As a modern car owner, understanding your vehicle’s computer system is becoming increasingly important. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is essentially the brain of your car, managing everything from engine performance to emissions. An Ecu Programmer Obd2 tool can be your key to unlocking hidden potential and diagnosing issues within this complex system. Let’s dive into how these tools work and how they can empower you to take control of your car’s performance and health.
OBD2 Scanners: Your Gateway to Vehicle Diagnostics
OBD2 scanners have revolutionized vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Initially developed for emissions monitoring, these devices have evolved into powerful tools that provide a window into your car’s inner workings. They connect to your car’s On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port, a standardized interface present in most vehicles manufactured after 1996. This port allows the scanner to communicate with your car’s ECU and other control modules.
 Car Scanner | ANCEL
Car Scanner | ANCEL
Alt text: OBD2 scanner connected to a car’s OBD2 port for predictive vehicle maintenance, highlighting the diagnostic capabilities of ECU programmers.
ECU Coding: Reprogramming Your Car’s Brain
At the heart of vehicle customization and advanced diagnostics lies ECU coding. Think of it as software programming for your car’s computer. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) controls a vast array of engine and vehicle functions. ECU coding involves modifying the software within the ECU to adjust factory settings or enable new features. This can range from simple customizations to complex performance enhancements.
It’s important to distinguish between an OBD2 reader and an OBD2 scanner. While an OBD2 reader primarily reads basic trouble codes, an OBD2 scanner, especially when functioning as an ECU programmer OBD2, offers advanced capabilities. These include ECU coding, live data streaming, and bidirectional control, allowing for in-depth diagnostics and reprogramming.
Choosing the Right ECU Programmer OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the appropriate ECU programmer OBD2 scanner is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics and customization. Consider these factors when making your choice:
Vehicle Compatibility:
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your car’s make, model, and year. While OBD2 is standardized, specific protocols and features can vary, particularly with foreign or hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Corolla Cross. Verify the scanner’s specifications to confirm it supports your vehicle’s diagnostic system.
Connectivity: Bluetooth vs. Wired:
Decide between a Bluetooth OBD2 reader for wireless convenience or a wired scanner for a potentially more stable and faster connection. Bluetooth scanners are ideal for user-friendly operation with smartphones or tablets, while wired scanners are often preferred by professionals for their reliability in demanding environments.
Features and Functionality:
Basic scanners read and clear trouble codes, sufficient for basic diagnostics. However, for ECU programming and advanced analysis, look for scanners offering:
- Live Data Streaming: View real-time data from sensors like RPM, temperature, and O2 sensor readings.
- ECU Coding and Reprogramming: Communicate with the ECU to adjust settings, reset values, and update firmware.
- Special Functions: Access features like ABS diagnostics, airbag reset, and TPMS checks.
- Bidirectional Control: Send commands to vehicle systems to test components and functions.
- Graphing and Data Logging: Visualize sensor data and record it for in-depth analysis.
Ease of Use:
A user-friendly ECU programmer OBD2 scanner is essential. Look for clear displays, intuitive navigation, and easy-to-understand interfaces. Some scanners include mobile apps or computer software for enhanced control, software updates, and report saving.
Budget and Price Range:
OBD2 scanner prices vary widely. Basic models start affordably, while professional-grade scanners can be a significant investment. For simple code reading, a budget scanner may suffice. However, for ECU programming and advanced diagnostics, investing in a mid-range to high-end scanner ($150-$500+) with enhanced features is recommended.
App Support and Updates:
Many modern ECU programmer OBD2 scanners have companion apps for smartphones or tablets, expanding functionality and user experience. Check for compatibility with popular apps or dedicated proprietary apps. Regular software updates are crucial to ensure compatibility with newer vehicles and access to the latest features.
Further Reading: Demystifying the Car Scanner: Features and Uses of the Ancel X7
Getting Started with Your ECU Programmer OBD2 Tool
Initiating your journey with an ECU programmer OBD2 scanner is straightforward.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically situated under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner securely into the OBD2 port.
- Power On: Turn your car’s ignition to the “ON” position (without starting the engine).
- Follow Prompts: Power on the scanner and follow the on-screen instructions to connect to your vehicle.
Connecting your best car scanner is a simple plug-and-play process. Once connected, your scanner will begin communicating with your car’s computer system, giving you access to a wealth of diagnostic information and programming capabilities.
Understanding OBD2 Communication Protocols
OBD2 scanners communicate with vehicles using various protocols, including:
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most prevalent protocol in modern vehicles (post-2008), offering high-speed communication and support for complex systems.
- J1850 (SAE J1850): An older protocol used primarily in pre-CAN vehicles, with variations like J1850 PWM (Ford) and J1850 VPW (GM).
- ISO 9141-2: Used in older European and Asian vehicles (pre-2008).
- ISO 14230 (KWP2000 – Keyword Protocol 2000): An evolution of ISO 9141, used in vehicles transitioning to CAN.
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN-Bus): A specific CAN protocol implementation for OBD2 communication in post-2008 vehicles.
Understanding these protocols can be helpful in ensuring scanner compatibility with different vehicle makes and models, especially older ones.
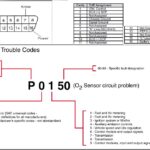
Decoding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes generated by your car’s computer when it detects a problem. These codes are your car’s way of communicating issues to you via the scanner. Common DTC examples include:
- P0300 – Random/multiple cylinder misfire
- P0171 – System too lean (Bank 1)
- P0420 – Catalytic converter efficiency below threshold (Bank 1)
- P0455 – Large evaporative emission system leak
- P0128 – Coolant thermostat temperature below regulating temperature
- P0456 – Small evaporative emission system leak
- P0442 – Evaporative emission system leak (small)
Your ECU programmer OBD2 scanner will display these codes, and you can use resources online or within the scanner’s software to understand their meaning and diagnose the problem.
Accessing Live Data for Real-Time Insights
Live data provides a stream of real-time information from your vehicle’s sensors. This data is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues and monitoring vehicle performance. Key sensors providing live data include:
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): Monitors exhaust oxygen levels for fuel efficiency.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Tracks throttle position for engine control.
- Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF): Measures air intake for fuel balance.
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT): Monitors engine temperature.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP): Measures intake manifold air pressure.
Analyzing live data with your ECU programmer OBD2 tool can pinpoint sensor malfunctions or performance issues that might not trigger a DTC.
Resetting Your ECU with an OBD2 Scanner
Resetting your ECU can sometimes resolve minor software glitches or clear learned values after repairs. Here are the general steps:
- Prepare Your Tools: Have your OBD2 scanner ready.
- Connect Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Ignition ON: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position (engine off).
- Power Scanner: Turn on your OBD2 scanner.
- Select Vehicle: Choose your vehicle’s details if prompted.
- Read DTCs: Retrieve and note any existing diagnostic trouble codes.
- Clear Codes: Select “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes” option to clear DTCs. This often resets the ECU.
- Verify Reset: Turn off ignition, disconnect scanner, restart engine, and check for warning lights or remaining codes.
Note: ECU reset procedures can vary between scanners and vehicle models. Always consult your scanner’s manual and vehicle repair information for specific instructions.
Benefits of ECU Coding and Programming
ECU coding offers numerous benefits, allowing you to:
- Improve Fuel Efficiency: Optimize engine parameters for better mileage.
- Enhance Horsepower and Performance: Adjust settings for increased power and responsiveness.
- Customize Vehicle Settings: Enable or disable features, personalize comfort settings.
- Diagnose and Repair Complex Issues: Access deeper diagnostic information for accurate repairs.
- Adapt to Modifications: Recode the ECU after installing performance parts or upgrades.
As Eric, a car enthusiast, discovered using the ANCEL X7 best code reader for cars, even minor ECU adjustments can lead to noticeable improvements in fuel economy and performance. “It felt like a whole new car,” he remarked after making ECU adjustments.
Empowering Your Automotive Journey with ECU Programmers
An ECU programmer OBD2 scanner is more than just a diagnostic tool; it’s a gateway to understanding and optimizing your vehicle. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a car owner seeking greater control, these tools provide the power to diagnose issues, customize settings, and unlock your car’s full potential. Embrace the capabilities of ECU programming and elevate your driving experience.
FAQs about ECU Programmers and OBD2 Scanners
Can any car use an OBD2 scanner for ECU coding?
Most cars manufactured after 1996 are OBD2 compliant and compatible with OBD2 scanners. However, ECU coding capabilities vary depending on the scanner and vehicle model. Check your scanner’s specifications and vehicle compatibility.
Is ECU coding safe for my car?
When performed correctly and with a reputable ECU programmer OBD2 tool, ECU coding is generally safe. It’s crucial to follow instructions carefully, research reliable coding procedures, and understand the parameters you are modifying. Incorrect coding can potentially lead to vehicle malfunctions.
How often should I perform ECU coding?
ECU coding is not a regular maintenance task. It is typically performed when you want to customize vehicle features, improve performance, or after making modifications that require ECU adjustments. Routine diagnostics with an OBD2 scanner, however, can be beneficial for regular vehicle health checks.
Recommended Similar Articles:
[Explore more articles on car diagnostics and OBD2 scanners on our blog.] (Link to blog category or related articles on cardiagnosticnearme.com)