Level 2 Chargers stand as a significant advancement over Level 1 options, providing notably quicker charging for your electric vehicle (EV) through alternating current (AC) power. In North America, these chargers typically operate on a 208/240 volt input, while in Europe, they utilize either a single-phase 230 volt or a three-phase 400 volt input. Predominantly designed for residential, professional, and public charging points, Level 2 chargers boast compatibility with the majority of EVs available today and are recognized as the most globally installed charger type. They are available in both wall-mounted configurations, which can be affixed to pedestals, and integrated all-in-one designs.
 Different types of Level 2 EV chargers for various installation needs
Different types of Level 2 EV chargers for various installation needs
Understanding AC vs. DC Charging for EVs
To fully grasp electric vehicle charging, differentiating between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) is crucial. Both current types are integral to EV charging duration and the overall battery management system of electric vehicles.
Alternating Current (AC) Explained
The standard electricity supplied from the grid to homes and offices is AC. This current is characterized by its periodic directional changes, enabling efficient long-distance transmission, making AC the worldwide standard for power distribution. Level 2 EV chargers operate using AC power for both input and output.
Direct Current (DC) Explained
Conversely, EV batteries store energy as direct current, which flows unidirectionally. DC electricity is essential for powering electronic devices directly. When a Level 2 EV charging station is used, the EV receives AC power, which its onboard converter then transforms into DC for battery storage and vehicle operation.
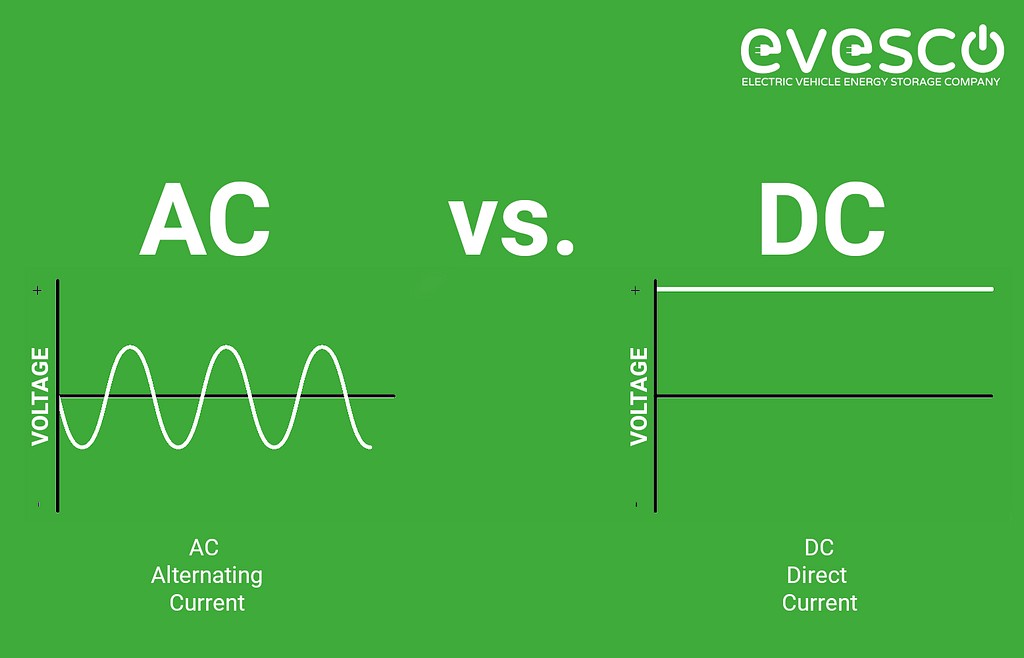 Visual comparison of AC and DC power flow in EV charging
Visual comparison of AC and DC power flow in EV charging
The Role of AC and DC in EV Charging Processes
Electric vehicles utilize a power conversion process when charged via a Level 2 EV charger. The AC power from the charger is converted into DC by the car’s internal converter before being stored in the battery and used to power the vehicle.
Level 1 and Level 2 charging systems both rely on AC power, converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard converter. In contrast, Level 3 charging, or DC fast charging, directly supplies DC power to the battery. This is achieved because the AC to DC conversion happens within the Level 3 charging station itself, bypassing the vehicle’s onboard converter and allowing for quicker power delivery compared to Level 2 charging.
A clear understanding of AC and DC electricity in EV charging clarifies the charging process and how different EV charger levels power your vehicle.
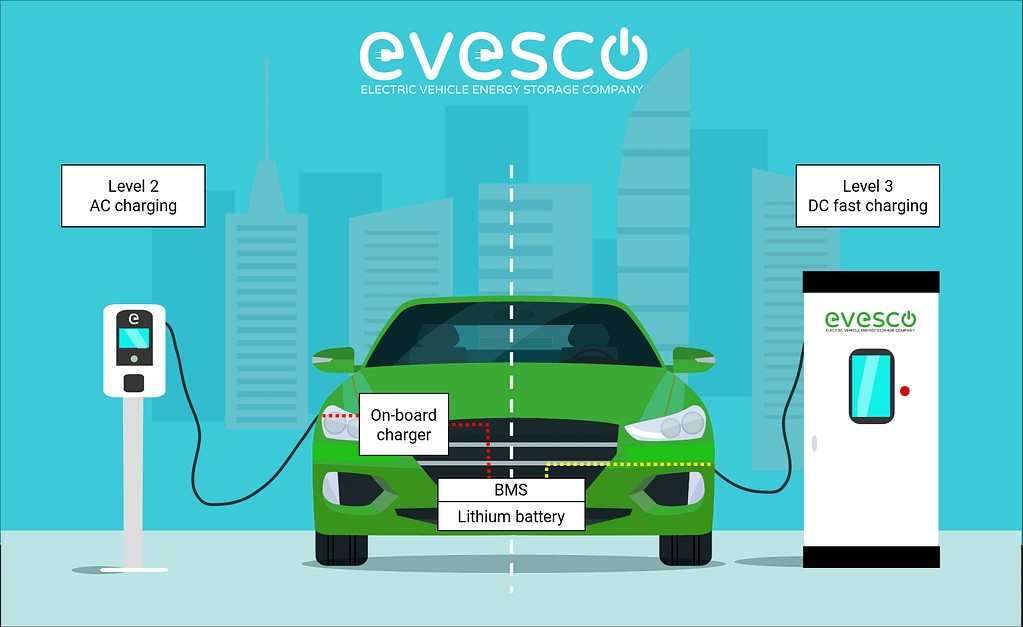 Graphical representation of the differences between AC and DC fast charging power delivery
Graphical representation of the differences between AC and DC fast charging power delivery
The charging curves for AC and DC charging differ significantly. Level 2 EV charging (AC) provides a steady power flow, limited by the onboard converter’s capacity. DC fast charging, however, starts with a high power peak, which gradually decreases as the battery management system reduces power demand as it nears full capacity. The illustration below highlights these charging curve differences.
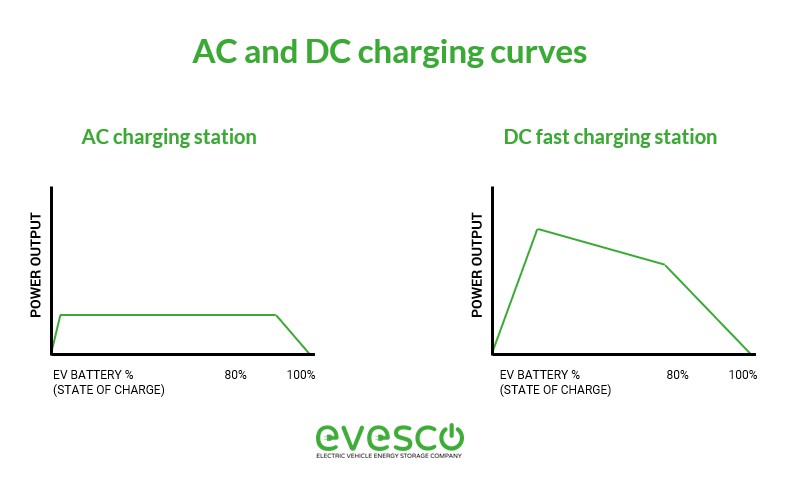 Charging curves comparison for Level 2 AC and Level 3 DC EV charging
Charging curves comparison for Level 2 AC and Level 3 DC EV charging
Level 2 EV Charging Speed: What to Expect?
Level 2 charger speeds vary from 3 to 19.2 kilowatts (kW) in the US and up to 22 kW in Europe, adding approximately 10 to 75 miles (16 – 120 km) of driving range per charging hour. Actual charging speed depends on both the charger’s output and the EV’s charging capabilities, including its acceptance rate. A Level 2 charger can be up to 19 times faster than a Level 1 charger but is slower than Level 3 DC fast charging.
| Charging Level | Output Power Range | Estimated Charge time (40 kWh) | Estimated Range Per Hour of EV Charging | EV Connector Type | User Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 2 (L2) | 3 kW – 22 kW (19.2 kW for USA) | 2 – 13 hours | 10 – 75 miles (16 – 120 km) | Type 1 – J1772 (USA & Japan) Type 2 – Mennekes (Europe) GB/T AC (China) |
Home, workplace, overnight charging, hotels, long stay car parks, and public charging |
Level 2 Charger Charging Times: A Closer Look
The time it takes to charge an EV with a Level 2 charger is determined by factors like the charger’s power output, the EV’s charge acceptance rate, and its battery size. While various conditions can affect charging times, the following are estimates based on an EV capable of utilizing the charger’s full power and adding 40 kWh of battery capacity—the average EV battery capacity).
| Level 2 Charger Output Power | Charge Time (hours) |
|---|---|
| 3 kW | 13.3 |
| 7 kW | 5.7 |
| 11 kW | 3.6 |
| 19.2 kW | 2.1 |
| 22 kW | 1.8 |
Note that these charging times are approximate and can vary based on the specific EV model.
Tethered vs. Untethered Level 2 Chargers: Which is Right for You?
Level 2 EV chargers come in tethered and untethered variants. Understanding their differences, advantages, and disadvantages is key to choosing the right Level 2 charger.
Tethered EV Chargers: Convenience at Your Fingertips
Tethered chargers have a permanently attached cable and connector, eliminating the need for a separate cable. They are user-friendly and always ready for immediate charging. However, connector type limits compatibility. Tethered Level 2 chargers are favored in North America.
Advantages of Tethered EV Chargers
- Convenience and Ease: Tethered chargers offer a seamless charging experience with the cable always ready, removing the hassle of manual cable connection and disconnection. Ideal for users who frequently forget their charging cables.
- Transparent Pricing: The cost of the tethered cable is included in the charger’s price, simplifying budgeting without additional cable purchases.
Considerations for Tethered EV Chargers
- Length Limitations: Cable length is predetermined by the manufacturer. Longer cables may incur extra costs and need to be specified at purchase.
- Size and Space: The attached cable increases the charger’s size, potentially requiring more space and additional cable management accessories for neatness.
- Cable Theft Risk: Tethered cables are susceptible to theft for their scrap value.
- Wear and Tear: Fixed cables are prone to wear and may require future replacement.
Untethered EV Chargers: Flexibility and Maintainability
Untethered chargers lack a fixed cable, requiring users to use their own detachable charging cable. These are connected via a socket on the charger. Untethered Level 2 chargers are commonly used in Europe.
Advantages of Untethered EV Chargers
- Maintenance Ease: Untethered units are more compact and neater without a cable. Fewer components mean less maintenance and potential replacements.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, untethered chargers are less expensive upfront as they exclude the charging cable.
- Flexibility: Users can choose cable lengths and upgrade cables as technology advances without replacing the entire unit.
Considerations for Untethered EV Chargers
- Reduced Convenience: Users must manually attach and detach the cable for each charge, adding an extra step compared to tethered chargers.
- Not Always User-Friendly: Charging is impossible if the user forgets or lacks a compatible charging cable.
Level 2 Charging Connectors and Plugs: Global Standards
Different EV charging connectors and plug types are standard across different regions. Level 2 charging primarily uses four connector types.
Type 1 (J1772): North American Standard
The Type 1 connector (J1772 or J Plug) is the standard in North America and Japan. It supports up to a 19.2 kW EV charger at 80 amps using a single-phase 240-volt input. Most EVs and plug-in hybrids in North America, except Teslas, use the Type 1 J1772 connector.
Type 2 (Mennekes): European Standard
The Type 2 connector, or Mennekes, is standard in Europe, Australia, and parts of Africa and the Middle East. It supports up to 7.6 kW at 32 amps single-phase 230-volt and 22 kW at 32 amps three-phase 400-volt input.
GB/T (AC): China’s Charging Standard
GB/T is the standard connector for AC EV charging in China, supporting up to 7.4 kW with a single-phase input. While visually similar to the European Type 2 connector, its internal wiring is different, making them incompatible.
 GB/T AC EV charging connector and plug detailed view
GB/T AC EV charging connector and plug detailed view
NACS (North American Charging Standard): Tesla’s Connector
NACS, developed by Tesla, is used in North America and previously known as the Tesla Supercharger connector. It supports both AC and DC charging for Tesla vehicles. The Level 2 AC version supports up to 48 Amps on a single-phase 240-volt input.
 NACS EV charging connector and plug detailed view
NACS EV charging connector and plug detailed view
Optimal Locations for Level 2 Charger Installations
Level 2 chargers are versatile and efficient in various settings, providing convenient EV charging solutions. Ideal installation locations include:
Home Charging
Home installation of Level 2 chargers is perfect for overnight charging, providing sufficient range for daily commutes and short trips, offering convenience for EV owners.
Workplace Charging Solutions
Workplaces are strategic sites for Level 2 chargers, enabling employees to charge during work hours, promoting EV adoption among staff. Workplace chargers also attract and retain environmentally conscious employees and serve as a valuable benefit.
Public Charging Stations
Public Level 2 charging stations offer crucial charging access for EV drivers away from home or work, including locations like community centers, parks, event venues, and roadside stops. They are essential for EV users without home charging options.
Commercial Property Charging
Commercial properties such as retail centers, restaurants, long-stay parking, and hotels benefit from Level 2 chargers. They support EV fleets, encourage longer customer visits, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Strategically placed Level 2 chargers are vital for supporting widespread EV adoption, meeting diverse user needs, and seamlessly integrating EV charging into daily life, making EV ownership more appealing.
Incentives for Level 2 Charger Installation
Many governments offer incentives to boost EV adoption and EV charging infrastructure. EV charging incentives include tax credits, rebates, and grants. In the U.S., numerous Level 2 and DC fast charger incentives are available by state, including utility rebates.
Level 2 charging is a practical, efficient, and convenient method for charging electric vehicles at home, work, and in public. Understanding Level 2 charging—speeds, connectors, incentives—equips you to decide if Level 2 charging stations are the right choice for your needs, contributing to a more sustainable transportation future.
Explore Level 2 Charging Stations with Media Screens
Step into the future of EV charging with Level 2 stations featuring media screens! These advanced stations not only charge EVs but also offer a dynamic platform for entertainment and information, enhancing the charging experience.
Discover AC Media Screen Chargers
You Might Also Be Interested In:
 Battery energy storage system for home backup power during outages
Battery energy storage system for home backup power during outages
The Necessity of Battery Energy Storage During Power Outages
Categories: Blog, Energy Storage, Lithium, Power Sonic, Pulse
Stay prepared with reliable energy solutions as power outages become more frequent across North America…
Read More…
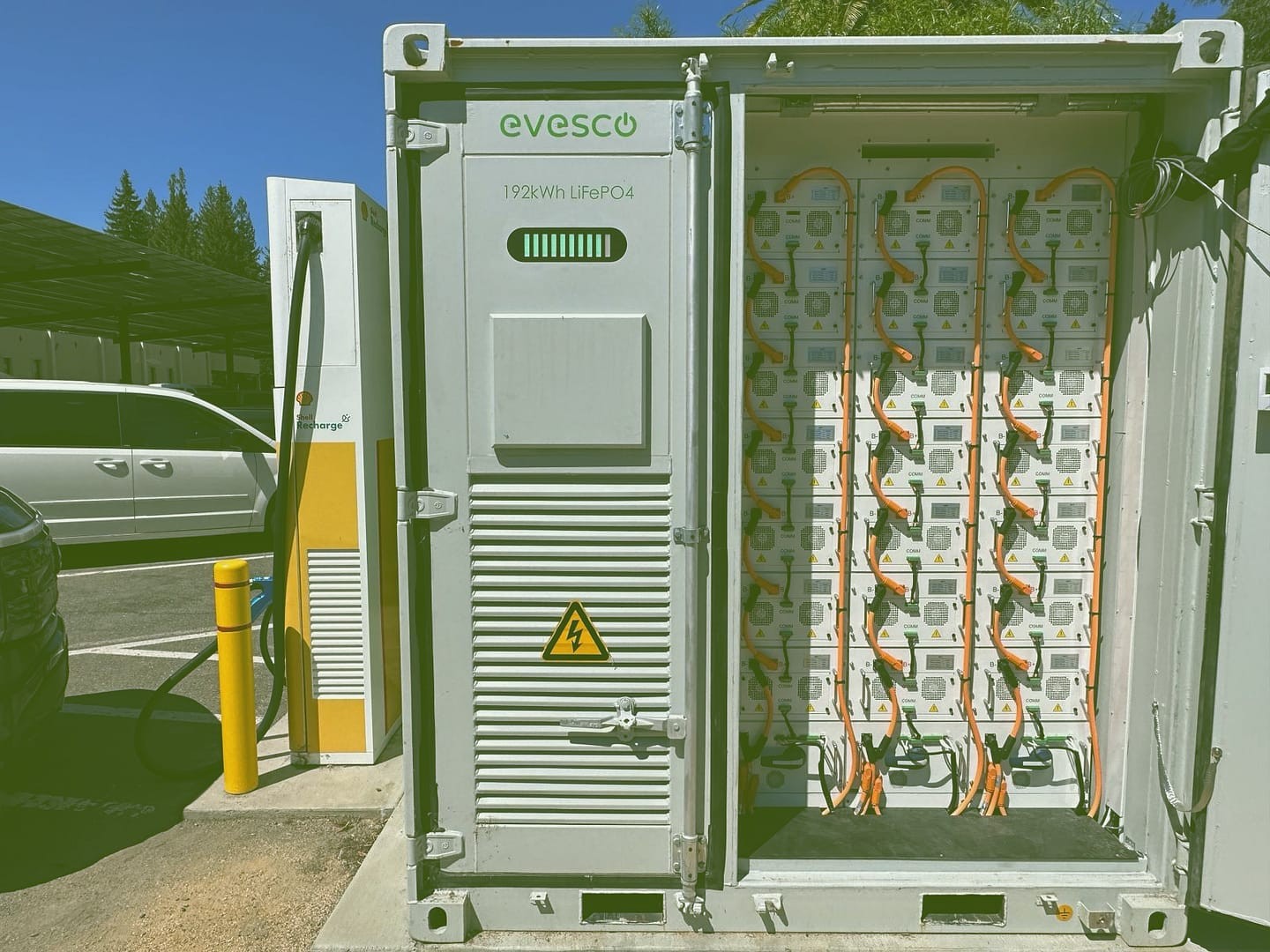
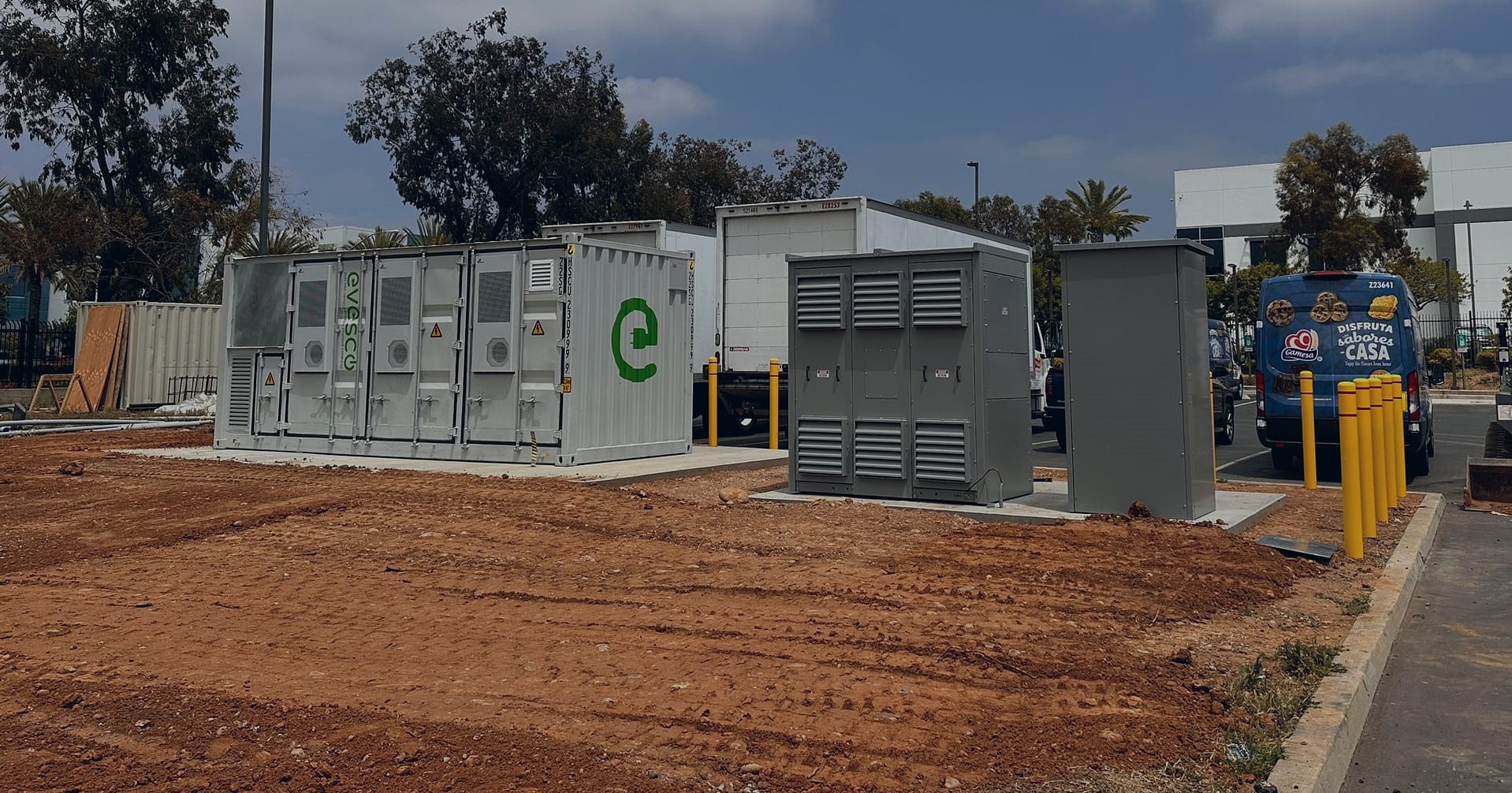 Battery-buffered EV charging system illustration
Battery-buffered EV charging system illustration
Battery-Buffered EV Charging Explained
Categories: Blog, Evesco
Explore how battery-buffered EV charging addresses grid capacity challenges and enhances charging infrastructure…
Read More…
 Energy storage system applications across various sectors
Energy storage system applications across various sectors
Energy Storage Applications: Front-of-the-Meter vs. Behind-the-Meter
Categories: Blog, Evesco
Discover the critical role of energy storage systems in the global transition to clean energy and sustainable consumption…
Read More…