The OBD2 connector, your car’s diagnostic port, is crucial for vehicle maintenance and repair. While OBD2 connector repair might seem straightforward, it often presents challenges. Finding the correct connectors and terminals can be difficult, and even when available, selecting the right parts requires expertise. This guide provides essential information to navigate Obd2 Connector Replacement effectively, ensuring a durable and reliable fix.
Understanding the OBD2 Connector
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) connector is a standardized 16-pin interface mandated in all cars manufactured from 1996 onwards. This standardization is beneficial as it allows any generic OBD2 scanner to access essential vehicle data, regardless of the car manufacturer. However, it’s important to note that while the OBD2 standard ensures access to certain basic data, automakers often include proprietary data beyond this standard, which may not be accessible with generic scan tools.
OBD2 Connector Pinout
Understanding the pin configuration is crucial when dealing with OBD2 connector replacement. Here’s a breakdown of the standard OBD2 pin positions:
- Pin 1: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pins 2 & 10: SAE J1850 Bus (network communication)
- Pin 3: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pins 6 & 14: CAN Bus High and Low (network communication)
- Pins 7 & 15: ISO9140 K-Line (network communication)
- Pins 8, 9, 11, 12, 13: Manufacturer Discretion
- Pin 16: Battery Positive (constant power supply)
Common Causes of OBD2 Connector Damage
Pin 16, the battery positive pin, is frequently the victim of damage. Several factors contribute to OBD2 connector issues:
- Blown Fuse: Pin 16 is often fused, and this fuse can blow due to faulty aftermarket accessories connected to the OBD2 port or overloads in shared circuits. While a blown fuse itself doesn’t damage the connector, improper testing methods can.
- Physical Damage from Probes: The primary cause of OBD2 connector damage is careless testing. Using probes incorrectly, forcing them into terminals where they don’t fit, can severely damage both the terminals and the connector housing. This is a leading reason for needing OBD2 connector repair.
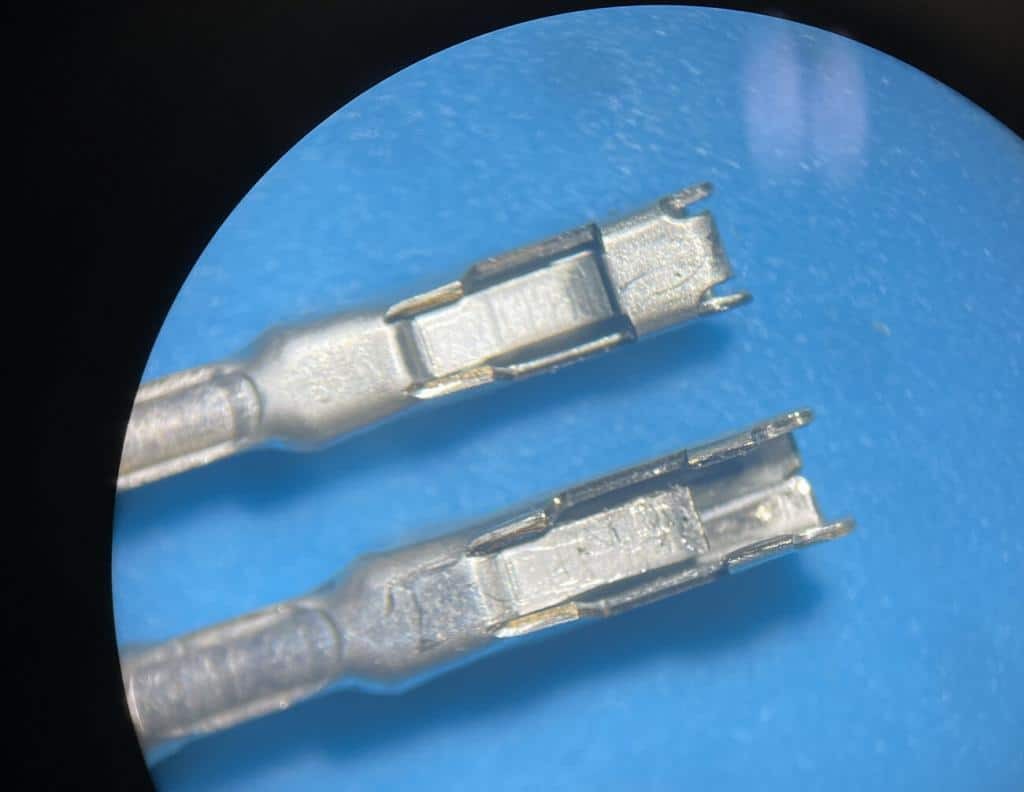 One good terminal and one damaged terminal under a microscope
One good terminal and one damaged terminal under a microscope
Alt text: Comparison of a damaged OBD2 connector terminal and a new terminal, highlighting common damage.
- Aftermarket Accessories: Devices like insurance tracking dongles, aftermarket gauges, and data recorders, constantly plugged into the OBD2 port, can cause problems. Lower quality aftermarket devices may have oversized male pins that stretch out the female terminals in the car’s OBD2 connector.
- Excessive Current Draw: Some aftermarket devices draw more current from pin 16 than the connector is designed to handle continuously. The OBD2 port is intended to power scan tools for short diagnostic sessions, not to constantly power high-current devices while the car is running.
The Myth of Universal OBD2 Connectors
Despite the OBD2 standard, connectors are not universally identical. While any male OBD2 connector will physically plug into any female OBD2 port, the way these connectors are mounted in vehicles and how terminals are secured within the connector varies significantly across car makes and models. Connector suppliers offer a vast array of connector housings (the plastic part) and terminals (the metal contacts), reflecting this diversity.
The Pitfalls of Cheap Aftermarket OBD2 Connectors
Low-cost OBD2 connectors available online might seem like an attractive quick fix. However, these often come with significant drawbacks. A major issue is that they rarely fit the original mounting brackets in the car. This necessitates makeshift mounting solutions, like self-tapping screws, which are not durable or reliable long-term.
More critically, the quality of terminals in these cheap connectors is often substandard. The metal used is frequently too soft and lacks the proper springiness of OEM terminals. While these connectors might provide an initial “repair,” their longevity is questionable.
Considering the labor involved in OBD2 connector replacement, using inferior parts is false economy. Replacing terminals on a pigtail, accessing the wiring by removing dash components, and soldering connections is time-consuming. Using subpar parts increases the risk of premature failure and repeat repairs, leading to higher costs in the long run, both for repair shops and vehicle owners.
Sourcing OEM OBD2 Connector Parts from Dealerships
Purchasing replacement parts from the car manufacturer’s dealership is generally the best approach for quality and fit. Using Toyota as an example, while dealerships may initially state that a complete OBD2 connector assembly is unavailable as a single part number, individual components can be sourced.
Vehicle-specific wiring diagrams, often accessible through manufacturer service information websites (like Toyota’s TIS), are invaluable resources. By clicking on the OBD2 connector in the wiring diagram and accessing the component information box, you can often find the part number for the plastic connector housing.
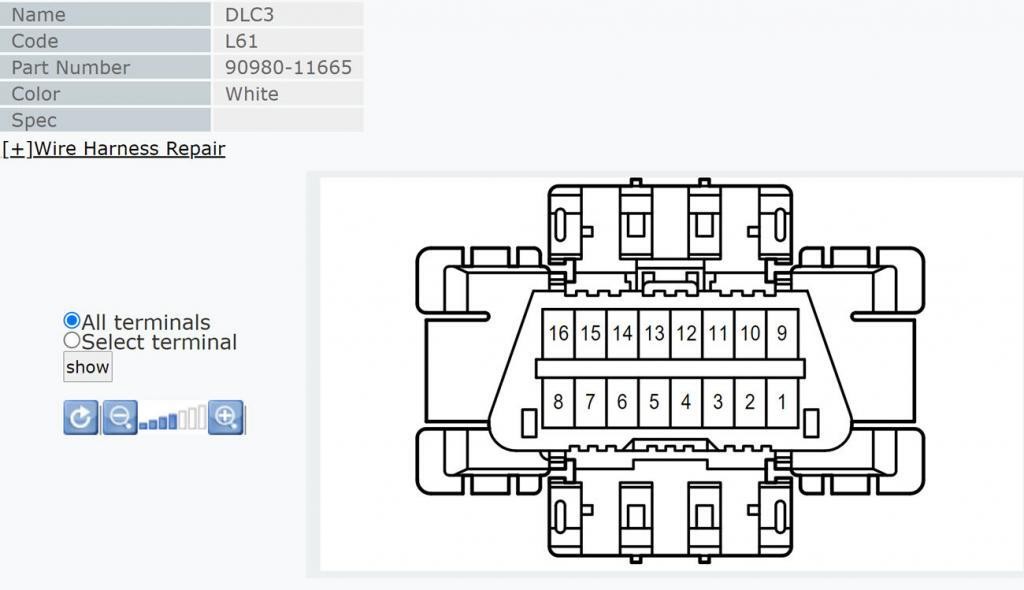 OBD2 connector picture and part number from the Toyota service manual
OBD2 connector picture and part number from the Toyota service manual
Alt text: Toyota service manual diagram showing the OBD2 connector and its part number 90980-11665, useful for ordering replacement parts.
For Toyota, a common OBD2 connector housing part number is 90980-11665. Interestingly, this part number information can also be found in older, pre-electronic service manuals by searching for “part number of connectors.”
However, obtaining the correct metal terminals can be more challenging. Dealership parts departments may not readily identify the compatible terminals. In some cases, contacting experienced parts managers or even service foremen with a deep knowledge of parts can be helpful in locating the correct terminal part numbers. Sometimes, resourceful dealership staff may even have a stock of salvaged terminals that they are willing to provide.
For Toyota vehicles, a frequently used OBD2 repair terminal part number is 82998-05010. This terminal is confirmed to fit Gen3 Prius models and likely many other Toyota vehicles.
While OEM terminals like 82998-05010 offer superior quality and fit, they can be relatively expensive for individual terminals. This higher cost reflects warehousing, distribution, and markup, but the increased reliability and reduced risk of future issues often justify the investment.
 OBDII terminal for connector repair from Toyota. Part number 82998-05010
OBDII terminal for connector repair from Toyota. Part number 82998-05010
Alt text: Toyota OEM OBD2 connector terminal, part number 82998-05010, a high-quality replacement option for reliable repairs.
Exploring Aftermarket Connector and Terminal Suppliers
Companies like Connector Experts specialize in reproducing OEM-quality connectors and terminals. These suppliers can be a valuable alternative to dealerships, offering comparable quality parts at more competitive prices. For example, Connector Experts’ terminal part number TERM86 has been identified as a compatible and high-quality alternative to OEM Toyota terminals, often at a significantly lower cost. While these aftermarket terminals may not include a pigtail wire, their quality, material hardness, and dimensions closely match OEM specifications.
Major electronic component distributors like Mouser also carry a wide range of automotive connectors and terminals. However, navigating their extensive catalogs to find the precise part can be complex and time-consuming.
Crimping OBD2 Terminals for a Professional Repair
Proper crimping is essential for a reliable OBD2 connector repair. While most mechanics own wire crimpers, standard crimpers are often designed for larger, older-style automotive terminals and may not be suitable for the smaller, open-barrel terminals used in OBD2 connectors.
Investing in high-quality crimpers designed for small, open-barrel terminals is crucial for creating factory-quality crimps. Brands like Engineer (Japanese manufacturer) offer specialized crimpers that produce precise and secure crimps, ensuring optimal electrical contact and long-term durability of the OBD2 connector repair.
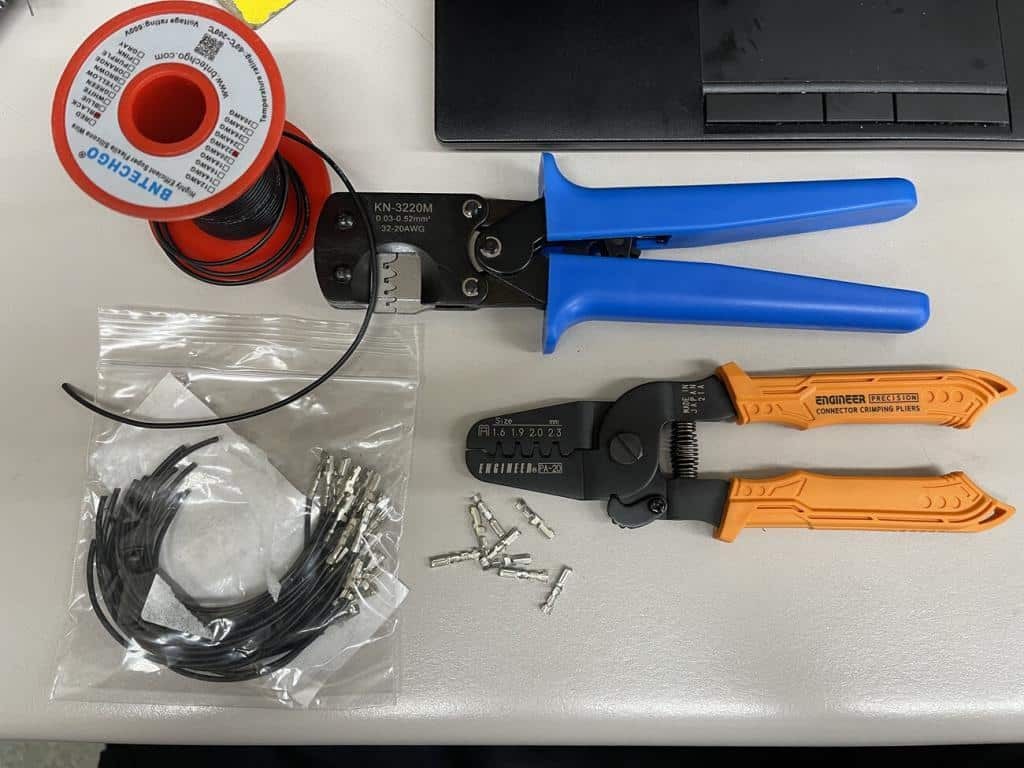 Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
Wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire on a table
Alt text: Essential tools for OBD2 connector replacement: wire crimpers, pigtails, terminals, and wire, ensuring proper and durable connections.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Quality in OBD2 Connector Replacement
While OBD2 connector replacement might appear simple, achieving a lasting and reliable repair requires attention to detail and the use of quality parts. Choosing OEM or reputable aftermarket connectors and terminals, combined with proper crimping techniques, is crucial. Avoid the temptation of cheap, inferior parts, as they can lead to premature failure and increased costs in the long run. By prioritizing quality and utilizing the right resources, you can ensure a successful and durable OBD2 connector replacement, maintaining the essential diagnostic capabilities of your vehicle.
