Level 2 Chargers represent a significant upgrade from Level 1, delivering faster charging speeds through alternating current (AC) power. In North America, these chargers typically operate on a 208/240 volt input, while in Europe, they utilize single-phase 230 volts or three-phase 400 volts. Universally compatible with the vast majority of electric vehicles on the road, Level 2 chargers are the most commonly deployed charging solution worldwide, finding homes in residential garages, workplaces, and public charging stations. They are available in various formats, from wall-mounted units, which can be adapted for pedestal installation, to integrated all-in-one systems.
 Types of Level 2 EV chargers
Types of Level 2 EV chargers
Understanding AC vs. DC Charging for EVs
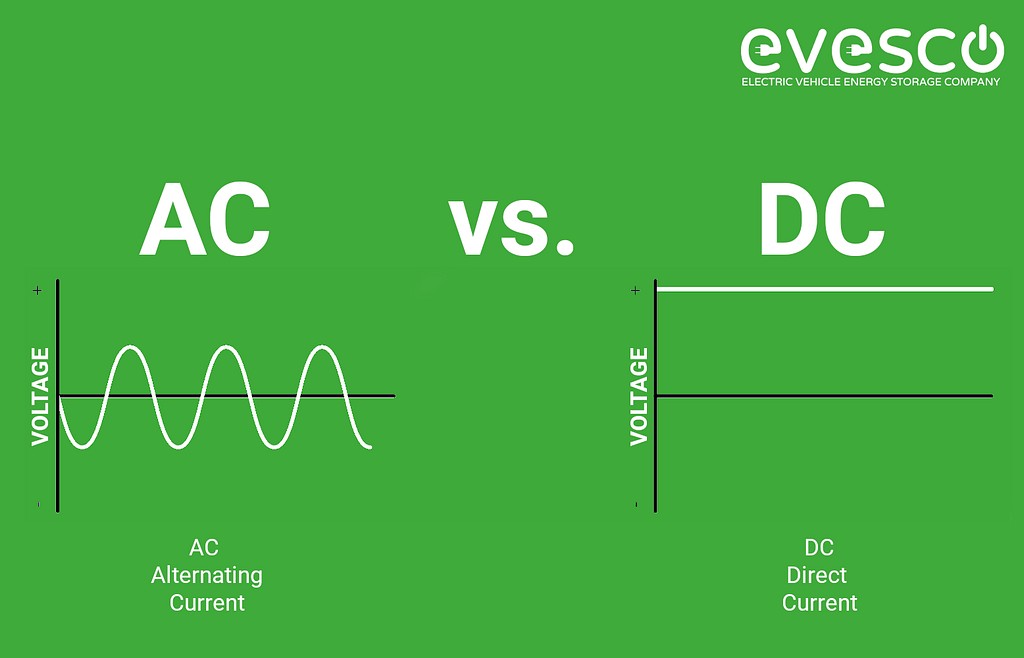
To effectively understand electric vehicle charging, it’s crucial to differentiate between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Both are fundamental to EV charging speeds and the overall battery management process within electric vehicles.
Alternating Current (AC) Explained
AC power is the standard electricity delivered from the grid, powering homes and businesses. Characterized by its periodic change in direction, AC is efficiently transmitted over long distances, making it the global standard for power distribution. Level 2 EV chargers utilize AC power for both input and output.
Direct Current (DC) Explained
In contrast, EV batteries store energy as direct current, which flows in a single direction. DC power is essential for directly powering electronic devices. When an EV connects to a Level 2 charging station, it receives AC power, which is then converted into DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger for battery storage and vehicle operation.
 AC vs DC
AC vs DC
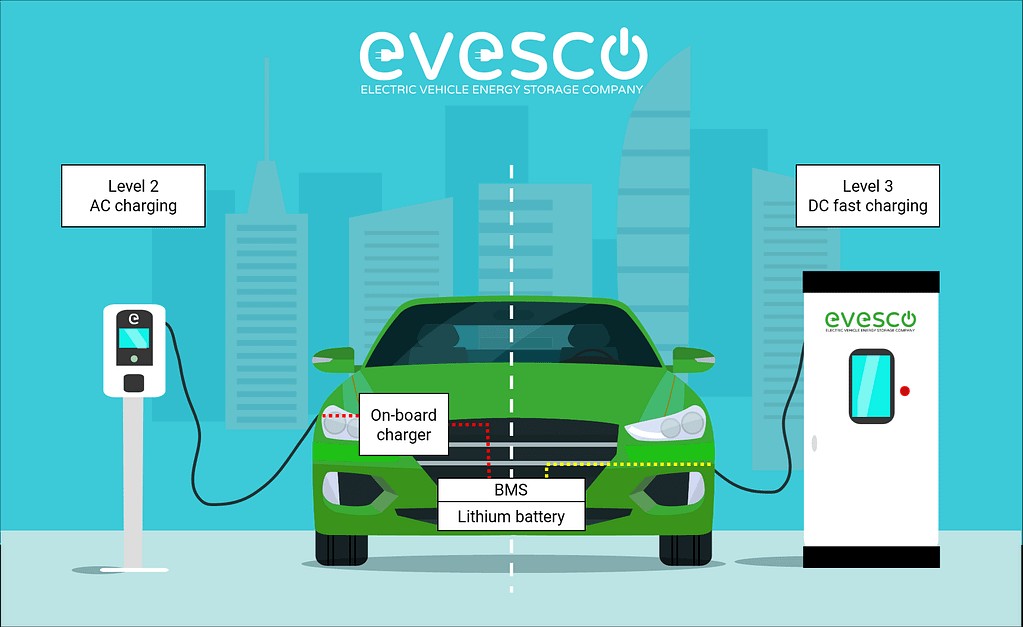
The Role of AC and DC in EV Charging Levels
Level 1 and Level 2 charging systems rely on AC power, which the EV converts to DC using its onboard charger. Level 3 charging, or DC fast charging, differs significantly by directly supplying DC power to the battery. This is achieved because the AC-to-DC conversion occurs within the Level 3 charging station itself, bypassing the vehicle’s onboard converter. This direct DC supply allows Level 3 chargers to deliver much faster charging compared to Level 2 options.
Understanding the distinction between AC and DC power is key to grasping how different EV charger levels operate and deliver power to your electric vehicle, impacting charging times and infrastructure needs.
 Difference between AC and DC fast charging
Difference between AC and DC fast charging
The charging dynamics of AC (Level 2) and DC charging are also distinct. Level 2 AC charging provides a consistent power flow, limited by the onboard converter’s capacity to process power. Conversely, DC fast charging delivers a high initial power surge that gradually decreases as the battery approaches full capacity, regulated by the battery management system. This difference in charging curves is visually represented below.
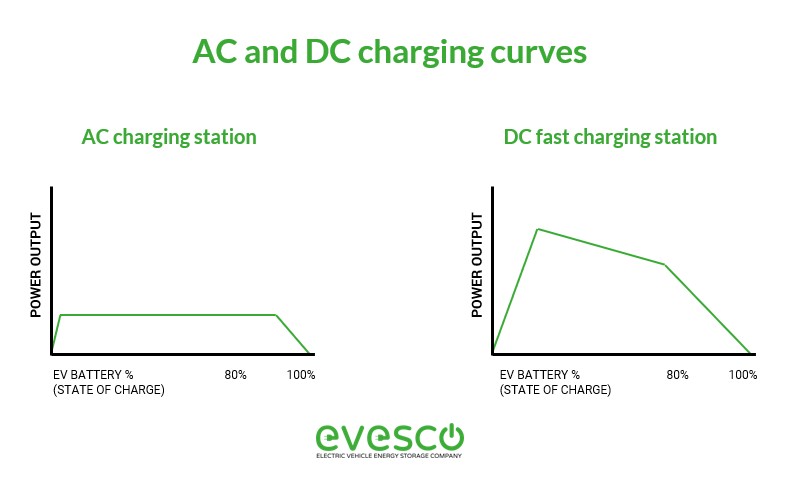 Level 2 (AC) and Level 3 (DC) charging curves
Level 2 (AC) and Level 3 (DC) charging curves
Level 2 EV Charging Speed: What to Expect
Level 2 chargers in the U.S. offer charging rates from 3 kW to 19.2 kW, and up to 22 kW in Europe, adding approximately 10 to 75 miles (16 – 120 km) of driving range per hour of charge. The actual charging speed is determined by both the charger’s power output and the EV’s onboard charging system capabilities, specifically its charge acceptance rate. Level 2 charging is significantly faster, up to 19 times quicker than Level 1 charging. However, it remains slower than Level 3 DC fast charging.
| Charging Level | Output Power Range | Estimated Charge time (40 kWh) | Estimated Range Per Hour of EV Charging | EV Connector Type | User Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 2 (L2) | 3 kW – 22 kW (19.2 kW for USA) | 2 – 13 hours | 10 – 75 miles (16 – 120 km) | Type 1 – J1772 (USA and Japan)Type 2 – Mennekes (Europe)GB/T AC (China) | Home, workplace, overnight charging, hotels, long stay car parks, and public charging |
Level 2 Charger Charging Times: Key Factors
The time it takes to charge an EV with a Level 2 charger depends on several factors: the charger’s power output, the EV’s maximum charge acceptance rate, and the battery pack’s size. While numerous variables can influence charging duration, the table below provides estimated charging times for adding 40 kWh of battery capacity to an EV that can utilize the EV charger’s full power. (40 kWh represents the average EV battery capacity).
| Level 2 Charger Output Power | Charge Time (hours) |
|---|---|
| 3 kW | 13.3 |
| 7 kW | 5.7 |
| 11 kW | 3.6 |
| 19.2 kW | 2.1 |
| 22 kW | 1.8 |
Note that these are approximate times and can vary based on the specific EV model and real-world charging conditions.
Tethered vs. Untethered Level 2 Chargers: Choosing the Right Type
Level 2 chargers are available in two primary configurations: tethered and untethered. Understanding the pros and cons of each type is essential when selecting a Level 2 charger for your needs.
Tethered Level 2 Chargers
Tethered chargers come with an attached charging cable and connector, offering immediate readiness and ease of use. They are particularly popular in North America due to their convenience.
Advantages of Tethered EV Chargers:
- Convenience: The integrated cable means the charger is always ready for use, simplifying the charging process, especially useful if you frequently charge at the same location.
- All-Inclusive Pricing: The cost of the cable is included in the charger price, eliminating the need for separate cable purchases.
Considerations for Tethered EV Chargers:
- Cable Length Limitations: The fixed cable length might restrict placement flexibility, and longer cables may incur additional costs.
- Size and Cable Management: The attached cable can increase the charger’s physical footprint, potentially requiring additional cable management solutions.
- Cable Security: Tethered cables are susceptible to theft for scrap value, a factor to consider for exposed installations.
- Wear and Tear: As exposed components, tethered cables are subject to wear and may require eventual replacement.
Untethered Level 2 Chargers
Untethered chargers lack an attached cable, requiring users to provide their own. This type is more common in Europe, offering flexibility and potentially lower initial costs.
Advantages of Untethered EV Chargers:
- Easier Maintenance: Without an integrated cable, untethered units are more compact and have fewer parts subject to wear or damage.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, untethered chargers are less expensive upfront as they exclude the cable cost.
- Flexibility and Future-Proofing: Users can choose cable lengths as needed and upgrade cables independently of the charger as technology evolves.
Considerations for Untethered EV Chargers:
- Reduced Convenience: Requiring a separate cable adds an extra step to each charging session.
- Cable Dependency: Users must possess and remember to bring their charging cable, which may be inconvenient or prohibitive for some.
Level 2 Charging Connectors and Plugs: Regional Standards
EV charging connectors and plugs vary globally, with four main types used for Level 2 charging.
Type 1 (J1772) Connector
The Type 1 connector (J1772), prevalent in North America and Japan, supports up to 19.2 kW charging at 80 amps using a single-phase 240-volt supply. It’s the standard for nearly all EVs in North America, excluding Tesla models.
Type 2 (Mennekes) Connector
The Type 2 (Mennekes) connector is standard in Europe, Australia, and parts of Africa and the Middle East. It supports up to 7.6 kW at 32 amps single-phase 230V and 22 kW at 32 amps three-phase 400V.
GB/T (AC) Connector
GB/T is China’s standard AC charging connector, capable of up to 7.4 kW output with a single-phase input. While visually similar to the Type 2 connector, its internal wiring is different and incompatible.
 GB/T AC charging connector, socket, and plug
GB/T AC charging connector, socket, and plug
NACS (North American Charging Standard) Connector
NACS, developed by Tesla, is becoming increasingly adopted in North America. Previously known as the Tesla Supercharger connector, it supports both AC and DC charging. In its Level 2 AC configuration, it can deliver up to 48 amps on a single-phase 240V supply.
Optimal Locations for Level 2 Charger Installation
Level 2 chargers are versatile and suitable for a variety of locations, enhancing EV accessibility and convenience.
Residential Charging
Home installation of Level 2 chargers is ideal for overnight charging, providing ample range for daily commutes and errands. It offers convenience and independence for EV owners.
Workplace Charging
Workplaces are strategic locations for Level 2 chargers, enabling employees to charge during work hours. This supports EV adoption by staff, serves as an employee benefit, and attracts environmentally conscious talent.
Public Charging Stations
Public Level 2 charging stations are essential for EV drivers on the go, particularly those without home charging options. Ideal locations include community centers, parks, recreational areas, and travel plazas.
Commercial Properties
Retail centers, restaurants, hotels, and long-term parking facilities benefit from Level 2 charger installations. They attract EV-driving customers, encourage longer visits, and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability.
Strategically placed Level 2 chargers are crucial for supporting widespread EV adoption, catering to diverse user needs and integrating seamlessly into daily routines.
Incentives for Level 2 Charger Adoption
Many governmental and utility programs offer incentives like tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage EV adoption and the installation of EV charging infrastructure, including Level 2 chargers. In the U.S., numerous state and local incentives are available for both Level 2 and DC fast chargers.
Level 2 charging is a practical, efficient, and user-friendly solution for EV charging at home, work, and in public spaces. Understanding the specifics of Level 2 charging—from speed and connectors to incentives—empowers informed decisions about adopting this vital EV charging technology.
Level 2 Charging Stations with Integrated Media Screens
Explore the cutting edge of EV charging with Level 2 stations featuring media screens. These advanced chargers not only power EVs but also offer dynamic digital displays for entertainment, information, and advertising, enhancing the user experience.
AC Media Screen Chargers
Explore Further: Related Topics
 Battery energy storage system providing backup power to a home during a planned outage caused by severe weather
Battery energy storage system providing backup power to a home during a planned outage caused by severe weather
Why Battery Energy Storage is Essential During Planned Power Outages
Stay Prepared and Powered: The Growing Need for Reliable Energy Solutions During Outages Across North America, utility companies are increas…
Read More…
 Battery energy storage and EV charging battery buffered
Battery energy storage and EV charging battery buffered
Battery-Buffered EV Charging
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is driving rapid growth in charging infrastructure, posing new challenges for grid capacity, deployment…
Read More…
 Application of energy storage systems
Application of energy storage systems
Energy Storage Applications: Front-of-the-Meter vs. Behind-the-Meter
As the global shift towards clean energy continues, energy storage systems are critical in transforming how we generate, store, and consume …
Read More…