For owners and enthusiasts of the classic 90 Chevy Silverado, understanding its diagnostic system is crucial for maintenance and repair. Unlike modern vehicles that use the standardized OBD2 system, the 1990 Silverado utilizes an older OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics Generation 1) system, specifically the Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL). This difference often leads to questions about compatibility with contemporary OBD2 readers and the possibility of conversion.
This article delves into the specifics of the 90 Chevy Silverado’s OBD1 ALDL system, clarifies the pin assignments, explores the feasibility of using OBD2 readers, and guides you through understanding your truck’s diagnostic interface.
Decoding the 90 Chevy Silverado OBD1 ALDL Connector
The OBD1 system in your 1990 Chevy Silverado is accessed through a 12-pin ALDL connector, which is distinct from the 16-pin OBD2 connectors found in later vehicles. It’s essential to understand the function of each pin in this connector to effectively diagnose your truck. Based on available information, here’s a breakdown of the pin assignments:
- Pin A: Ground. This is a crucial ground connection for diagnostic tools.
- Pin B: ALDL Data Output (ECM/Codes Only). This pin transmits diagnostic data and trouble codes from the Engine Control Module (ECM).
- Pin C: Canister Purge Solenoid Test. This pin is used for testing the canister purge solenoid system.
- Pin D: Not Used. This pin is typically not connected in most applications.
- Pin E: Serial Data (Scanner Tool Data). This pin is used for data communication with scan tools, providing real-time data from the ECM.
- Pin F: Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) or Overdrive (O/D) Relay. For automatic transmissions, this pin relates to the TCC. In standard transmissions, it may be connected to the O/D relay.
- Pin G: Fuel Pump. This pin can be used to directly power the fuel pump for testing purposes.
It’s important to note that while some sources mention 7 pins being used in the 12-pin connector, the above list details the most commonly identified and functionally relevant pins for diagnostic purposes. Pins H, J, K, and L are generally not connected or used in standard diagnostic procedures for this system.
Understanding ALDL Data Communication: Baud Rates and Interfaces
The 90 Chevy Silverado OBD1 system communicates using serial data, but at different speeds compared to OBD2. The ALDL system typically uses baud rates of 160 baud or 8192 baud, depending on the specific function and diagnostic tool. Pin M is often associated with the 8192 baud rate for higher-speed data transmission, potentially used with more advanced scanners.
The original poster mentioned considering a circuit for a 160 baud ALDL hardware interface. The reason for using 160 baud over 8192 baud often comes down to simplicity and compatibility with older or simpler diagnostic tools and interfaces. 160 baud is a slower communication rate, which can be easier to implement in basic interface circuits.
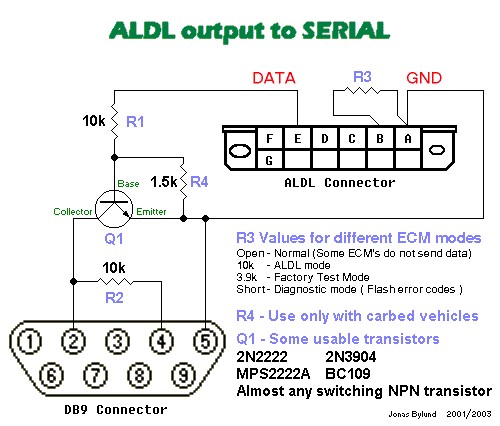 160 Baud ALDL Hardware Interface Circuit Diagram 160 Baud ALDL Hardware Interface
160 Baud ALDL Hardware Interface Circuit Diagram 160 Baud ALDL Hardware Interface
This circuit diagram illustrates a basic interface that converts the ALDL data signal into a pseudo RS232 level for connection to a computer’s serial port. The explanation provided with the diagram highlights important considerations:
- R3 Resistor: Initially, it’s recommended to try the interface without the R3 resistor (often 10k). While some vehicles may require it to initiate data transmission, it can alter the ECM’s operating mode, potentially affecting idle speed and disabling spark knock retard.
- R4 Resistor: The R4 resistor should generally not be used with fuel-injected vehicles. It’s specifically for some carbureted vehicles that might not work with the standard interface. If needed, it might also require using a 4800 baud setting, suggesting different communication protocols in those specific cases.
The mention of an 8192 baud pin and the provided circuit diagrams indicate that while the 90 Chevy Silverado uses OBD1, there were variations in implementation and communication speeds even within the OBD1 era.
 Cable Wiring Diagram
Cable Wiring Diagram
For reference when building or understanding these interfaces, the RS232 pin assignment is crucial for connecting to computer serial ports:
Can You Convert a 90 Chevy Silverado OBD1 to OBD2 Reader?
Directly “converting” an OBD1 system to be fully compatible with OBD2 readers is not a straightforward process and generally not feasible or necessary. OBD1 and OBD2 are fundamentally different diagnostic systems with different communication protocols, connector types, and data structures.
Here’s why direct conversion is problematic:
- Different Protocols: OBD1 systems like ALDL use proprietary protocols that are distinct from the standardized protocols (like CAN, ISO 9141, PWM, VPW) used in OBD2.
- ECM Limitations: The ECM in a 1990 Chevy Silverado is designed to communicate using OBD1 protocols. It lacks the hardware and software to natively support OBD2 communication.
- Connector Difference: The physical 12-pin ALDL connector is incompatible with the 16-pin OBD2 connector.
What are the realistic options for diagnostics on a 90 Chevy Silverado?
-
Using an OBD1/ALDL Scanner: The most direct and effective approach is to use a scanner specifically designed for OBD1 systems and ALDL. These scanners can communicate with the ECM using the correct protocols and interpret the diagnostic data. While potentially less common than OBD2 scanners, OBD1 scanners are still available, especially those geared towards classic and older vehicles.
-
ALDL to RS232 Interfaces and Software: As indicated by the circuit diagrams, you can build or purchase ALDL to RS232 interfaces. These interfaces allow you to connect your 90 Chevy Silverado’s ALDL port to a computer’s serial port. Combined with appropriate diagnostic software (often free or low-cost), you can read diagnostic codes and live data on your computer. Examples of software include WinALDL and similar programs designed for ALDL systems.
-
OBD1 to OBD2 Adapters (Limited Functionality): While you might find OBD1 to OBD2 connector adapters, these adapters do not magically convert the diagnostic protocol. They simply change the physical connector. In most cases, plugging an OBD2 reader into an OBD1 system using just an adapter will not work. OBD2 readers are not designed to understand OBD1 protocols.
-
Focus on OBD1 Diagnostic Procedures: Understanding the fundamentals of the OBD1 ALDL system and its pinouts allows for manual diagnostic procedures, such as reading trouble codes by flashing the Check Engine Light (Service Engine Soon light). Terminals “A” and “B” on the ALDL connector are key for activating the self-diagnostics mode, as described in the original text:
ALDL Terminals “A” and “B”
These terminals are the only ones used to activate the self-diagnostics mode. Terminal A is grounded to the body chassis. Terminal B is routed back through the under dash connector, to ecm terminal A9. Connecting A and B together, with the ignition key in the “on” position, engine not running will activate the diagnostic mode (explained later). This mode used while the engine is running is used to monitor the O2 sensor for proper operating status. Leaving these terminals unconnected is the normal driving mode.By grounding pin A and connecting it to pin B, you can initiate the diagnostic mode, and the ECM will flash the “Check Engine” light in patterns to represent diagnostic trouble codes. You would then need an OBD1 code chart specific to 1990 Chevy Silverado to interpret these flashes.
Conclusion: Working with Your 90 Chevy Silverado’s OBD1 System
While the desire to use modern OBD2 readers on a 1990 Chevy Silverado is understandable, it’s important to recognize the limitations and differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems. Direct “conversion” to OBD2 is not a practical solution.
Instead, the most effective approaches for diagnosing your 90 Chevy Silverado involve:
- Utilizing dedicated OBD1/ALDL scanners.
- Employing ALDL to RS232 interfaces with computer-based diagnostic software.
- Understanding and utilizing the built-in OBD1 self-diagnostic capabilities of the ALDL system for basic code reading.
By focusing on these OBD1-compatible methods, you can effectively diagnose and maintain your classic Chevy Silverado, ensuring its continued performance and reliability. Remember to consult your vehicle’s service manual and reliable online resources for specific OBD1 code charts and diagnostic procedures relevant to your 1990 Chevy Silverado.