Most car owners and even seasoned mechanics are familiar with OBD2 scanners for diagnosing engine issues. However, when it comes to the crucial Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), or airbags, standard scanners often fall short. If you’re looking to ensure the safety of your vehicle and passengers, understanding the importance of a specialized Obd2 Scanner For Airbag systems is paramount. This article will guide you through what to look for in an obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics, how to identify airbag sensor problems, and the steps to effectively check and clear airbag codes.
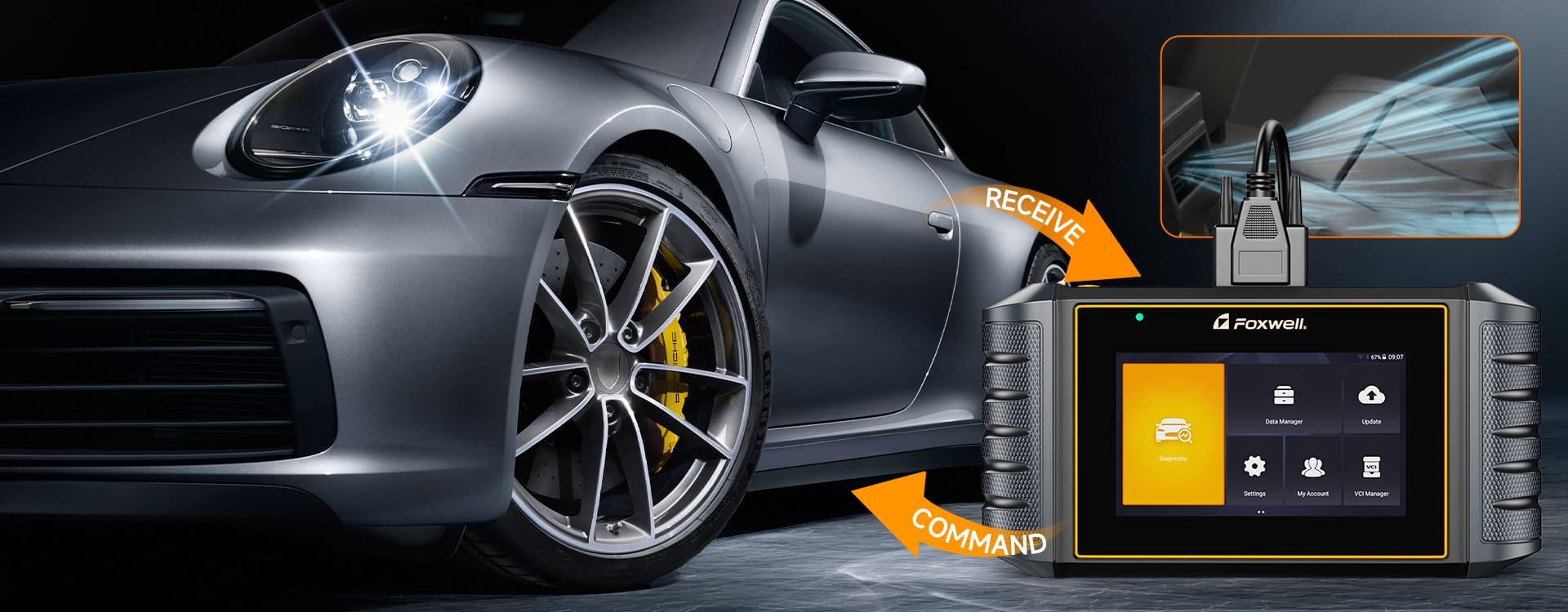 Connect Car Scanner | Foxwell
Connect Car Scanner | Foxwell
Why You Need a Specialized OBD2 Scanner for Airbag Codes
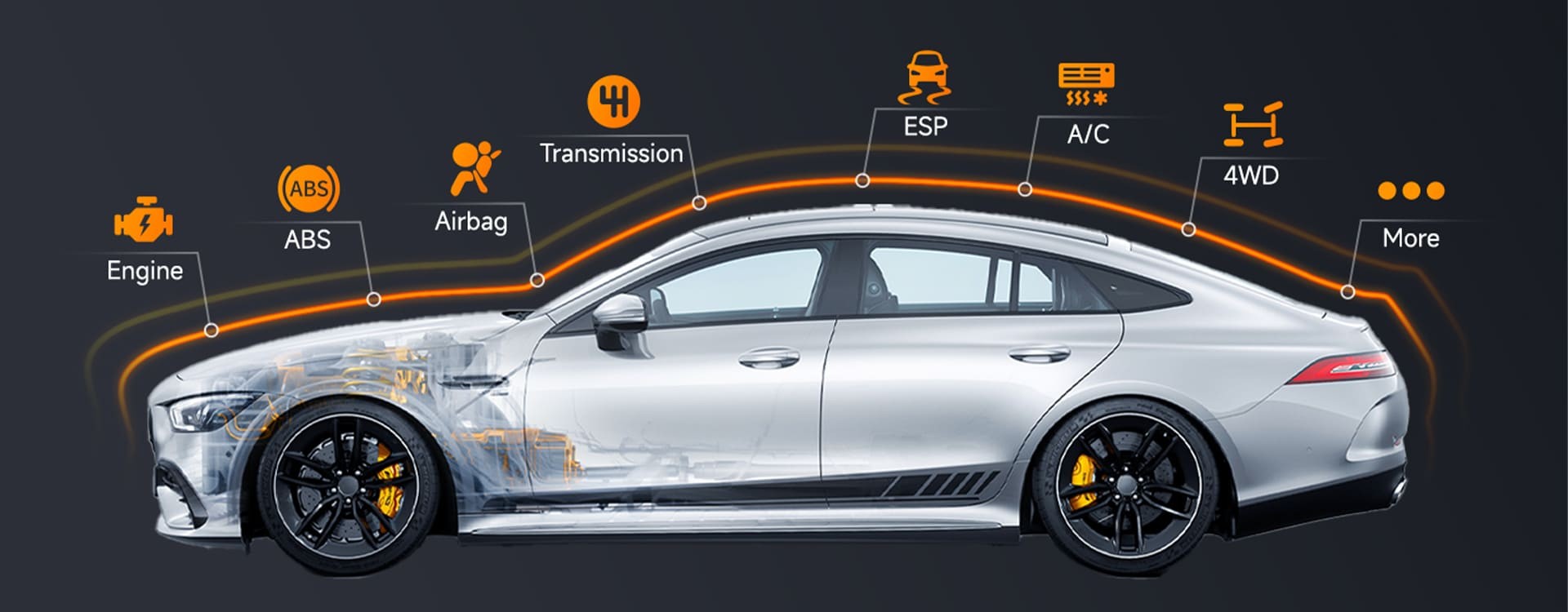
While basic OBD2 scanners are excellent for reading engine and transmission fault codes, they are typically not equipped to communicate with the complex systems that control your vehicle’s airbags. Diagnosing issues within the SRS requires a more advanced tool – an obd2 scanner for airbag systems. These specialized scanners are designed with the software and hardware necessary to delve into the SRS, read detailed fault codes, and provide valuable insights to guide your repairs.
Think of it this way: a standard OBD2 scanner is like a general physician, great for common ailments. But for specialized issues like those within your airbag system, you need a specialist – in this case, an obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics. These advanced tools not only read airbag codes but also offer comprehensive diagnostic information that helps pinpoint the exact problem, saving you time and potentially costly guesswork. For both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts dedicated to vehicle safety, investing in the right obd2 scanner for airbag functionality is essential.
Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner for Airbag Systems
When selecting an obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics, several critical features will ensure it meets your needs and provides accurate, reliable results. Here’s what to prioritize:
1. SRS System Compatibility: The Core Requirement
- Specialized Software: The most fundamental aspect of an obd2 scanner for airbag use is its software. It must be specifically programmed to communicate with your vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). This specialized software enables the scanner to access and interpret the unique codes generated by the airbag system, which are different from standard engine or transmission codes.
- Regular Firmware Updates: The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with new models and SRS technologies emerging regularly. An effective obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics should support firmware updates. These updates ensure the scanner remains compatible with the latest vehicle models and their evolving SRS systems, keeping your tool relevant and accurate over time.
2. Enhanced Diagnostic Functions: Going Beyond Basic Code Reading
- Full-System Diagnostics: An obd2 scanner for airbag should ideally offer full-system diagnostic capabilities. This means it shouldn’t be limited to just the engine and transmission but should extend to all vehicle systems, crucially including the SRS. This broad diagnostic capability allows you to read, interpret, and clear codes not just from the airbag system but from other safety-related systems as well.
- Live Data Streaming for SRS: For in-depth diagnostics, live data streaming is invaluable. An obd2 scanner for airbag that provides live data streaming allows you to monitor real-time data from airbag system sensors. This can be instrumental in diagnosing intermittent issues or pinpointing the exact sensor that is malfunctioning, leading to more precise and effective repairs.
3. Comprehensive Vehicle Coverage: Broad Compatibility is Key
- Wide Range of Makes and Models: The best obd2 scanner for airbag use will support a wide array of vehicle makes and models. This universal compatibility ensures that your investment is versatile and can be used across different brands, including domestic, European, and Asian vehicles. Whether you work on a variety of cars or own multiple vehicles of different brands, broad coverage is essential.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Beyond generic OBD2 codes, the ability to read manufacturer-specific codes is crucial for accurate airbag system diagnostics. Vehicle manufacturers often have proprietary codes that provide more detailed information about faults within their specific SRS implementations. An obd2 scanner for airbag capable of reading these manufacturer-specific codes offers a deeper level of diagnostic accuracy.
4. User-Friendly Interface: Ease of Use for Efficient Diagnostics
- Intuitive Display: When working with complex systems like airbags, a clear and easy-to-read display is vital. An obd2 scanner for airbag with an intuitive display helps users quickly understand diagnostic information. This includes clear presentation of fault codes and, importantly, detailed descriptions of what those codes mean, often suggesting possible causes and fixes directly on the screen.
- Guided Diagnostics: For users who are not expert mechanics, some advanced obd2 scanner for airbag tools offer guided diagnostics. These systems provide step-by-step instructions to help diagnose and resolve issues indicated by fault codes. This feature can be particularly helpful for DIYers or those less familiar with airbag system intricacies.
5. Advanced Features: For Professional-Level Diagnostics
- Bi-Directional Control: For more advanced and thorough diagnostics, bi-directional control is a significant feature in an obd2 scanner for airbag systems. This functionality allows the scanner to not just read data but also send commands to the vehicle’s SRS system. This enables in-depth testing of components and system functions, going beyond simple code reading to actively assess system health.
- ECU Programming Capabilities: While less commonly needed for routine diagnostics, some high-end obd2 scanner for airbag tools offer ECU programming. This advanced capability allows for software updates and modifications to the vehicle’s electronic control unit. In the context of airbags, this might be used for resetting the SRS module after repairs or updates, although this is generally a feature more relevant for professional workshops dealing with complex electronic issues.
Identifying a Faulty Airbag Sensor
Wondering if an airbag sensor is the source of your SRS warning light? Recognizing the signs of a failing airbag sensor is the first step toward ensuring your safety systems are functioning correctly. Here’s how to determine if your airbag sensor might be bad:
1. The Airbag Warning Light: The Most Obvious Indicator
The most direct signal that something is amiss within your airbag system, potentially involving a faulty sensor, is the illumination of the airbag warning light on your dashboard. This light, often depicted as a seated person with a deployed airbag, is designed to alert you to any detected problems in the SRS. If this light remains constantly on or flashes intermittently while driving, it strongly suggests a malfunction within the airbag system, and a sensor issue is a common culprit. This warning should never be ignored, as it indicates that your airbags might not deploy correctly in the event of a collision.
2. Error Codes: Diagnostic Confirmation
For a more definitive diagnosis, an obd2 scanner for airbag codes is indispensable. Connecting such a scanner to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and initiating an SRS system scan will reveal any stored error codes. Specific codes like B1100, B1102, or B1103 are frequently associated with airbag sensor malfunctions. These codes provide specific information about the nature of the problem. Your scanner’s manual or online resources can help you interpret these codes accurately. This step is crucial for pinpointing whether a sensor is indeed the problem.
3. Physical Inspection: Visual Clues
Sometimes, a physical inspection of the airbag sensors themselves can reveal obvious issues. Airbag sensors are typically located in areas prone to impact or environmental exposure, such as the front bumper, near the radiator, or within the passenger compartment. Carefully inspect these sensors for any signs of physical damage like cracks, fractures, or impact marks. Also, check for corrosion, particularly on the sensor connectors and wiring, which can disrupt electrical signals and cause malfunctions. Loose connections are another common problem; ensure that all connectors are securely attached. This hands-on approach can sometimes quickly identify visible sensor problems.
4. Performance Issues: Airbag Deployment Concerns
While definitively testing airbag deployment is not advisable or safe, understanding potential performance issues related to sensors is important. A malfunctioning airbag sensor can lead to delayed or improper airbag deployment in a collision. In situations like minor fender-benders where airbags might be expected to deploy but do not, a faulty sensor could be the reason. However, it’s crucial to note that airbags are designed to deploy only in significant collisions, so non-deployment in a minor incident isn’t always indicative of a sensor problem. Nevertheless, any concerns about airbag deployment should be thoroughly investigated using an obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics and professional assessment.
Steps to Diagnose a Bad Airbag Sensor Systematically
Diagnosing a bad airbag sensor involves a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and safety. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Connect a Diagnostic Scanner for SRS Codes
Begin by using an advanced diagnostic scanner specifically designed to read SRS codes. Standard, basic OBD2 scanners will not be sufficient for accessing airbag system data. Locate your vehicle’s OBD2 port, usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. With the ignition turned to the “On” position (but engine off), plug the scanner into the OBD2 port. Follow the scanner’s prompts to initiate a scan of the SRS system and retrieve any stored fault codes.
Step 2: Interpret the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Once the scan is complete, your obd2 scanner for airbag codes will display a series of DTCs related to the SRS. Consult your scanner’s manual or an online DTC database to understand the meaning of each code. Pay close attention to codes that specifically indicate sensor issues, such as those related to circuit malfunctions, signal implausibility, or sensor performance. Accurate interpretation of these codes is crucial for directing your diagnostic efforts effectively.
Step 3: Inspect the Sensor and Electrical Connections
Based on the error codes and your vehicle’s service information, locate the suspect airbag sensor. Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the sensor itself and its surrounding electrical connections. Look for any physical damage to the sensor, such as cracks or breaks. Carefully examine the wiring harness and connectors for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. To ensure a good connection, try unplugging and replugging the connectors securely. Sometimes, simply reseating a loose connector can resolve intermittent sensor issues.
Step 4: Test Sensor Resistance with a Multimeter (Advanced)
For a more in-depth assessment, and if you are comfortable with basic electrical testing, you can use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the specified resistance values for the airbag sensor. Disconnect the sensor and use the multimeter to measure its resistance. If the measured resistance is outside the manufacturer’s specified range or if you detect no continuity (an open circuit), it is likely that the sensor is faulty and needs replacement. This step requires caution and reference to the correct technical documentation for your vehicle model.
Step 5: Seek Professional Assistance When Needed
If you are unsure about any step of the diagnostic process, or if you lack the tools or expertise to perform electrical testing or airbag system repairs, it is always best to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic. Airbag systems are critical safety components, and incorrect handling or diagnosis can lead to system malfunctions or accidental airbag deployment, which can be dangerous. A professional mechanic has the specialized tools, knowledge, and experience to accurately diagnose and repair airbag system issues, ensuring your vehicle’s safety systems are functioning correctly. Never compromise on safety when dealing with airbag systems.
How to Check Airbag Codes Step-by-Step
Checking airbag codes accurately requires the right tools and a systematic approach. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to check airbag codes using an obd2 scanner for airbag systems:
Step-by-Step Process to Check Airbag Codes Effectively
1. Gather the Necessary Tools and Information
- Diagnostic Scanner for SRS: Ensure you have an advanced diagnostic scanner that is specifically capable of reading SRS (airbag) codes. A standard OBD2 scanner will likely not work for this purpose.
- Vehicle Service Manual (Recommended): While not always essential, having your vehicle’s service manual can be very helpful. It provides specific information about your car’s OBD2 port location, SRS system details, and potentially, guidance on interpreting codes specific to your vehicle model.
2. Locate the OBD2 Port in Your Vehicle
- Find the OBD2 Port Location: The OBD2 port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of your vehicle. Common locations include near the steering column or in the footwell area.
- Consult Your Vehicle Manual (If Needed): If you are having trouble locating the OBD2 port, refer to your vehicle’s service manual. Alternatively, online resources or guides specific to your car model can also provide this information. In some cases, the port might be hidden behind a small panel or cover.
3. Prepare Your Vehicle for Scanning
- Turn Off the Engine Completely: Ensure the vehicle’s engine is completely turned off before you connect the diagnostic scanner.
- Turn Ignition to “On” Position (Engine Off): Insert your car key into the ignition and turn it to the “On” position. This powers up the vehicle’s electrical systems and the SRS module without starting the engine. This is necessary for the scanner to communicate with the airbag system.
4. Connect the Diagnostic Scanner to the OBD2 Port
- Plug in the Scanner Securely: Take your obd2 scanner for airbag diagnostics and firmly plug its connector into the OBD2 port you located in step 2. Ensure it is securely connected to establish proper communication.
- Power On the Scanner (If Required): Some OBD2 scanners will power on automatically once connected to the vehicle and ignition is on. Others may have a separate power button that you will need to switch on.
5. Navigate the Scanner Menu to Access SRS Diagnostics
- Select Vehicle Make, Model, and Year: Once the scanner is powered on and connected, you will typically need to input your vehicle’s information. This usually involves selecting the make, model, and year of your car from the scanner’s menu. This ensures the scanner uses the correct diagnostic protocols for your specific vehicle.
- Choose the SRS System Option: Within the scanner’s main menu, navigate to the diagnostic options. Look for and select the option related to the SRS or Airbag system. The labeling may vary slightly depending on the scanner manufacturer, but common terms include “SRS,” “Airbag,” or “Safety Restraint System.”
6. Read and Retrieve the Airbag Fault Codes
- Initiate the SRS System Scan: Once you have selected the SRS system, follow the prompts on your obd2 scanner for airbag to initiate a scan of the airbag system. This command tells the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s SRS control module and check for any stored fault codes.
- Retrieve and Display Codes: The scanner will communicate with the SRS module and retrieve any stored diagnostic trouble codes. These codes will then be displayed on the scanner’s screen.
- Note Down the Codes: Carefully record each fault code displayed by the scanner. You can either write them down or use the scanner’s memory function to save them. Most scanners will also provide a brief description of each code, which can be helpful for initial understanding.
7. Interpret the Airbag Codes to Understand the Issues
- Refer to Scanner’s Manual or Code Library: Your obd2 scanner for airbag likely comes with a manual or has a built-in code library that can help you interpret the fault codes. Consult these resources to understand the meaning of each code and what system or component it relates to.
- Research Codes Online: For more detailed information, you can also search for the specific fault codes online. Numerous automotive websites and online forums maintain extensive databases of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) with detailed explanations, potential causes, and possible fixes.
8. Clear the Airbag Codes (After Addressing the Issue)
- Important: Fix the Underlying Problem First: It is crucial to understand that clearing airbag codes should only be done AFTER you have correctly diagnosed and repaired the underlying issue that caused the codes to appear in the first place. Simply clearing the codes without fixing the problem is not a solution, and the airbag warning light will likely reappear.
- Navigate to Clear Codes Option: Once you have addressed the problem, use your obd2 scanner for airbag again. Navigate through the scanner’s menu to find the option to clear codes, specifically for the SRS system. This option might be labeled as “Clear SRS Codes,” “Reset Airbag System,” or similar.
- Clear the Codes: Follow the on-screen prompts to execute the command to clear the codes. The scanner will send a command to the vehicle’s SRS module to clear the stored fault codes from its memory.
9. Verify the Fix and Re-scan the System
- Re-scan the SRS System: After clearing the codes, it’s a good practice to perform another scan of the SRS system using your obd2 scanner for airbag. This is to ensure that no new codes have appeared and that the original codes have indeed been cleared.
- Check the Airbag Warning Light on Dashboard: After clearing the codes and re-scanning, check your vehicle’s dashboard. The airbag warning light should now be off. If the light remains on, it indicates that there may still be unresolved issues within the SRS, and further diagnosis is needed.
Tips for Effective Airbag System Diagnosis
- Keep Scanner Software Updated: Regularly update the software of your obd2 scanner for airbag. Updates ensure compatibility with newer vehicle models and the latest diagnostic protocols, improving accuracy and functionality.
- Don’t Hesitate to Seek Professional Help: If you are uncertain about interpreting the codes, diagnosing the problem, or performing repairs on the airbag system, it is always advisable to consult a professional mechanic. Airbag systems are critical safety features, and professional expertise is crucial for ensuring they function correctly.
By following these detailed steps, you can effectively use an obd2 scanner for airbag systems to check and diagnose airbag codes, contributing significantly to the safety and proper functioning of your vehicle’s crucial safety systems.
 All System Car Scanner | Foxwell
All System Car Scanner | Foxwell
Will an Airbag Light Turn Off By Itself? Understanding Airbag Warning Lights
A common question among vehicle owners is whether an airbag warning light will simply turn off on its own. The answer is generally no; an airbag light is designed to stay illuminated until the underlying issue is properly resolved and the fault codes are cleared using a diagnostic tool, such as an obd2 scanner for airbag systems. Here’s why:
Reasons Why the Airbag Light Typically Remains On
1. Persistent Fault Codes: Memory of the Problem
- Stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a problem occurs within your vehicle’s airbag system, the onboard computer, or ECU (Engine Control Unit), detects the issue and stores a specific fault code. Simultaneously, it triggers the airbag warning light on your dashboard to alert you to the problem. This warning light is a crucial safety notification.
- Manual Reset Requirement: Even if the underlying issue that initially triggered the fault is temporarily resolved or becomes intermittent, the fault codes remain stored in the ECU’s memory. These stored codes are what keep the airbag warning light illuminated. The light will not turn off automatically; it requires a manual reset. This reset is typically achieved by using a diagnostic scanner to specifically clear these fault codes from the ECU. This ensures that the system has been checked and any acknowledged problems are actively addressed, not just temporarily disappeared.
2. Safety Precaution: Ensuring System Integrity
- Driver Notification and Safety Assurance: The airbag warning light serves as a vital safety precaution. It is intentionally designed to remain on when a fault is detected to continuously notify the driver of a potential problem within the airbag system. This constant reminder is crucial because a malfunctioning airbag system may not deploy correctly in a collision, jeopardizing passenger safety.
- System Verification Necessity: The airbag light is engineered to stay illuminated until the vehicle’s system confirms that it is fully operational again. This verification process involves not just resolving the initial fault but also explicitly checking and clearing the stored fault codes. This step confirms that the system has been assessed, repaired, and is now functioning as intended. The system needs this positive confirmation to turn off the warning light, ensuring that the driver is not misled into believing the system is functional when it might not be.
How to Clear the Airbag Light Effectively
To clear the airbag light and ensure your SRS is functioning correctly, follow these steps:
Step 1: Diagnose the Root Cause of the Problem
- Utilize an OBD2 Scanner for Airbag Systems: The first and most critical step is to accurately diagnose why the airbag light is on. Connect an advanced diagnostic scanner that is capable of reading and clearing SRS codes to your vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Read the Fault Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the specific fault codes stored within the SRS system. These codes provide essential clues about the nature of the problem.
- Interpret the Codes to Identify the Issue: Carefully interpret the fault codes. This will help you pinpoint the underlying issue that is causing the airbag light to illuminate. Common causes can include faulty airbag sensors, problems with wiring or connectors, or issues within the airbag control module itself.
Step 2: Rectify the Identified Problem
- Repair or Replace Defective Components: Based on the diagnostic codes and your interpretation, take action to fix the identified issue. This might involve repairing damaged wiring, replacing a faulty airbag sensor, or addressing issues with other components of the airbag system.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you are not experienced with vehicle repairs, especially those involving safety-critical systems like airbags, it is highly recommended to seek assistance from a qualified professional mechanic. Incorrect repairs to the airbag system can have serious safety consequences.
Step 3: Clear the Fault Codes Using the Scanner
- Use the Scanner to Clear Codes: After you have completed the necessary repairs to address the identified problem, you will need to use your diagnostic scanner again to clear the stored fault codes.
- Navigate to the Clear SRS Codes Option: In your scanner’s menu, find and select the option to clear SRS codes or reset the airbag system.
- Execute the Clear Codes Command: Follow the prompts on the scanner to execute the command to clear the codes. This action will instruct the vehicle’s ECU to erase the stored fault codes related to the airbag system.
Step 4: Confirm the Airbag Light is Off
- Check the Dashboard Warning Light: After clearing the fault codes, check your vehicle’s dashboard to ensure that the airbag warning light is no longer illuminated. If the light has turned off, it typically indicates that the system is now functioning correctly, and the fault has been successfully addressed and acknowledged by the vehicle’s system.
When the Airbag Light Persists: Further Investigation
- Persistent Warning Light Indicates Unresolved Issues: If, after clearing the codes, the airbag light remains on, it is a strong indication that there are still unresolved issues within the SRS system. It means either the initial problem was not completely fixed, or there may be additional, related problems.
- Re-scan for New or Remaining Fault Codes: In such cases, re-scan the vehicle’s SRS system immediately using your obd2 scanner for airbag. Check to see if any new fault codes have appeared or if the original codes are still present. New codes can provide further clues to the ongoing issue, while persistent codes suggest the original repair was not effective.
- Further, More In-depth Inspection May Be Required: A persistent warning light often necessitates a more thorough and in-depth inspection of the airbag system. This might involve using more advanced diagnostic tools, performing more detailed component testing, or seeking professional diagnostic services. It is essential to address a persistent airbag warning light to ensure the safety of your vehicle’s occupants.
Understanding that an airbag light will not clear itself and following these steps to diagnose, repair, and clear codes will help you maintain the safety and reliability of your vehicle’s airbag system. Remember, prompt attention to airbag system warnings is crucial for safety.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety with the Right OBD2 Scanner for Airbag Diagnostics
In conclusion, while standard OBD2 scanners serve a purpose for basic engine diagnostics, they are insufficient when it comes to the critical Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). For accurate and effective diagnostics of your vehicle’s airbags, investing in a specialized obd2 scanner for airbag systems is essential. If your airbag warning light illuminates, it’s a clear signal to take action. Utilize an advanced scanner to accurately diagnose and address the underlying issues, and remember that clearing the codes manually after repair is a necessary step to turn off the warning light. Promptly addressing any airbag system problems is not just about maintaining your vehicle; it’s about prioritizing safety for yourself and your passengers. Choosing the right obd2 scanner for airbag functionality is a crucial investment in vehicle safety and peace of mind.
FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2 Scanners and Airbag Codes
Can a basic OBD2 scanner read airbag codes?
No, most basic or standard OBD2 scanners cannot read airbag codes. These scanners are typically designed to read engine and emission-related codes only. To access airbag (SRS) codes, you need an advanced or specialized OBD2 scanner that specifically lists SRS or airbag system diagnostics as a feature. Always check the scanner’s specifications to confirm SRS compatibility.
What kind of OBD2 scanner do I need to read airbag codes?
To read airbag codes, you need an advanced or professional-grade OBD2 scanner. These scanners are equipped with the necessary software and hardware to communicate with your vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). Look for scanners that explicitly state they offer “SRS diagnostics,” “airbag code reading,” or “full system diagnostics” which includes airbags. Examples include scanners from brands like Foxwell, Autel, Launch, and Thinkcar, specifically models that are advertised for full-system or SRS capabilities.
Why can’t all OBD2 scanners read airbag codes?
The reason basic OBD2 scanners can’t read airbag codes comes down to their design and intended function. Standard OBD2 protocols, mandated for emissions-related diagnostics, primarily focus on engine and powertrain systems. Airbag systems, along with other safety and body control systems, operate on different communication protocols and require more sophisticated diagnostic tools to access and interpret their data. Advanced scanners are built with broader system coverage and specialized software to communicate with these additional modules, including the SRS, which basic scanners simply lack. This expanded capability is what enables them to read airbag codes and perform more comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.