It’s common for vehicle owners to look for the OBD2 port in their cars for diagnostics and troubleshooting. If you’re searching for the OBD2 location on your 1994 Ford Ranger, it’s important to understand that your vehicle is equipped with an OBD1 system, not OBD2. This means you won’t find the standard OBD2 port you might expect in newer vehicles.
However, diagnosing your 1994 Ford Ranger is still possible and relatively straightforward using the OBD1 system and the Check Engine Light (CEL). This guide will help you locate the OBD1 connector and understand how to retrieve diagnostic codes from your 1994 Ford Ranger.
Understanding the OBD1 System in Your 1994 Ford Ranger
The 1994 Ford Ranger, being a model from the early to mid-1990s, utilizes the older OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics 1) system. Unlike the standardized OBD2 system that became commonplace later, OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific and less uniform.
Therefore, instead of looking for a standard OBD2 port, you need to locate the OBD1 connector specific to your 1994 Ford Ranger.
Locating the OBD1 Connector on Your 1994 Ford Ranger
The OBD1 connector on your 1994 Ford Ranger is located in the engine bay. Here’s how to find it:
- Open the hood of your Ford Ranger.
- Look for a gray, oblong connector. This connector is typically found on the passenger side of the engine bay.
- Check near the engine fuse box or along the firewall. The connector may be clipped to the engine fuse box or simply hanging nearby.
- Identify the “EEC” cap (if present). The OBD1 connector may have a protective cap on it, often labeled “EEC” (Electronic Engine Control).
To help you visualize, here’s an example of what the OBD1 connector might look like:
 Ford Ranger OBD1 Connector
Ford Ranger OBD1 Connector
Image: Example of an OBD1 connector similar to what you might find on a 1994 Ford Ranger.
You will notice that alongside the larger OBD1 connector, there is usually a single gray connector on the same wiring harness. This single connector is crucial for initiating the diagnostic test.
Reading OBD1 Codes on Your 1994 Ford Ranger Using the CEL
Since your 1994 Ford Ranger uses OBD1, you cannot use a standard OBD2 scanner. Instead, you will use the Check Engine Light (CEL) on your dashboard to read the diagnostic trouble codes. This process involves using a jumper wire to put the EEC system into test mode.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to reading OBD1 codes:
- Locate the OBD1 connector in the engine bay as described above.
- Prepare a jumper wire or paper clip. You’ll need a small piece of wire or an unfolded paper clip to create a connection between two pins in the OBD1 connector.
- Identify the “Self-Test Input” and “Signal Return” slots. Refer to the diagram below to locate these slots on your OBD1 connector.
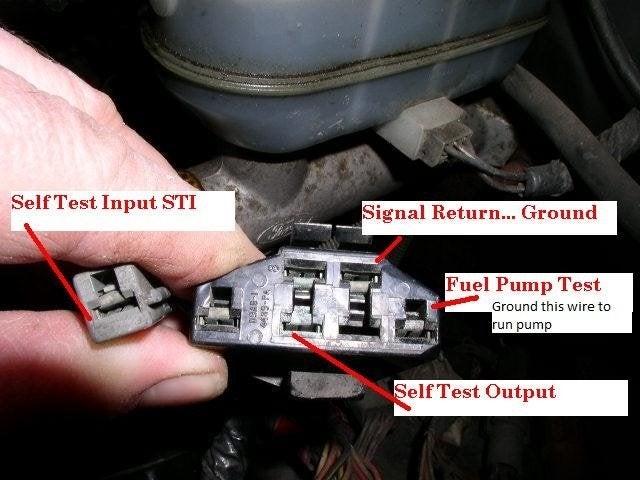 Ford OBD1 Connector Pinout
Ford OBD1 Connector Pinout
Image: Diagram illustrating the pin layout of a Ford OBD1 connector, highlighting the “Self Test Input” and “Signal Return” slots.
- Turn the ignition key to the “OFF” position.
- Use the jumper wire to connect the “Self Test Input” (single gray connector) to the “Signal Return” slot on the larger OBD1 connector.
- Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine. This will power up the vehicle’s electrical system and engage the EEC test mode.
- Observe the Check Engine Light (CEL). After a brief pause as the computer boots up, the CEL will begin to flash out diagnostic codes.
Understanding OBD1 Code Flashing Patterns
The 1994 Ford Ranger OBD1 system uses 3-digit codes. The CEL will flash in a sequence to represent these codes. For example:
- Code 116: One flash, short pause, one flash, short pause, six flashes, LONG pause. This sequence indicates code 116.
The system will display all stored codes and then repeat them. Once the codes repeat, you have successfully read all the diagnostic codes stored in the computer’s memory.
Code 111: A code 111 indicates “System Pass” or “No codes present,” meaning no fault codes are currently stored in the computer’s memory.
You can find a comprehensive list of 3-digit OBD1 Ford codes at resources like The Ranger Station:
The Ranger Station – 3 Digit Ford OBD-I EEC-IV Trouble Codes
Link: Resource for 3-digit Ford OBD1 trouble codes to help you interpret the flashes from your Check Engine Light.
Clearing OBD1 Codes on Your 1994 Ford Ranger
After diagnosing and addressing the issue indicated by the OBD1 codes, you might want to clear the codes from the computer’s memory. Here’s how:
- Ensure the key is in the “ON” position (engine off) and the jumper wire is still connected.
- Remove the jumper wire. Simply disconnecting the jumper wire while the key is still on will clear the stored diagnostic codes.
- Turn the ignition key to the “OFF” position and remove the jumper wire completely.
If you simply turn off the key and remove the jumper without removing it while the key is “ON”, the codes will be saved in memory.
Why Clear Codes?
Clearing codes is a good practice after repairs. It allows you to see if any new codes reappear after driving the vehicle, indicating whether the issue is resolved or if there are still underlying problems. For instance, temporary issues like “bad gas” might trigger codes, but these codes become irrelevant once the issue is resolved. Clearing the codes helps avoid confusion and ensures you are addressing current problems.
Conclusion
While you won’t find an OBD2 port on your 1994 Ford Ranger, diagnosing your vehicle using the OBD1 system and the Check Engine Light is a manageable process. By locating the OBD1 connector in the engine bay, using a simple jumper wire, and understanding the CEL flashing patterns, you can effectively retrieve and interpret diagnostic codes. This method provides valuable insights into your vehicle’s health and helps you address any potential issues, keeping your classic Ford Ranger running smoothly.