Encountering a check engine light (CEL) in your 2012 Honda Accord can be unsettling, but it’s your car’s way of communicating potential issues. Instead of dreading that illuminated dashboard icon, view it as a helpful signal guiding you toward resolving a problem. Modern vehicles like your Honda Accord utilize sophisticated onboard diagnostic systems, and understanding how to access and interpret these systems is the first step in effective car maintenance. This guide will walk you through understanding OBD2 systems, retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and what those codes might mean for your 2012 Honda Accord.
Understanding OBD2 and Your 2012 Honda Accord
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system implemented in vehicles in the mid-1990s. It’s designed to monitor various vehicle systems, from emissions control to engine performance. When the system detects an anomaly, it triggers the CEL and stores a DTC in the car’s computer. For your 2012 Honda Accord, this system is invaluable for identifying problems early and preventing more significant damage.
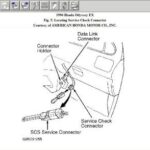
While older vehicles might have required more complex methods to retrieve codes, your 2012 Honda Accord is equipped with a standardized OBD2 port, making the process straightforward. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
Retrieving OBD2 Codes from Your 2012 Honda Accord
The most efficient way to retrieve OBD2 codes from your 2012 Honda Accord is by using an OBD2 scanner. These scanners are readily available online and at auto parts stores, ranging from basic code readers to more advanced scan tools. Here’s how to use one:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: In your 2012 Honda Accord, it’s usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: With the ignition off, plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn Ignition to “ON”: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine. This powers up the car’s electronics and the OBD2 system.
- Follow Scanner Instructions: Most scanners will power on automatically and guide you through the process. You’ll typically select “Read Codes” or a similar option.
- Record the Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Write these codes down exactly as they appear.
For example, you might encounter a code like P0113 or something related to 2012 Honda Accord Obd2 011 000b (though “011 000b” is not a standard OBD2 code format, it might be a fragment of a more complex issue or a misreading. We will address this further). Note down all codes present, as multiple codes can sometimes be related or point to a more complex underlying problem.
Understanding OBD2 Code Format: Decoding “P0113” and Beyond
OBD2 codes are standardized across manufacturers, making diagnosis more universal. They follow a specific format:
-
First Character (Letter): Indicates the system:
- P: Powertrain (engine and transmission)
- B: Body (body control modules)
- C: Chassis (braking and suspension systems)
- U: Network/Communication (communication between onboard computers)
-
Second Character (Digit): Indicates code type:
- 0: Generic (SAE standardized codes)
- 1, 2, 3: Manufacturer-specific (enhanced codes beyond generic)
-
Third Character (Digit): Indicates the subsystem:
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 2: Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3: Ignition System or Misfire
- 4: Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5: Vehicle Speed Controls and Idle Control System
- 6: Computer Output Circuit
- 7: Transmission
-
Fourth and Fifth Characters (Digits): Specific fault code number, further refining the problem area.
For instance, P0113 breaks down as:
- P: Powertrain
- 0: Generic code
- 1: Fuel and Air Metering
- 13: Specific fault – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
This detailed structure helps pinpoint the area of the problem. When you see a code, you can start to understand the general system affected and then research the specific meaning of the numerical part.
Addressing “2012 Honda Accord OBD2 011 000b” and Potential Misunderstandings
The term “2012 honda accord obd2 011 000b” as a code is not a standard OBD2 format. OBD2 codes are typically structured as described above (e.g., Pxxxx, Cxxxx, Bxxxx, Uxxxx). “011 000b” might be:
- A Misreading or Partial Code: Perhaps the scanner displayed a partial or incorrect reading. Ensure your scanner is properly connected and functioning. Try rescanning.
- A Fragment of a Larger Issue: It could be a part number, a reference number from a specific diagnostic tool, or a user-generated reference related to a broader problem they are researching online.
- Misinformation: It’s possible this is a misunderstanding of OBD2 codes in general.
If you are encountering “011 000b” in your research or from a less reliable source, focus on getting the correct OBD2 code using a scanner. Once you have the accurate P-code (or B, C, or U code), you can effectively diagnose the issue.
Common OBD2 Codes for 2012 Honda Accord and Potential Issues
While a comprehensive list of all possible OBD2 codes is extensive, here are some common categories and examples relevant to a 2012 Honda Accord:
-
P0XXX – Fuel and Air Metering Issues:
- P0171, P0172 – System Too Lean or Too Rich: Indicates problems with the fuel-air mixture, potentially due to vacuum leaks, MAF sensor issues, or fuel system problems.
- P0131-P0167 – Oxygen Sensor Codes: Relate to issues with oxygen sensors that monitor exhaust gases. These are critical for emissions and fuel efficiency.
- P0101-P0103 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Codes: MAF sensor measures air entering the engine; problems can lead to incorrect fuel mixture.
- P0111-P0113 – Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Codes: IAT sensor measures air temperature; malfunctions can affect fuel calculations.
-
P03XX – Misfire Codes:
- P0300 – Random Misfire Detected: Engine misfires randomly across cylinders.
- P0301-P0306 (and higher) – Cylinder Specific Misfires: Misfire in a specific cylinder (e.g., P0301 is cylinder 1). Misfires can be caused by spark plug issues, ignition coil problems, fuel injector faults, or compression issues.
-
P04XX – Emission Control System Codes:
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold: Indicates the catalytic converter is not working efficiently to reduce emissions.
- P0440-P0457 – Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Codes: EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Common causes include loose gas caps, purge valve problems, or leaks in the system.
- P0401, P0404 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Codes: EGR system recirculates exhaust gas to reduce NOx emissions. Issues can affect engine performance.
-
P05XX – Vehicle Speed, Idle Control, and Auxiliary Inputs Codes:
- P0505-P0507 – Idle Air Control (IAC) System Codes: IAC system controls engine idle speed. Issues can lead to rough idling or stalling.
- P0500, P0501 – Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Codes: VSS provides speed information; problems can affect speedometer, transmission shifting, and cruise control.
-
P06XX, P07XX – Computer and Transmission Codes:
- P0600-P0606 – ECM/PCM Codes: Indicate problems with the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM), the car’s main computer.
- P0700 and P07XX Transmission Codes: Indicate issues within the automatic transmission system.
Important Note: This is not an exhaustive list. Always consult a reliable OBD2 code database or repair manual specific to your 2012 Honda Accord for detailed code definitions and potential causes. Websites like the NHTSA or reputable automotive diagnostic sites can be valuable resources.
Beyond OBD2 Codes: When to Seek Professional Help
While OBD2 codes provide valuable starting points, they don’t always pinpoint the exact problem. Sometimes, further diagnosis is needed. Consider seeking professional help from a certified mechanic if:
- You are uncomfortable working on your car.
- You are unsure how to interpret the codes.
- The problem seems complex or involves safety-critical systems like brakes or airbags.
- You have cleared the codes, but the CEL returns quickly.
- You have multiple codes and are unsure where to start.
- After addressing a code, the issue persists.
A professional technician has advanced diagnostic tools, experience, and in-depth knowledge to accurately diagnose and repair your 2012 Honda Accord. They can perform further tests, such as sensor testing, circuit analysis, and system inspections, to get to the root cause of the problem.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with OBD2 Knowledge
Understanding OBD2 systems and how to retrieve and interpret codes is a valuable skill for any 2012 Honda Accord owner. While encountering a CEL can be initially concerning, it’s an opportunity to engage with your car’s diagnostics and take proactive steps in maintenance. By using an OBD2 scanner and consulting reliable resources, you can gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s health, address minor issues promptly, and make informed decisions about when professional help is needed. Remember, addressing issues early can save you time, money, and prevent more serious problems down the road, keeping your 2012 Honda Accord running smoothly for years to come.