The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, and 2024 witnessed the emergence of a new ransomware group making waves across critical sectors: Hellcat. This sophisticated cybercriminal entity is not just another ransomware gang; Hellcat employs a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, amplifying its reach and impact by providing its malicious tools to affiliates. Targeting critical infrastructure, government bodies, educational institutions, and energy companies, Hellcat distinguishes itself with double extortion tactics and a disturbing psychological element aimed at victim humiliation. This article delves into the operations of Hellcat, analyzing their notable activities and the techniques they employ, providing crucial insights for organizations to bolster their defenses against this rising threat.
Understanding the Hellcat Ransomware Group
Hellcat surfaced in the dark web forums in 2024, quickly establishing itself as a significant player in the ransomware arena. Operating under the RaaS model, Hellcat provides its ransomware infrastructure and tools to affiliates, allowing less sophisticated cybercriminals to launch attacks while Hellcat takes a share of the illicit profits. This model has proven highly effective in expanding the reach of ransomware attacks, making groups like Hellcat a considerable concern for global cybersecurity.
What sets Hellcat apart is not just their technical capabilities but also their psychological warfare tactics. They utilize double extortion, a common ransomware technique involving both data encryption and data theft. However, Hellcat takes it a step further by incorporating elements of humiliation and public pressure into their attacks. This indicates a calculated approach to maximize victim distress and increase the likelihood of ransom payment.
Hellcat’s Notable Cyber Attacks: A Timeline of Disruption
To understand the scope and impact of Hellcat’s operations, examining their recent attacks is crucial. The following incidents highlight Hellcat’s targets and methods during November and December 2024.
Schneider Electric SE Breach (November 2, 2024)
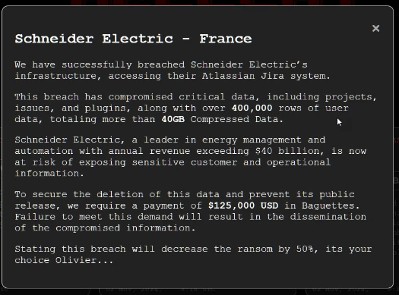 Schneider Electric SE ransom demand
Schneider Electric SE ransom demand
In early November 2024, Hellcat targeted Schneider Electric SE, a major French energy company. The cyberattack successfully infiltrated Schneider Electric’s internal Jira project management system, resulting in the compromise of approximately 400,000 rows of user data and the exfiltration of over 40GB of sensitive information. This data breach included personal details of Schneider Electric employees and customers, with around 75,000 unique email addresses and full names exposed. Adding insult to injury, Hellcat demanded a ransom of $125,000 USD, mockingly requesting payment in “Baguettes,” emphasizing their intent to humiliate the victim organization.
Tanzania’s College of Business Education Data Leak (November 4, 2024)
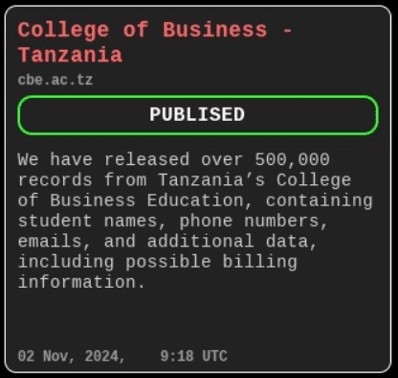 Tanzania’s College of Business data leak
Tanzania’s College of Business data leak
Just days after the Schneider Electric attack, Hellcat, in collaboration with another threat actor named “Hikkl-Chan,” claimed responsibility for leaking over 500,000 records from Tanzania’s College of Business Education. This data breach exposed sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII) of students, faculty, and staff. The collaboration with “Hikkl-Chan” is noteworthy, especially given this actor’s prior involvement in the massive VKontakte (VK) data leak, suggesting a network of cybercriminals working together to amplify their impact and data breaches.
Major U.S. University Root Access Sale (November 14, 2024)
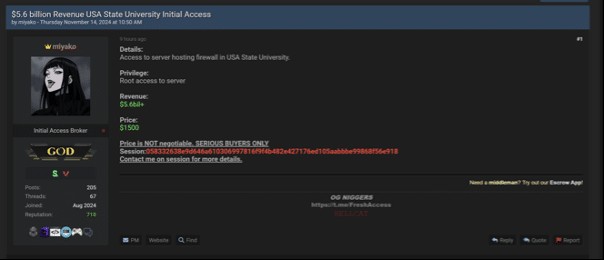 Sale of root access for U.S. university
Sale of root access for U.S. university
Mid-November saw Hellcat shift focus to the education sector in the United States, targeting a major university with substantial annual revenue. Instead of a direct ransomware attack, Hellcat offered root access to the university’s server for sale on dark web forums for a mere $1,500 USD. Gaining root access to a university server could have catastrophic consequences, potentially compromising student records, financial systems, and critical operational data. The relatively low price for such access might indicate Hellcat’s strategy to diversify their income streams and leverage compromised access for further attacks or data exploitation by other cybercriminals.
French Energy Distribution Company Server Access Offered (December 1, 2024)
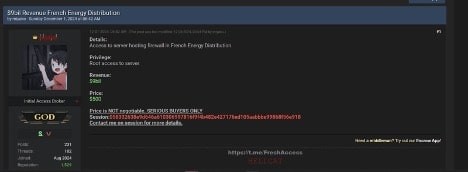 Sale of root access for French energy distribution company
Sale of root access for French energy distribution company
Continuing their focus on the energy sector and European targets, Hellcat targeted a French energy distribution company in early December. Similar to the US university attack, Hellcat offered root access to this company’s server for sale, this time at an even lower price of $500 USD. Targeting energy distribution companies highlights the potential for Hellcat to disrupt critical infrastructure and cause widespread impact beyond financial losses.
Iraq City Government Server Access Auction (December 1, 2024)
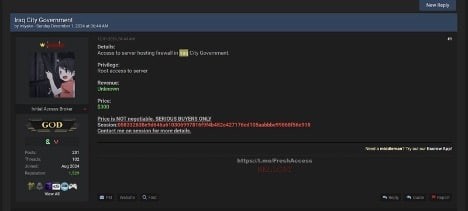 Sale of root access for Iraq city government
Sale of root access for Iraq city government
On the same day as the French energy company incident, Hellcat advertised root access to servers belonging to an Iraq city government for sale at $300 USD. This attack underscores Hellcat’s willingness to target government entities and potentially disrupt essential public services. The targeting of the Iraqi government is also notable considering past cyber incidents involving Iraqi voter data, indicating a persistent interest in compromising sensitive government information.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of Hellcat Ransomware
Analyzing Hellcat’s attacks reveals several key Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) that cybersecurity professionals should be aware of:
- Zero-Day Vulnerability Exploitation: Hellcat demonstrates the capability to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in widely used enterprise tools, as seen in the Schneider Electric SE attack, which leveraged a vulnerability in Jira.
- Firewall and Critical Infrastructure Targeting: Attacks against the U.S. university and French energy distribution company indicate a focus on compromising firewalls and critical infrastructure components to gain deeper network access.
- Privilege Escalation: A core element of Hellcat’s attacks involves escalating privileges to root or administrator levels, granting them complete control over compromised systems.
- Double Extortion: Hellcat consistently employs double extortion tactics, exfiltrating sensitive data before encrypting systems. This maximizes pressure on victims to pay the ransom to avoid both operational disruption and data leaks.
Conclusion: Countering the Hellcat Ransomware Threat
The emergence of Hellcat ransomware in 2024 represents a significant escalation in the cybercrime landscape. Their RaaS model and double extortion tactics, combined with a focus on psychological manipulation, make them a particularly dangerous threat. Organizations in critical sectors like government, education, and energy must prioritize robust cybersecurity measures to defend against ransomware attacks like those perpetrated by Hellcat. Staying informed about evolving TTPs and investing in proactive security solutions are essential steps in mitigating the risk posed by this increasingly sophisticated cyber threat. The fight against ransomware is ongoing, demanding constant vigilance and adaptation to stay ahead of cybercriminals like the Hellcat ransomware group.
Strengthening Your Defenses Against Hellcat with Cato SASE Cloud
The Cato SASE Cloud Platform offers a robust security stack designed to effectively disrupt the ransomware attack chain, including threats like Hellcat. Key components of Cato’s security architecture provide crucial protection layers:
- Cato IPS (Intrusion Prevention System): Leveraging continuously updated threat intelligence feeds, Cato IPS actively blocks access to websites and hosts known to be associated with malware distribution, ransomware command-and-control, and phishing campaigns. It also detects and blocks lateral movement within the network, which is often used by ransomware to spread.
- Cato FWaaS (Firewall as a Service): Cato FWaaS prevents users from accessing malicious websites that may host ransomware payloads, effectively blocking initial infection vectors.
- Cato NGAM (Next-Generation Anti-Malware): Providing an additional layer of defense integrated with Cato ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access), Cato NGAM engines actively prevent malicious downloads and block ransomware execution on user devices, further minimizing the attack surface and potential damage.
By implementing a comprehensive security platform like Cato SASE Cloud, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against Hellcat and other advanced ransomware threats, ensuring business continuity and data protection in an increasingly dangerous cyber environment.
