Rack-and-pinion steering has become the dominant steering system in today’s cars, light trucks, and SUVs, prized for its simplicity and efficiency. This mechanism is ingeniously designed to translate the rotational movement of your steering wheel into the linear motion required to turn your vehicle’s wheels. At its heart is the rack-and-pinion gearset, a marvel of engineering encased within a metal housing, with each end of the rack extending outwards to connect with the steering mechanism.
Key Components of a Rack & Pinion Steering System
To grasp how rack and pinion steering operates, it’s crucial to understand its fundamental parts:
- Pinion Gear: This circular gear is attached to the steering shaft. When you rotate the steering wheel, you’re directly turning the pinion gear.
- Steering Rack: A toothed linear gear that meshes with the pinion gear. As the pinion rotates, its teeth engage with the rack’s teeth, causing the rack to move either left or right.
- Tie Rods: These rods connect to each end of the steering rack. They are crucial links that transmit the rack’s linear motion to the steering arms.
- Steering Arms: Attached to the wheel spindles, the steering arms are levers that pivot the wheels in response to the movement of the tie rods.
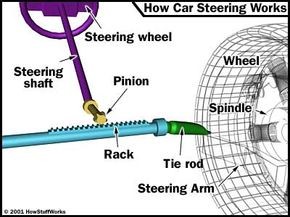 Rack and Pinion Steering System Diagram: Illustrating the key components including the rack, pinion gear, tie rods, steering arm, and spindle in a typical automotive setup.
Rack and Pinion Steering System Diagram: Illustrating the key components including the rack, pinion gear, tie rods, steering arm, and spindle in a typical automotive setup.
How Rack & Pinion Converts Motion and Reduces Effort
The rack-and-pinion system performs two essential functions in your vehicle’s steering:
- Motion Conversion: It expertly transforms the rotational input from the steering wheel into the linear motion needed to steer the wheels left or right. This direct mechanical linkage provides a responsive and precise steering feel.
- Gear Reduction: The gearset inherently provides a gear reduction. This mechanical advantage makes it significantly easier for the driver to turn the wheels, especially considering the weight and friction involved in moving the front wheels of a vehicle.
In most passenger cars, achieving a full turn from lock to lock (wheels turned completely to one side to the other) requires approximately three to four full rotations of the steering wheel.
Understanding Steering Ratio
The steering ratio is a critical specification that defines the relationship between steering wheel input and wheel turn output. It’s calculated as the ratio of the steering wheel rotation angle to the corresponding wheel rotation angle. For example, a steering ratio of 18:1 means that for every 18 degrees you turn the steering wheel, the wheels turn 1 degree.
A higher steering ratio implies that more steering wheel rotation is needed for a given wheel turn, demanding less effort due to increased mechanical advantage. Conversely, a lower steering ratio results in quicker steering response, as less steering wheel movement translates to a larger wheel turn. Sportier vehicles often utilize lower steering ratios for enhanced agility and quicker reaction to driver input. While requiring slightly more steering effort, the faster response is often preferred in performance driving scenarios.
Variable Ratio Steering for Optimized Handling
To balance responsiveness and ease of use, some vehicles employ variable-ratio rack-and-pinion steering. This sophisticated system utilizes a steering rack with varying tooth pitch – tighter in the center and wider towards the ends. This design provides quicker steering response during initial turns when the rack is near its center, enhancing maneuverability in situations like cornering and lane changes. As the steering wheel is turned further towards its limits, the wider tooth pitch reduces sensitivity, making it easier to control the vehicle at larger steering angles and reducing the effort required at parking speeds.
Power Rack & Pinion Steering: Assisted Steering for Comfort
In power steering systems, the rack-and-pinion mechanism is adapted to incorporate hydraulic or electric assistance. Power rack-and-pinion systems feature a cylinder integrated into the rack housing, containing a piston connected to the rack.
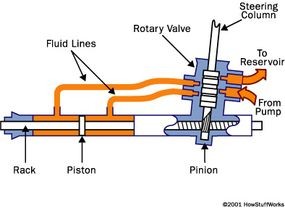 Power Rack and Pinion Steering Mechanism: Diagram showing the internal cylinder and piston responsible for providing power assist in a rack and pinion steering system.
Power Rack and Pinion Steering Mechanism: Diagram showing the internal cylinder and piston responsible for providing power assist in a rack and pinion steering system.
By applying hydraulic pressure to either side of the piston, the system assists the driver in moving the rack, significantly reducing the effort required to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds or when maneuvering larger vehicles. This power assist enhances driving comfort and reduces driver fatigue, particularly in everyday driving conditions.
In conclusion, rack-and-pinion steering stands as a testament to effective mechanical design, providing a blend of simplicity, reliability, and responsive control that has made it the industry standard for modern vehicles. Its ability to efficiently convert motion and provide variable steering ratios, especially when combined with power assist, delivers a comfortable and confident driving experience across a wide range of vehicles.

