ISO 15765-2).
For multi-frame requests on your Silverado, you may need to implement flow control. In practice, this can often be achieved by sending a static flow control frame shortly after the initial request. CANedge configuration examples are available to guide this setup. Furthermore, ensure your CAN software (like the CANedge MF4 decoders) supports ISO-TP for proper multi-frame response handling.
 OBD2-multi-frame-request-message-vehicle-identification-number
OBD2-multi-frame-request-message-vehicle-identification-number
Alt Text: OBD2 multi-frame request message example for Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), showing ISO-TP communication for retrieving VIN data from a vehicle like a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Example 1: Retrieving the VIN from Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
To get the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) from your Silverado using OBD2, you use Mode 0x09 and PID 0x02. This typically requires multi-frame communication because the VIN is longer than 8 bytes.
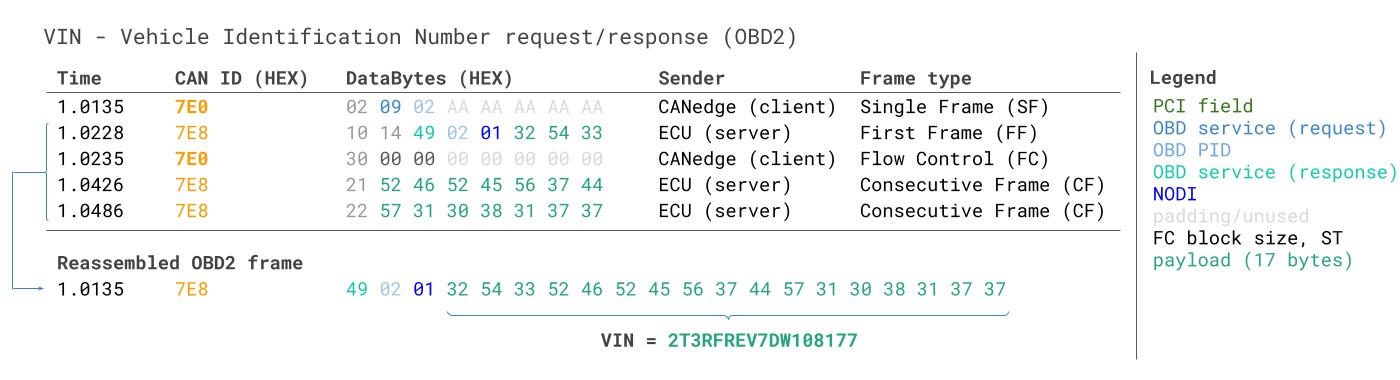 VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
VIN Vehicle Identification Number OBD2 Example multi-frame
The process involves:
- Request: Tester tool sends a Single Frame request with Mode 0x09 (Vehicle Info) and PID 0x02 (VIN).
- Response: The Silverado responds with a multi-frame response:
- First Frame: Contains the start of the VIN data and indicates the total message length.
- Consecutive Frames: Follow with the remaining VIN data segments.
The VIN data is usually encoded in ASCII within the data bytes of the multi-frame response. You’ll need to reassemble these frames and convert the HEX data to ASCII to read the VIN.
Example 2: OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
Requesting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) also often involves multi-frame responses, especially if multiple DTCs are stored in your Silverado’s ECU. To retrieve DTCs, use Mode 0x03 (“Show stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes”). No PID is needed in the request.
Alt Text: OBD2 DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code DBC interpretation example, showing how DTC bytes are decoded into category and code values, used for analyzing trouble codes from a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
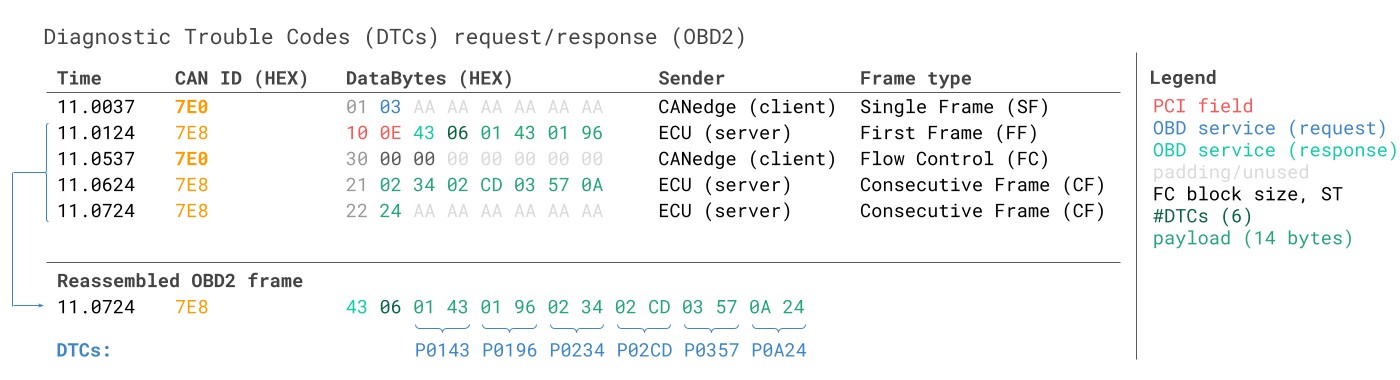 OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
OBD2 Diagnostic Trouble Codes DTC CAN Bus Request Response Example
The process is:
- Request: Send a Single Frame request with Mode 0x03.
- Response: The Silverado responds with a multi-frame response containing:
- The number of DTCs stored.
- 2 bytes for each DTC, encoded according to SAE J1979/ISO 15031-6.
Each 2-byte DTC value needs to be decoded. The first two bits indicate the DTC category (e.g., P-powertrain, C-chassis), and the remaining 14 bits form a 4-digit hexadecimal code. You can use OBD2 DTC lookup tools (like repairpal.com) to find the meaning of these codes.
Use Cases for OBD2 Data Logging from Your 2008 Silverado 2500HD
OBD2 data logging from vehicles like your 2008 Silverado 2500HD has numerous practical applications:
Alt Text: OBD2 data logger in use in a car, representing on-board diagnostics and data logging applications for vehicles like the 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Logging Data from Your Silverado for Performance and Efficiency
- Fuel Efficiency: Monitor fuel consumption, engine load, and speed to optimize driving habits and reduce fuel costs for your Silverado 2500HD.
- Driving Behavior Analysis: Track speed, RPM, and acceleration patterns to improve driving style.
- Prototype Testing: If you’re testing aftermarket parts or modifications on your Silverado, OBD2 logging can provide data to validate performance and compatibility.
- Insurance Telematics: OBD2 data can be used for usage-based insurance models.
obd2 logger
Link to OBD2 data logger product page.
Alt Text: OBD2 real-time streaming diagnostics setup, showing data streaming via USB for live vehicle monitoring, applicable to diagnosing a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Real-Time Diagnostics for Your Silverado
- Live Data Monitoring: Use an OBD2 interface to stream real-time data for diagnosing issues as they occur. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting intermittent problems on your 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
- Vehicle Health Checks: Regularly monitor key parameters to proactively identify potential maintenance needs.
obd2 streaming
Link to OBD2 streaming interface product page.
Alt Text: OBD2 data logger for predictive maintenance, illustrating telematics and IoT applications for vehicle health monitoring, beneficial for managing a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Predictive Maintenance for Fleet Management
- Fleet Monitoring: For businesses operating a fleet of Silverado 2500HD trucks, OBD2 data can be streamed to the cloud for predictive maintenance, helping to prevent breakdowns and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Proactive Issue Detection: Identify early warning signs of potential failures based on trend analysis of OBD2 data.
predictive maintenance
Link to predictive maintenance solutions page.
Alt Text: Black box CAN logger for insurance and warranty applications, representing vehicle data recording for accident analysis and diagnostics, relevant for a 2008 Silverado 2500HD.
Vehicle Black Box Recording
- Accident Analysis: In the event of an incident, OBD2 data logged around the time of the event can provide valuable insights for accident reconstruction and analysis.
- Warranty and Dispute Resolution: OBD2 logs can serve as a ‘black box’ record for warranty claims or disputes related to vehicle operation.
can bus blackbox
Link to black box CAN logger product page.
Do you have a specific OBD2 data logging use case in mind for your 2008 Silverado 2500HD? Reach out for free expert advice!
Contact us
Link to contact page.
Explore our guides section for more introductory articles, or download our comprehensive ‘Ultimate Guide’ PDF for a deep dive into CAN bus technology.
Ready to start logging and streaming OBD2 data from your 2008 Silverado 2500HD?
Get your OBD2 data logger today!
Buy now Contact us
Call to action links to product purchase and contact page.
Recommended Resources
OBD2 DATA LOGGER: EASILY LOG & CONVERT OBD2 DATA
Link to OBD2 data logger product page.
 CANedge2 – Dual CAN Bus Telematics Dongle CANEDGE2 – PRO CAN IoT LOGGER
CANedge2 – Dual CAN Bus Telematics Dongle CANEDGE2 – PRO CAN IoT LOGGER
Link to CANedge2 product page.
CAN BUS INTERFACE: STREAMING OBD2 DATA WITH SAVVYCAN
Link to CAN bus interface product page.
